Abstract
Purpose
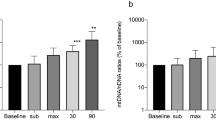
Strenuous exercise induces a rapid and transient elevation of cell free DNA (cfDNA) concentration in blood plasma. The detection of cfDNA in the presence of plasma nucleases could indicate an association of cfDNA with protective vesicular structures. Several cell types release extracellular vesicles (EVs), including exosomes and shedding microvesicles, which are known to mediate the exchange of proteins and nucleic acids (largely RNA) between cells. Here, we assessed whether EVs play a role in the exercise-dependent release of cfDNA in blood plasma.
Methods
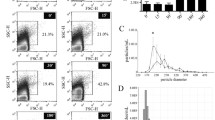
Venous blood collected from healthy volunteers before and after incremental treadmill exercise was separated into vesicular (EV) and soluble fractions. Nuclear and mitochondrial DNA content in plasma supernatants and EV fractions was determined by quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR).
Results
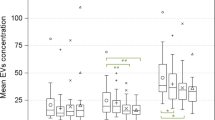
We show that the majority of cfDNA is located in the plasma supernatants. Only minute amounts of DNA were observed in the EV-associated fractions including microvesicles and exosomes. Nuclear and mitochondrial DNA species differ in terms of their quantities in the several plasma fractions.
Conclusions
Our results indicate that cfDNA liberated in response to acute physical exercise is not released by vesicular means and circulates in a soluble form in blood plasma which could indicate different biological functions exerted by cfDNA and EVs. The different nature of DNA species in plasma has major implications for the preparation of plasma and other bodily fluids prior to analysis.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- cfDNA:
-
Cell free DNA
- EV:
-
Extracellular vesicles
- Flot-1:
-
Flotillin-1
- IAT:
-
Individual anaerobic threshold
- LOQ:
-
Limit of quantification
- MV:
-
Microvesicles
- MVB:
-
Multivesicular bodies
- NET:
-
Neutrophil extracellular trap
- qPCR:
-
Quantitative real-time PCR
- SN:
-
Supernatant
- VO2max :
-
Maximal oxygen consumption
References
Aatonen M, Gronholm M, Siljander PR (2012) Platelet-derived microvesicles: multitalented participants in intercellular communication. Semin Thromb Hemost 38:102–113. doi:10.1055/s-0031-1300956
Adeva-Andany M, Lopez-Ojen M, Funcasta-Calderon R, Ameneiros-Rodriguez E, Donapetry-Garcia C, Vila-Altesor M, Rodriguez-Seijas J (2014) Comprehensive review on lactate metabolism in human health. Mitochondrion 17C:76–100. doi:10.1016/j.mito.2014.05.007
Atamaniuk J, Vidotto C, Tschan H, Bachl N, Stuhlmeier KM, Muller MM (2004) Increased concentrations of cell-free plasma DNA after exhaustive exercise. Clin Chem 50:1668–1670. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2004.034553
Atamaniuk J, Stuhlmeier KM, Vidotto C, Tschan H, Dossenbach-Glaninger A, Mueller MM (2008) Effects of ultra-marathon on circulating DNA and mRNA expression of pro- and anti-apoptotic genes in mononuclear cells. Eur J Appl Physiol 104:711–717. doi:10.1007/s00421-008-0827-2
Atamaniuk J, Vidotto C, Kinzlbauer M, Bachl N, Tiran B, Tschan H (2010) Cell-free plasma DNA and purine nucleotide degradation markers following weightlifting exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 110:695–701. doi:10.1007/s00421-010-1532-5
Balaj L, Lessard R, Dai L, Cho YJ, Pomeroy SL, Breakefield XO, Skog J (2011) Tumour microvesicles contain retrotransposon elements and amplified oncogene sequences. Nature Commun 2:180. doi:10.1038/ncomms1180
Beiter T, Fragasso A, Hudemann J, Niess AM, Simon P (2011) Short-term treadmill running as a model for studying cell-free DNA kinetics in vivo. Clin Chem 57:633–636. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2010.158030
Beiter T, Fragasso A, Hudemann J, Schild M, Steinacker J, Mooren FC, Niess AM (2014) Neutrophils release extracellular DNA traps in response to exercise. J Appl Physiol 117:325–333. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00173.2014
Bellingham SA, Guo BB, Coleman BM, Hill AF (2012) Exosomes: vehicles for the transfer of toxic proteins associated with neurodegenerative diseases? Front Physiol 3:124. doi:10.3389/fphys.2012.00124
Blagosklonny MV (2000) Cell death beyond apoptosis Leukemia 14:1502–1508
Bobrie A, Colombo M, Raposo G, Thery C (2011) Exosome secretion: molecular mechanisms and roles in immune responses. Traffic 12:1659–1668. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01225.x
Breitbach S, Tug S, Simon P (2012) Circulating cell-free DNA: an up-coming molecular marker in exercise physiology. Sports Med 42:565–586. doi:10.2165/11631380-000000000-00000
