Abstract
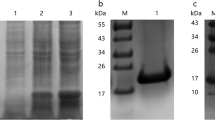
Actin depolymerizing factor (ADF) is an essential actin-binding protein that plays a key role in the control of actin dynamics and actin-based motility processes in intracellular parasites. To determine the effects of diclazuril on ADF gene of second-generation merozoites (mz-ADF) mRNA expression in Eimeria tenella, mz-ADF gene was cloned by RT-PCR from extracted RNA in second-generation merozoite of E. tenella and successfully expressed by pET-28a vector in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3). Results showed that the full length of the cloned cDNA sequence of the mz-ADF gene is 476 bp including an ORF of 375 bp. The sequence has 100% homology with a published sequence of sporozoite stage E. tenella ADF mRNA (GenBank EF195234.1). The recombinant protein was induced to be expressed by 1 mM isopropyl β-d-1-thiogalactopyranoside in vitro. Sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis showed that 16.99 kDa fusion protein existed in solvable form. Compared with the infected/control group, mz-ADF mRNA expression level was downregulated by 63.86% in the infected/treatment group with the treatment of diclazuril. In conclusion, the data presented here indicate that mz-ADF gene participates in an important role in the invasion host of E. tenella. Downregulation of mz-ADF mRNA expression enrich the mechanism study of diclazuril on E. tenella.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe H, Obinata T, Minamide LS, Bamburg JR (1996) Xenopus laevis actin-depolymerizing factor/cofilin: a phosphorylation-regulated protein essential for development. J Cell Biol 132:871–885
Augustine RC, Vidali L, Kleinman KP, Bezanilla M (2008) Actin depolymerizing factor is essential for viability in plants, and its phosphoregulation is important for tip growth. Plant J 54:863–875
Bernstein BW, Bamburg JR (2004) A proposed mechanism for cell polarization with no external cues. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 58:96–103
Carlier MF, Laurent V, Santolini J, Melki R, Didry D, Xia GX, Hong Y, Chua NH, Pantaloni D (1997) Actin depolymerizing factor (ADF/Cofilin) enhances the rate of filament turnover: Implication in actin-based motility. J Cell Biol 136:1307–1322
Chen CY, Wong EI, Vidali L, Estavillo A, Hepler PK, Wu HM, Cheung AY (2002) The regulation of actin organization by actin-depolymerizing factor in elongating pollen tubes. Plant cell 14:2175–2190
Didry D, Carlier MF, Pantaloni D (1998) Synergy between actin depolymerizing factor/cofilin and profilin in increasing actin filament turnover. J Biol Chem 273:25602–25611
Fuhrmanna J, Käs J, Stevens A (2007) Initiation of cytoskeletal asymmetry for cell polarization and movement. J Theor Biol 249:278–288
Leadsham JE, Gourlay CW (2008) Cytoskeletal induced apoptosis in yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta 1783:1406–1412
Liu LH, Li J, Xu LX, Li XR, He TW (2006) Separation and purification of second-generation merozoites of Eimeria tenella. Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine 38:38–40
Maciver SK, Hussey PJ (2002) The ADF/cofilin family: actin-remodeling proteins. Genome Biol 3:3007.1–3007.12
Maes L, Coussement W, Vanparijs O, Marsboom R (1988) In vivo action of the anticoccidial diclazuril (Clinacox®) on the developmental stages of Eimeria tenella: a histological study. J Parasitol 74:931–938
Michelot A, Berro J, Guérin C, Boujemaa-Paterski R, Staiger CJ, Martiel JL, Blanchoin L (2007) Actin-filament stochastic dynamics mediated by ADF/cofilin. Curr Biol 17:825–833
Nodeh H, Mansoori B, Rahbari S, Modirsanei M, Aparnak P (2008) Assessing the effect of diclazuril on the intestinal absorptive capacity of broilers infected with experimental coccidiosis, using D-xylose absorption test. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 31:265–267
Ono S (2007) Mechanism of depolymerization and severing of actin filaments and its significance in cytoskeletal dynamics. Int Rev Cytol 258:1–82
Prodon F, Hanawa K, Nishida H (2009) Actin microfilaments guide the polarized transport of nuclear pore complexes and the cytoplasmic dispersal of Vasa Mrna during GVBD in the ascidian Halocynthia roretzi. Dev Biol 330:377–388
Russell DG (1983) Host cell invasion by Apicomplexa: an expression of the parasite’s contractile system? Parasitology 87:199–209
Santos JM, Lebrun M, Daher W, Soldati D, Dubremetz JF (2009) Apicomplexan cytoskeleton and motors: key regulators in morphogenesis, cell division, transport and motility. Int J Parasitol 39:153–162
Sibley LD (2004) Intracellular parasite invasion strategies. Science 304:248–253
Staiger CJ, Blanchoin L (2006) Actin dynamics: old friends with new stories. Curr Opin Plant Biol 9:554–562
Tammana TV, Sahasrabuddhe AA, Mitra K, Bajpai VK, Gupta CM (2008) Actin-depolymerizing factor, ADF/cofilin, is essentially required in assembly of Leishmania flagellum. Mol Microbiol 70:837–852
Verheyen A, Maes L, Coussement W, Vanparijs O, Lauwers F, Vlaminckx E, Borgers M, Marsboom R (1988) In vivo action of the anticoccidial diclazuril (Clinacox®) on the developmental stages of Eimeria tenella: an ultrastructural evaluation. J Parasitol 74:939–949
Xie MQ, Fukata T, Gilbert JM, McDougald LR (1991) Evaluation of anticoccidial drugs in chicken embryos. Parasitol Res 77:595–599
Xu JH, Qin ZH, Liao YS, Xie MQ, Li AX, Cai JP (2008) Characterization and expression of an actin-depolymerizing factor from Eimeria tenella. Parasitol Res 103:263–270
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by central grade public welfare fundamental science fund for scientific research institute (contract grant number: 2008JB09).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Bh., Wang, Hw., Xue, Fq. et al. Actin-depolymerizing factor of second-generation merozoite in Eimeria tenella: clone, prokaryotic expression, and diclazuril-induced mRNA expression. Parasitol Res 106, 571–576 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-009-1699-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-009-1699-z