Abstract
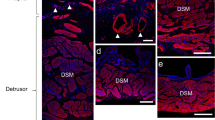
The urinary bladder experiences both distension and contraction as a part of the normal filling and emptying cycle. To empty properly, tension generated intracellularly in a smooth muscle cell must be smoothly and efficiently transferred across its sarcolemma to the basement membrane, which mediates its binding to both the extracellular matrix and to other cells. As a consequence of urethral obstruction, the bladder cannot generate appropriate force to contract the organ, thereby leading to inefficient emptying and associated sequelae. In this study, an animal model of urethral obstruction was utilized to study the membrane-associated structures that transfer tension across the sarcolemma of bladder smooth muscle cells. Immunohistochemical localization of key components of the smooth muscle tension transfer apparatus (TTA) was performed utilizing specific antibodies against:(1) the α-chains of type IV collagen, a basement membrane component, and (2) β-sarcoglycan, an integral membrane protein that is a participant in the physical linkage between the cytoskeleton and the basement membrane. We demonstrate, in obstructed animals, that there is a pronounced disruption of the TTA with a physical displacement of these two components that can be demonstrated at the level of the light microscope using scanning confocal microscopy. Electron microscopy further demonstrates significant increases in the size of the junctional plaques between smooth muscle cells.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barresi R et al (2000) Expression of gamma-sarcoglycan in smooth muscle and its interaction with the smooth muscle sarcoglycan-sarcospan complex. J Biol Chem 275(49):38554–38560
Betto R et al (1999) Ecto-ATPase activity of alpha-sarcoglycan (adhalin). J Biol Chem 274(12):7907–7912
Borza DB et al (2001) The NC1 domain of collagen IV encodes a novel network composed of the alpha 1, alpha 2, alpha 5, and alpha 6 chains in smooth muscle basement membranes. J Biol Chem 276(30):28532–28540
Boselli JM et al (1981) Fibronectin: its relationship to basement membranes. I. Light microscopic studies. Collagen Related Res 1(5):391–404
Chang SL et al (1998) Role of type III collagen in bladder filling. Neurourol Urodyn 17(2):135–145
Cohn RD, Campbell KP (2000) Molecular basis of muscular dystrophies. Muscle Nerve 23(10):1456–1471
Crosbie RH et al (1999) Membrane targeting and stabilization of sarcospan is mediated by the sarcoglycan subcomplex. J Cell Biol 145(1):153–165
Deveaud CM et al (1998) Molecular analysis of collagens in bladder fibrosis. J Urol 160(4):1518–1527
Draviam R et al (2001) Confocal analysis of the dystrophin protein complex in muscular dystrophy. Muscle Nerve 24(2):262–272
Ervasti JM, Campbell KP (1991) Membrane organization of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex. Cell 66(6):1121–1131
Ewalt DH et al (1992) Is lamina propria matrix responsible for normal bladder compliance?. J Urol 148(2Pt 2):544–549
Fadic R et al (1997) Muscle pathology and clinical features of the sarcolemmopathies. Pedi Neurol 16(1):79–82
Gabella G, Uvelius B (1990) Urinary bladder of rat: fine structure of normal and hypertrophic musculature. Cell Tissue Res 262(1):67–79
Gabella G, Uvelius B (1994) Reversal of muscle hypertrophy in the rat urinary bladder after removal of urethral obstruction. Cell Tissue Res 277(2):333–339
Gabella G, Uvelius B (1999) Structural changes in the rat bladder after acute outlet obstruction. Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl 201:32–37
Gosling JA et al (2000) Correlation between the structure and function of the rabbit urinary bladder following partial outlet obstruction. J Urol 163(4):1349–1356
Howard PS, Macarak EJ (1989) Localization of collagen types in regional segments of the fetal bovine aorta. Labo Invest 61(5):548–555
Levin RM et al (2000) Obstructive response of human bladder to BPH vs rabbit bladder response to partial outlet obstruction: a direct comparison. Neurourol Urodyn 19(5):609–629
