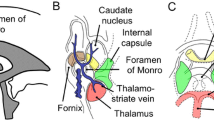
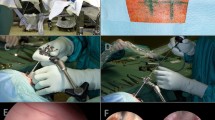
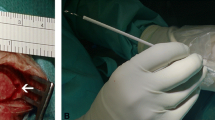
Abstract
Background
Safe and radical excision of pediatric fourth ventricular tumors is by far the best line of management. Pediatric fourth ventricular tumor surgery is a challenge for neurosurgeons. The aim of the study is to present the authors’ experience and to evaluate the possible benefits of neuro-navigated intraoperative ultrasonography (NIOUS) during the surgery of fourth ventricular tumors in children.
Methods
Nonrandomized clinical trial study was conducted on 60 children with fourth ventricular tumors who were treated at Children’s Cancer Hospital-Egypt. Mean age was 5.2 (±2.6) years. Thirty cases were operated upon utilizing the conventional microneurosurgical techniques. Another 30 cases were operated upon utilizing the NIOUS technique.
Results
Total tumor excision was achieved in 29 cases (96.7 %) of NIOUS group versus 24 cases (80 %) in the conventional group. Mean operative time NIOUS group was 150 min [standard deviation (SD) = 18.28) versus 140.6 min (SD = 18.6) in the conventional group (p value = 0.055). The mean operative blood loss was 67.5 ml (SD = 17) in NIOUS group versus 71 ml (SD = 15.4) in the conventional group. Postoperative cerebellar mutism occurred in one case (3.3 %) of NIOUS group versus in six cases (20 %) of the conventional group.
Conclusions
Integration of navigated intraoperative ultrasonography in surgery of pediatric fourth ventricular tumors is a useful technology. It safely monitors maximum stepwise tumor excision. It is associated with less operative morbidity without significantly added operative time. It is a real-time, cost-effective, easily applicable, and easily interpretable tool that could substitute the use of intraoperative MRI especially in pediatric neurosurgery.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akdemir H, Oktem IS, Menku A, Tucer B, Kamasak K, Tugcu B (2009) Neuronavigation by intraoperative ultrasound during intracranial cavernoma resection. Neurosurg Q 19:185–189
Aquilina K, Edwards P, Strong S (2006) Principles and practice of image-guided neurosurgery. In: Moore AJ, Newell DW (eds) Tumor neurosurgery principles and practice. Springer, London, p 132
Benveniste RJ, Germano I (2005) Correlation of factors predicting intraoperative brain shift with successful resection of malignant brain tumors using image guided techniques. Surg Neurol 63:542–549
Chen D, Wei X, Yin Q, Guan J, Pan W, Wang C, Liu Y (2009) The microscopic surgical treatment for tumor of posterior cranial fossa in children. Clin Oncol Cancer Res 6:95–99
El Beltagy MA, Aggag M, Kamal M (2010) Role of intraoperative ultrasound in resection of pediatric brain tumors. Childs Nerv Syst 26(9):1189–1193
Flitter MA, Buchheit WA, Murtagh F, Lapayowker MS (1975) Ultrasound determination of cerebrospinal fluid shunt patency. J Neurosurgery 42:728–730
Fu B, Zhao JZ, Yu LB (2008) The application of ultrasound in the management of cerebral arteriovenous malformation. Neurosci Bull 24(6):387–394
Hammoud MA, Ligon BL, ElSouki R, Shi WM, Schomer DR, Sawaya R (1996) Use of intraoperative ultrasound for localizing tumours and determining the extent of resection: a comparative study with magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurosurg 84:737–741
Huang X, Zhang J, Yang H, Yu T (2010) Use of intraoperative ultrasonography to monitor surgery for large acoustic neuromas: a pilot study. J Med Ultrasonics 37:15–19
Kanev PM, Foley CM, Miles D (1997) Ultrasound tailored functional hemispherectomy for surgical control of seizures in children. J Neurosurg 86:762–767
