Abstract
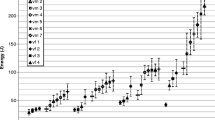
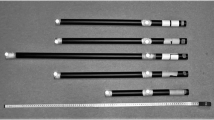
A common form of violence investigated in legal medicine is blunt trauma caused by striking with different objects. The injuries and medical consequences have been widely examined, whereas the forces and especially the energies acting on impact have rarely been analyzed. This study focuses on how the impact energy of different striking objects depends on their characteristics. A total of 1170 measurements of horizontal strikes against a static and relatively heavy pendulum have been acquired with 13 volunteers. The main focus was laid on how the weight, the length, and the center of mass of the different striking objects influenced the striking energy. The results show average impact energies in the range of 67.3 up to 311.5 J for men with an optimum weight of about 1.3 kg with its center of mass in the far end quarter for a 1-m-long striking object. The average values for women range from 30 to 202.6 J, with an optimum weight between 1.65 and 2.2 kg and similar settings for the center of mass as the men. Also, the impact energies are getting higher with shorter object lengths and reach a maximum at a length of about 0.3 to 0.4 m. The male volunteers’ impact energy was on average by 84.2 % higher than the values of the female volunteers, where the impact masses were very similar and the impact velocities played the key role.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Purdue B, Fernando GC (1989) The mechanism of fatal cardiopulmonary injury caused by a blow from a golf club. Forensic Sci Int 42(1–2):125–30
Levy AS, Bromberg J, Jasper D (1994) Tibia fractures produced from the impact of a baseball bat. J Orthop Trauma 8(2):154–8
Bryant DD, Greenfield R, Martin E (1992) Musculoskeletal trauma: the baseball bat. J Natl Med Assoc 8(11):957–60
Calcaterra C (2015) Nine-year-old bat boy dies after being struck by a bat in a college summer league game. NBCsports news site. http://mlb.nbcsports.com/2015/08/03/nine-year-old-bat-boy-dies-after-being-struck-by-a-bat-in-a-college-summer-league-game/. Accessed 10 September 2015
Kettner M, Ramsthaler F et al (2014) Blunt force impact to the head using a teeball bat: systematic comparison of physical and finite element modeling. Forensic Sci Med Pathol 10(4):513–7. doi:10.1007/s12024-014-9586-z
Ord RA, Benian RM (1995) Baseball bat injuries to the maxillofacial region caused by assault. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 53(5):514–7
Groleau GA, Tso EL, Olshaker JS, Barish RA, Lyston DJ (1993) Baseball bat assault injuries. J Trauma 34(3):366–72
Viano DC, Andrzejak DV, King AI (1992) Fatal chest injury by baseball impact in children: a brief review. Clin J Sport Med 2:161–5
Adamec J, Praxl L, Schneider K, Graw M (2001) Estimation of effective mass of longish rigid instruments in head impacts. Int J Legal Med 125:763–771. doi:10.1007/s00414-010-0490-0
Golman AJ, Danelson KA, Gaewsky JP, Stitzel JD (2015) Implementation and validation of thoracic side impact injury prediction metrics in a human body model. Comput Methods Biomech Miomed Engin 18(10):1044–55. doi:10.1080/10255842.2013.869319
Mole CG, Heyns M, Cloete T (2015) How hard is hard enough? An investigation of the force associated with lateral blunt force trauma to the porcine cranium. Leg Med (Tokyo) 17(1):1–8. doi:10.1016/j.legalmed.2014.07.008
Cooper GJ, Taylor DEM (1989) Biophysics of impact injury to the chest and abdomen. J R Army Med Corps 135:58–67
Yoganandan N et al (1995) Biomechanics of skull fracture. J Neurotrauma 12(4):659–68
Ota K, Bratincsak A (2014) Atrial fibrillation induced by commotio cordis secondary to a blunt chest trauma in a teenage boy. Pediatrics 135(1):e199
Link MS, Wang PJ, Pandian NG et al (1998) An experimental model of sudden death due to low-energy chest-wall impact (commotio cordis). N Engl J Med 338(25):1805–11
Kaplan JA, Karofsky PS, Volturo GA (1993) Commotio cordis in two amateur ice hockey players despite the use of commercial chest protectors: case reports. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 34(1):151–3
Lau IV (1983) Effect of timing and velocity of impact on ventricular myocardial rupture. J Biomech Eng 105(1):1–5
Lawson EE (1981) Prolonged central respiratory inhibition following reflex-induced apnea. J Appl Physiol 50(4):874–9
Compliance with ethical standards
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sprenger, F.D., Siegenthaler, L., Kneubuehl, B.P. et al. The influence of striking object characteristics on the impact energy. Int J Legal Med 130, 835–844 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-015-1268-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-015-1268-1