Breitbach S, Sterzing B, Magallanes C, Tug S, Simon P (2014) Direct measurement of cell-free DNA from serially collected capillary plasma during incremental exercise. J Appl Physiol 117:119–130. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00002.2014
Budnik LT, Kloth S, Baur X, Preisser AM, Schwarzenbach H (2013) Circulating mitochondrial DNA as biomarker linking environmental chemical exposure to early preclinical lesions elevation of mtDNA in human serum after exposure to carcinogenic halo-alkane-based pesticides. PLoS One 8:e64413. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0064413
Ceci R et al (2013) Oxidative stress responses to a graded maximal exercise test in older adults following explosive-type resistance training. Redox Biol 2C:65–72. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2013.12.004
Chaar V et al (2011) Effect of strenuous physical exercise on circulating cell-derived microparticles. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 47:15–25. doi:10.3233/CH-2010-1361
Chiu RW, Chan LY, Lam NY, Tsui NB, Ng EK, Rainer TH, Lo YM (2003) Quantitative analysis of circulating mitochondrial DNA in plasma. Clin Chem 49:719–726
Dickhuth HH, Yin L, Niess A, Rocker K, Mayer F, Heitkamp HC, Horstmann T (1999) Ventilatory, lactate-derived and catecholamine thresholds during incremental treadmill running: relationship and reproducibility. Int J Sports Med 20:122–127. doi:10.1055/s-2007-971105
El Messaoudi S, Rolet F, Mouliere F, Thierry AR (2013) Circulating cell free DNA: preanalytical considerations. Clin Chim Acta 424:222–230. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2013.05.022
Fatouros IG et al (2010) Time of sampling is crucial for measurement of cell-free plasma DNA following acute aseptic inflammation induced by exercise. Clin Biochem 43:1368–1370. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2010.08.020
Fruhbeis C, Frohlich D, Kuo WP, Kramer-Albers EM (2013) Extracellular vesicles as mediators of neuron-glia communication. Front Cell Neurosci 7:182. doi:10.3389/fncel.2013.00182
Frühbeis C, Helmig S, Tug S, Simon P, Krämer-Albers EM (2015) Physical exercise induces rapid release of small extracellular vesicles into the circulation. J Extracell Vesicles 4:28239. doi:10.3402/jev.v4.28239
Galeazzi M, Morozzi G, Piccini M, Chen J, Bellisai F, Fineschi S, Marcolongo R (2003) Dosage and characterization of circulating DNA: present usage and possible applications in systemic autoimmune disorders. Autoimmun Rev 2:50–55
Gould SJ, Raposo G (2013) As we wait: coping with an imperfect nomenclature for extracellular vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles. doi:10.3402/jev.v2i0.20389
Harding CV, Heuser JE, Stahl PD (2013) Exosomes: looking back three decades and into the future. J Cell Biol 200:367–371. doi:10.1083/jcb.201212113
Hergenreider E et al (2012) Atheroprotective communication between endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells through miRNAs. Nat Cell Biol 14:249–256. doi:10.1038/ncb2441
Holdenrieder S, Stieber P (2009) Clinical use of circulating nucleosomes. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 46:1–24. doi:10.1080/10408360802485875
Horstman LL, Jy W, Minagar A, Bidot CJ, Jimenez JJ, Alexander JS, Ahn YS (2007) Cell-derived microparticles and exosomes in neuroinflammatory disorders. Int Rev Neurobiol 79:227–268. doi:10.1016/S0074-7742(07)79010-4
Huang X et al (2013) Characterization of human plasma-derived exosomal RNAs by deep sequencing. BMC Genom 14:319. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-14-319
Jahr S, Hentze H, Englisch S, Hardt D, Fackelmayer FO, Hesch RD, Knippers R (2001) DNA fragments in the blood plasma of cancer patients: quantitations and evidence for their origin from apoptotic and necrotic cells. Cancer Res 61:1659–1665
Kahlert C et al (2014) Identification of double-stranded genomic DNA spanning all chromosomes with mutated KRAS and p53 DNA in the serum exosomes of patients with pancreatic cancer. J Biol Chem 289:3869–3875. doi:10.1074/jbc.C113.532267
Kalra H et al (2012) Vesiclepedia: a compendium for extracellular vesicles with continuous community annotation. PLoS Biol 10:e1001450. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1001450
Kowal J, Tkach M, Thery C (2014) Biogenesis and secretion of exosomes. Curr Opin Cell Biol 29C:116–125. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2014.05.004
Krämer-Albers EM et al (2007) Oligodendrocytes secrete exosomes containing major myelin and stress-protective proteins: trophic support for axons? Proteomics Clin Appl 1:1446–1461
