Abstract
Objectives
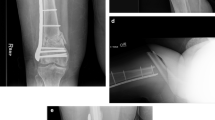
We report the application of a new fixed angle plate (NCB DF®, Zimmer inc. USA, Warsaw, IN) in the treatment of periprosthetic femur fractures. The NCB DF® combines conventional plating technique with polyaxial screw placement and angular stability.
Design
Prospective cohort study.
Setting
A single level-1 trauma center.
Patients
From May 2003 to December 2005, a total of 24 patients with periprosthetic femur fractures were treated. The NCB DF® femur plate was used in all cases. The average follow-up period was 12 months (3–31 months). Twelve patients had a periprosthetic fracture after total knee replacement (TKA) and 12 patients after total hip replacement (THA). The mean period from primary joint replacement to periprosthetic fracture was 8.2 years for the THA group and 7.2 years for the TKA group.
Intervention
A combined conventional/locking surgical technique was performed in all the cases.
Main outcome measures
Union, non-union, mal-union, duration of surgery, range of motion, postoperative mobility, subjective patient satisfaction and complications.
Results
The union rate was 90%, the mal-union rate 5% and the re-operation rate 15%. Postoperative mobility reached the preoperative level in all but for two patients. Three complications occurred relating to the implant or the procedure: one fatigue failure of the plate (non-union), one screw breakage, and one wound infection.
Conclusions
The NCB DF® combines conventional plating technique with polyaxial screw placement and angular stability. This combination technique shows promising results regarding union and mal-union rates in periprosthetic fractures in elderly and osteoporotic patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mittelmeier W, Stöckle U, Perka C, Schaser KD. Periprothetische Frakturen nach Knietotalendoprothetik. Der Unfallchirurg 2005. [Periprosthetic fractures after total knee replacement]
Su ET, DeWal H, Di Cesare PE (2004) Periprosthetic femoral fractures above total knee replacements. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 12:12–20
Ritter MA, Faris PM, Keating EM (1988) Anterior femoral notching and ipsilateral supracondylar femur fracture in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 3:185–187
Berry DJ (1999) Epidemiology: hip and knee. Orthop Clin North Am 30:183–90
Beals RK, Tower SS (1996) Periprosthetic fractures of the femur. An analysis of 93 fractures. Clin Orthop 327:238–246
Lewallen DG, Berry DJ (1998) Periprosthetic fracture of the femur after total hip arthroplasty. Treatment and results to date. Instr Course Lect 47:243–9
Chen F, Mont MA, Bachner RS (1994) Management of ipsilateral supracondylar femur fractures following total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 9:251–256
Mont MA, Maar DC (1994) Fractures of the ipsilateral femur after total hip arthroplasty. A statistical analysis of outcome based on 487 patients. J Arthroplasty 9:511–519
Althausen PL, Lee MA, Finkemeier CG, Meehan JP, Rodrigo JJ (2003) Operative stabilization of supracondylar femur fractures above total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 18:834–839
Kääb MJ, Stockle U, Schutz M, Stefansky J, Perka C, Haas NP. (2005) Stabilisation of perprosthetic fractures with angular stable internal fixation: a report of 13 cases. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg
Bong MR, Egol KA, Koval KJ, Kummer FJ, Su ET, Iesaka K, Bayer J, DiCesare PE (2002) Comparison of the LISS and a retrograde-inserted supracondylar intramedullary nail for fixation of periprosthetic distal femur fracture proximal to a total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 17:876–881
Wick M, Mueller EJ, Kutscha F, Hopf F, Muhr G (2004) Die operative Versorgung suprakondylärer Femurfrakturen bei liegender Knieendoprothese—LISS oder retrograder Nagel? Unfallchirurg 107:181–188. [Surgical treatment of supracondylar femur fractures with a TKR in situ—LISS or retrograde nail?]
Kuster MS, KR Grob R Howald TN Forster. (2000) The influence of screw placement on fracture motion, 9th edn. ESSKA Congress, London, p 319
Haidukewych GJ, Jacofsky DJ, Hansson AD (2003) Treatment of periprosthetic fractures around a total knee arthroplasty. J Knee Surg 16:111–117
Brady OH, Garbuz DS, Masri BA, Duncan CP (1999) Classification of the hip. Orthop Clin North Am 30:215–20
Rorabeck CH, Taylor JW (1999) Periprosthetic fractures of the femur complicating total knee arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am 30:265–277
Ricci WM, Loftus T, Cox C, Borelli J (2006) Locked plates combined with minimally invasive insertion technique for the treatment of periprosthetic supracondylar femur fractures above total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Trauma 20:190–196
Culp RW, Schmidt RW, Hanks G, Mak A, Esterhai JL, Heppeenstall RB (1987) Supracondylar fracture of the femur following prosthetic knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop 222:212–222
Davison BL (2003) Varus collapse of comminuted distal femur fractures after open reduction and internal fixation with a condylar buttress plate. Am J Orthop 32:27–30
Figgie MP, Goldberg VM, Figgie HE 3rd, Sobel M (1990) The results of treatment of supracondylar fracture above total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 5:267–276
Kregor PJ, Hughes JL, Cole PA (2001) Fixation of distal femoral fractures above total knee arthroplasty utilizing the less invasive stabilisation system (L.I.S.S.). Injury 32:64–75
Aro HT, Chao EY (1993) Bone healing patterns affected by loading, fracture fragment stability, fracture type und fracture site compression. Clin Orthop 293:8–17
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Erhardt, J.B., Grob, K., Roderer, G. et al. Treatment of periprosthetic femur fractures with the non-contact bridging plate: a new angular stable implant. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 128, 409–416 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-007-0396-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-007-0396-6