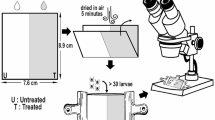
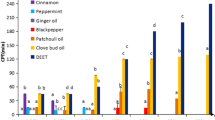
Abstract
The present study was based on assessments of the antiparasitic activities to determine the efficacies of acetone, chloroform, ethyl acetate, hexane, and methanol dried leaf, flower, and seed extracts of Cassia auriculata L., Rhinacanthus nasutus KURZ., Solanum torvum Swartz, Terminalia chebula Retz., and Vitex negundo Linn. were tested against larvae of cattle tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus Canestrini, 1887 (Acari: Ixodidae), adult of Haemaphysalis bispinosa Neumann, 1897 (Acarina: Ixodidae), hematophagous fly Hippobosca maculata Leach (Diptera: Hippoboscidae), nymph of goat-lice Damalinia caprae Gurlt (Trichodectidae), and adult sheep parasite Paramphistomum cervi Zeder, 1790 (Digenea: Paramphistomatidae). All plant extracts showed moderate parasitic effects after 24 h of exposure at 3,000 ppm; however, the highest parasite mortality was found in leaf ethyl acetate, flower methanol of C. auriculata, leaf and seed methanol of S. torvum, seed acetone of T. chebula, and leaf hexane extracts of V. negundo against the larvae of R. microplus (LC50 = 335.48, 309.21, 297.43, 414.99, 167.20, and 611.67 ppm; LC90 = 1571.58, 1111.82, 950.98, 1243.64, 595.31, and 1875.50 ppm), the leaf and flower methanol of R. nasutus, leaf and seed methanol of S. torvum, and seed methanol extracts of T. chebula against the nymph of D. caprae (LC50 = 119.26,143.10,164.93,140.47, and 155.98 ppm; LC90 = 356.77, 224.08, 546.20, 479.72, and 496.06 ppm), the leaf methanol of R. nasutus, leaf and seed methanol of S.torvum, and seed acetone of T. chebula against the adult of H. bispinosa (LC50 = 333.15, 328.98, 312.28, and 186.46 ppm; LC90 = 1056.07, 955.39, 946.63, and 590.76 ppm), the leaf methanol of C. auriculata, the leaf and flower methanol of R. nasutus, the leaf ethyl acetate of S. torvum against the H. maculata (LC50 = 303.36, 177.21, 204.58, and 211.41 ppm; LC90 = 939.90, 539.39, 599.43, and 651.90 ppm), and the leaf acetone of C. auriculata, the flower methanol of R. nasutus, the seed methanol of S. torvum, and the seed acetone of T. chebula were tested against the adult of P. cervi (LC50 = 180.54, 168.59, 200.89, and 87.08 ppm; LC90 = 597.51, 558.65, 690.37, and 433.85 ppm), respectively. Therefore, this study provides first report on the veterinary parasitic activity of plant extracts from Southern India.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhtar MS, Iqbal Z, Khan MN, Lateef M (2000) Anthelmint activity plants with particular reference to their use in animals in the Indo-Pakistan subcontinent. Small Rumi Res 38:99–107
Arthan D, Svasti J, Kittakoop P, Pittayakhachonwut D, Tanticharoen M, Thebtaranonth Y (2002) Antiviral isoflavonoid sulfate and steroidal glycosides from the fruits of Solanum torvum. Phytochemistry 59:459–463
Bagavan A, Kamaraj C, Rahuman AA, Elango G, Zahir AA, Pandiyan G (2009) Evaluation of larvicidal and nymphicidal potential of plant extracts against Anopheles subpictus Grassi, Culex tritaeniorhynchus Giles and Aphis gossypii Glover. Parasitol Res 104:1109–1117
Barthakur NN, Arnold NP (1991) Nutritive value of the chebulic myrobalan (Terminalia chebula Retz.) and its potential as a food source. Food Chem 40:213–219
Chah KF, Muko KN, Oboegbulem SI (2000) Antimicrobial activity of methanolic extract of Solanum torvum fruit. Fitoterapia 71:187–189
Chandramu C, Manohar RD, Krupadanam DGL, Dashavantha RV (2003) Isolation characterization and biological activity of betulinic acid and ursolic acid from Vitex negundo L. Phyto Res 17:129–134
Chattopadhyay RR, Bhattacharyya SK (2007) Terminalia chebula: an update. Pharmacog Rev 1:151–156
Chopra AK, Sharma MK, Upadhyay VP (1991) Effects of ayurvedic anthelmintics on phosphatase activity of Paramphistomum cervi. Indian J Parasitol 43(1):65–69
De Castro JJ (1997) Sustainable tick and tick borne disease control in livestock improvement in developing countries. Vet Parasitol 71:77–97
de Sousa LA, Soares SF, Pires HB Jr (2008) Evaluation of efficacy of ripe and unripe fruit oil extracts of Melia azedarach against Rhipicephalus Boophilus microplus Acari: ixodidae. Rev Bras Parasitol Vet 17(1):36–40