Lazaro-Ibanez E, Sanz-Garcia A, Visakorpi T, Escobedo-Lucea C, Siljander P, Ayuso-Sacido A, Yliperttula M (2014) Different gDNA content in the subpopulations of prostate cancer extracellular vesicles: apoptotic bodies, microvesicles, and exosomes. Prostate. doi:10.1002/pros.22853
Lee TH, Chennakrishnaiah S, Audemard E, Montermini L, Meehan B, Rak J (2014) Oncogenic ras-driven cancer cell vesiculation leads to emission of double-stranded DNA capable of interacting with target cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.07.109
Luga V et al (2012) Exosomes mediate stromal mobilization of autocrine Wnt-PCP signaling in breast cancer cell migration. Cell 151:1542–1556. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.11.024
Lui YY, Chik KW, Chiu RW, Ho CY, Lam CW, Lo YM (2002) Predominant hematopoietic origin of cell-free DNA in plasma and serum after sex-mismatched bone marrow transplantation. Clin Chem 48:421–427
Miranda KC et al (2010) Nucleic acids within urinary exosomes/microvesicles are potential biomarkers for renal disease. Kidney Int 78:191–199. doi:10.1038/ki.2010.106
Nagata S, Hanayama R, Kawane K (2010) Autoimmunity and the clearance of dead cells. Cell 140:619–630. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.02.014
Peinado H et al (2012) Melanoma exosomes educate bone marrow progenitor cells toward a pro-metastatic phenotype through MET. Nat Med 18:883–891. doi:10.1038/nm.2753
Pilsczek FH et al (2010) A novel mechanism of rapid nuclear neutrophil extracellular trap formation in response to Staphylococcus aureus. J Immunol 185:7413–7425. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1000675
Pisetsky DS (2009) Microparticles as biomarkers in autoimmunity: from dust bin to center stage. Arthritis Res Ther 11:135. doi:10.1186/ar2856
Raposo G, Stoorvogel W (2013) Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol 200:373–383. doi:10.1083/jcb.201211138
Revenfeld AL, Baek R, Nielsen MH, Stensballe A, Varming K, Jorgensen M (2014) Diagnostic and prognostic potential of extracellular vesicles in peripheral blood. Clin Ther 36:830–846. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2014.05.008
Rhead B et al (2010) The UCSC Genome Browser database: update. Nucleic Acids Res 38:D613–D619. doi:10.1093/nar/gkp939
Robbins PD, Morelli AE (2014) Regulation of immune responses by extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Immunol 14:195–208. doi:10.1038/nri3622
Schwarzenbach H, Hoon DS, Pantel K (2011) Cell-free nucleic acids as biomarkers in cancer patients. Nat Rev Cancer 11:426–437. doi:10.1038/nrc3066
Simons M, Raposo G (2009) Exosomes–vesicular carriers for intercellular communication. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21:575–581. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2009.03.007
Swarup V, Rajeswari MR (2007) Circulating (cell-free) nucleic acids–a promising, non-invasive tool for early detection of several human diseases. FEBS Lett 581:795–799. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2007.01.051
Thakur BK et al (2014) Double-stranded DNA in exosomes: a novel biomarker in cancer detection. Cell Res 24:766–769. doi:10.1038/cr.2014.44
Thery C (2011) Exosomes: secreted vesicles and intercellular communications. F1000 Biol Rep 3:15. doi:10.3410/B3-15
Thery C, Ostrowski M, Segura E (2009) Membrane vesicles as conveyors of immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol 9:581–593. doi:10.1038/nri2567
Valadi H, Ekstrom K, Bossios A, Sjostrand M, Lee JJ, Lotvall JO (2007) Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol 9:654–659. doi:10.1038/ncb1596
Walsh NP et al (2011) Position statement. Part one: Immune function and exercise. Exerc Immunol Rev 17:6–63
Yi J et al (2014) Increased plasma cell-free DNA level during HTNV infection: correlation with disease severity and virus load. Viruses 6:2723–2734. doi:10.3390/v6072723
Ziegler A, Zangemeister-Wittke U, Stahel RA (2002) Circulating DNA: a new diagnostic gold mine? Cancer Treat Rev 28:255–271
Acknowledgments
The work of CF and EMKA was supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, DFG grant KR 3668/1-1. The work of SH, PS and ST was supported by an internal funding of the Johannes Gutenberg-University of Mainz. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Fabio Fischetti.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Helmig, S., Frühbeis, C., Krämer-Albers, EM. et al. Release of bulk cell free DNA during physical exercise occurs independent of extracellular vesicles. Eur J Appl Physiol 115, 2271–2280 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-015-3207-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-015-3207-8