Koivukangas J, Louhisalmi Y, Alakuijala J, Oikarinen J (1993) Ultrasound-controlled neuronavigator-guided brain surgery. J Neurosurg 79:36–42
LeRoux PD, Berger MS, Ojemann GA, Wang K, Mack LA (1989) Correlation of intraoperative ultrasound tumour volumes and margins with preoperative computerized tomography scans. An intraoperative method to enhance tumour resection. J Neurosurg 71:691–698
Lindseth F, Ommedal S, Bang J, Unsgard G, Hernes TAN (2001) Image fusion of ultrasound and MRI as an aid for assessing anatomical shifts and improving overview and interpretation in ultrasound-guided neurosurgery. Int Congr Ser 1230:254–260
McGirt MJ, Attenello FJ, Datoo G, Gathinji M, Atiba ABS, Weingart JD, Carson B, Jallo GI (2008) Intraoperative ultrasonography as a guide to patient selection for duraplasty after suboccipital decompression in children with Chiari malformation type I. J Neurosurg Pediatrics 2:52–57
Nagle RC, Takeman MS, Shallat RF, Cohen RA (1986) Brain abscess aspiration in nursery with ultrasound guidance. J Neurosurg 65:557–559.12
Nimsky C, Ganslandt O, Hastreiter P, Fahlbusch R (2001) Intraoperative compensation for brain shift. Surg Neurol 56:357–365
Quencer RM, Montalvo BM (1986) Intraoperative cranial sonography. Neuroradiology 28:528–550
Ram Z, Shawker TH, Bradford MH, Doppman JL, Oldfield EH (1995) Intraoperative ultrasound-directed resection of pituitary tumors. J Neurosurg 83:225–230
Rasmussen A Jr, Lindseth F, Rygh OM, Berntsen EM, Selbekk T, Xu J, Nagelhus Hernes TA, Harg E, Haberg A, Unsgaard G (2007) Functional neuronavigation combined with intraoperative 3D ultrasound: initial experiences during surgical resections close to eloquent brain areas and future directions in automatic brain shift compensation of preoperative data. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 149:365–378
Rubin JM, Dohrmann GJ (1983) A cannula for use in ultrasonically guided biopsies of the brain. J Neurosurg 59:905–907
Solheim O, Selbekk T, Lindseth F, Unsgård G (2009) Navigated resection of giant intracranial meningiomas based on intraoperative 3D ultrasound. Acta Neurochir 151:1143–1151
Tanaka K, Ito K, Waga T (1964) The localization of brain tumors by ultrasonic techniques. A clinical review of 111 cases. J Neurosurgery 23:135–147
Wang Y, Wang Y, Dong Y, Wang Y (2006) The value of intraoperative ultrasonography in neurosurgery. J Med Ultrasonics 33:61–64
Wang Y, Wang Y, Wang Y, Taniguchi N, Chen XC (2007) Intraoperative real-time contrast-enhanced ultrasound angiography: a new adjunct in the surgical treatment of arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 107:959–964
Whitehead WE, Jea A, Vachhrajani S, Kulkarni A, Drake JM (2007) Accurate placement of cerebrospinal fluid shunt ventricular catheters with real-time ultrasound guidance in older children without patent fontanelles. J Neurosurg (5 Suppl Pediatrics) 107:406–410
Yamasaio T, Moritake K, Takaya M, KagawaT NH, Akiyama Y, Kawahara M (1994) Intraoperative use of Doppler ultrasound and endoscopic monitoring in the stereotactic biopsy of malignant brain tumors. J Neurosurg 80:570–574
Zakrzewski K, Fiks T, Polis L, Liberski PP (2003) Posterior fossa tumours in children and adolescents. A clinicopathological study of 216 cases. Folia Neuropathol 41:251–252
Disclosures
The authors have no personal, financial, institutional interest or industry affiliations in any of the drugs, materials, or devices described in this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El Beltagy, M.A., Atteya, M.M.E. The benefits of navigated intraoperative ultrasonography during resection of fourth ventricular tumors in children. Childs Nerv Syst 29, 1079–1088 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-013-2103-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-013-2103-y