Martinez-Hernandez A et al (1981) Fibronectin: its relationship to basement membranes II Ultrastructural studies in rat kidney. Collagen Related Res 1(5):405–418
Matsumoto S et al (2003) Response of the fetal sheep bladder to urinary diversion. J Urol 169(2):735–739
Ninomiya Y et al (1995) Differential expression of two basement membrane collagen genes, COL4A6 and COL4A5, demonstrated by immunofluorescence staining using peptide-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Cell Biol 130(5):1219–1229
Ozawa E et al (1998) From dystrophinopathy to sarcoglycanopathy: evolution of a concept of muscular dystrophy. Muscle Nerve 21(4):421–438
Ozawa E, Hagiwara Y, Yoshida M (1999) Creatine kinase, cell membrane and Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Mol Cell Biochem 190(1–2):143–151
Rando TA (2001) The dystrophin-glycoprotein complex, cellular signaling, and the regulation of cell survival in the muscular dystrophies. Muscle Nerve 24(12):1575–1594
Sado Y et al (1995) Establishment by the rat lymph node method of epitope-defined monoclonal antibodies recognizing the six different alpha chains of human type IV collagen. Histochem Cell Biol 104(4):267–275
Saito K et al (2000) Differential expression of mouse alpha5(IV) and alpha6(IV) collagen genes in epithelial basement membranes. J Biochem (Tokyo) 128(3):427–434
Seki T et al (1998) Differential expression of type IV collagen isoforms, alpha5(IV) and alpha6(IV) chains, in basement membranes surrounding smooth muscle cells. Histochem Cell Biol 110(4):359–366
Stein R et al (2001a) The decompensated detrusor V: molecular correlates of bladder function after reversal of experimental outlet obstruction. J Urol 166(2):651–657
Stein R et al (2001b) The decompensated detrusor IV: experimental bladder outlet obstruction and its functional correlation to the expression of the ryanodine and voltage operated calcium channels. J Urol 165(6Pt 2):2284–2288
Sweeney HL, Barton ER (2000) The dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex: what parts can you do without?. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(25):13464–1346
Timpl R (1996) Macromolecular organization of basement membranes. Curr Opi Cell Biol 8(5):618–624
Timpl R et al (2000) Structure and function of laminin LG modules. Matrix Biol 19(4):309–317
Timpl R, Brown JC (1996) Supramolecular assembly of basement membranes. Bioessays 18(2):123–32
Urabe N et al (2002) Basement membrane type IV collagen molecules in the choroid plexus, pia mater and capillaries in the mouse brain. Arch Histol Cytol 65(2):133–143
Villarreal FJ, Dillmann WH (1992) Cardiac hypertrophy-induced changes in mRNA levels for TGF-beta 1, fibronectin, and collagen. Am J Physiol 262(6Pt 2):H1861–H1866
Williamson RA et al (1997) Dystroglycan is essential for early embryonic development: disruption of Reichert’s membrane in Dag1-null mice. Hum Mol Genet 6(6):831–841
Yoshida M. Ozawa E (1990) Glycoprotein complex anchoring dystrophin to sarcolemma. J Biochem (Tokyo) 108(5):748–752
Yurchenco PD, Amenta PS, Patton BL (2004) Basement membrane assembly, stability and activities observed through a developmental lens. Matrix Biol 22(7):521–538
Zheng K et al (1999) Absence of the alpha6(IV) chain of collagen type IV in Alport syndrome is related to a failure at the protein assembly level and does not result in diffuse leiomyomatosis. Am J Pathol 154(6):1883–1891
Zhu X et al (2001) Overexpression of gamma-sarcoglycan induces severe muscular dystrophy. Implications for the regulation of Sarcoglycan assembly. J Biol Chem 276(24):21785–21790
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NIH grants DK45419, DK54987, DK48215 and the O’Brien Center DK052620.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Macarak, E.J., Schulz, J., Zderic, S.A. et al. Smooth muscle trans-membrane sarcoglycan complex in partial bladder outlet obstruction. Histochem Cell Biol 126, 71–82 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-005-0135-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-005-0135-4