Devendra C (1995) Animal production systems in South East and East Asia: potential challenges for research. In: Proc Global agenda for livestock research, ILRI, January 18–20, pp 41–48
Duraipandiyan V, Ayyanar M, Ignacimuthu S (2006) Antimicrobial activity of some ethnomedicinal plants used by Paliyar tribe from Tamil Nadu, India. BMC Comp Alt Med 6:35–42
FAO (2004) Ticks: Acaricide Resistance: Diagnosis Management and Prevention In: Guidelines Resistance Management and Integrated Parasite Control in Ruminants. FAO Animal Production and Health Division, Rome
Fernandes FF (2001) Toxicological effects and resistance to pyretroids in Boophilus microplus from Goia´s Brasil. Arq Bras Med Vet Zootec 53:548–552
Fernandes FF, Freitas EPS (2007) Acaricidal activity of an oleoresinous extract from Copaifera reticulata (Leguminosae: Caesalpinioideae) against larvae of the southern cattle tick, Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: Ixodidae). Vet Parasitol 147(1–2):150–154
Fernandes FF, Freitas EPS, Costa AC, Silva IG (2005) Larvicidal potential of Sapindus saponaria to control the cattle tick Boophilus microplus. Pesq Agropec Bras 40:1243–1245
Garg SK, Katoch R, Bhushan C (1998) Efficacy of flumethrin pour-on against Damalinia caprae of goats (Capra hircus). Trop Anim Health Prod 30:273–278
Grover IS, Bala S (1992) Antimutagenic activity of Terminalia chebula (myrobalan) in Salmonella typhimurium. Ind J Exp Bio 30:339–341
Hanna REB, Williamson DS, Mattison RG, Nizami WA (1988) Seasonal reproduction in Paramphistomum epiclitum and Gastrothylax crumenifer, rumen paramphistomes of the indian water buffalo, and comparison with the biliary paramphistome Gigantocotyle explanatum. Int J Parasitol 18:513–521
Joshi P (1986) Fish stuper fying plants employed by tribal of southern Rajasthan—a probe. Curr Sci 55:647–650
Kamaraj C, Rahuman AA, Bagavan A (2008) Antifeedant and larvicidal effects of plant extracts against Spodoptera litura (F.), Aedes aegypti L. and Culex quinquefasciatus Say. Parasitol Res 103(2):325–331
Kamaraj C, Bagavan A, Rahuman AA, Zahir AA, Elango G, Pandiyan G (2009) Larvicidal potential of medicinal plant extracts against Anopheles subpictus Grassi and Culex tritaeniorhynchus Giles (Diptera: Culicidae). Parasitol Res 104(5):1163–1171
Kosalge SB, Fursule RA (2009) Investigation of licicidal activity of some plants from satpuda hills. Int J Pharm Tech Res 1:564–567
Lee SH, Ryu SY, Sang U, Lee CO, No ZK, Kim SK, Ahn JW (1995) Hydrolyzable tannins and related compound having cyotoxic activity from the fruits of Terminalia chebula. Arch Pharm Res 18:118–120
Lu Y, Luo J, Huang X, Kong L (2009) Four new steroidal glycosides from Solanum torvum and their cytotoxic activities. Steroids 74:95–101
Minjauw B, Mc Leod A (2003) Tick-borne diseases and poverty. The impact of ticks and tick-borne diseases on the livelihood of small scale and marginal livestock owners in India and eastern and southern Africa. DFID Animal Health Programme, Centre for Tropical Veterinary Medicine, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh
Nalamwar VP, Khadabadi SS, Aswar PB, Kosalge SB, Rajurkar RM (2009) In vitro licicidal activity of different extracts of Acorus calamus linn. (Araceae) Rhizome. Int J PharmTech Res 1(1):96–100
Ndebia EJ, Kamga R, Nchunga-Anye Nkeh B (2007) Analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties of aqueous extract from leaves of Solanum torvum (Solanaceae). Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med 4:240–244
Neogi NC, Baliga PAC, Srivastava RK (1963) Anthelmintic activity of some indigenous drugs. J Indian Med Assoc 1:435–437
Prajapati V, Tripathi AK, Khanuja SPS, Kumar S (2003) Anti-insect screening of medicinal plants from Kukrail Forest, Luknow. Ind Pharma Bio 41:166–170
Reddy PJ, Krishna D, Murthy US, Jamil K (1992) A microcomputer FORTRAN program for rapid determination of lethal concentration of biocides in mosquito control. CABIOS 8:209–213
Ribeiro VL, Toigo E, Bordignon SA, Gonçalves K, von Poser G (2007) Acaricidal properties of extracts from the aerial parts of Hypericum polyanthemum on the cattle tick Boophilus microplus. Vet Parasitol 147(1–2):199–203
Ribeiro VL, Avancini C, Gonçalves K, Toigo E, von Poser G (2008) Acaricidal activity of Calea serrata (Asteraceae) on Boophilus microplus and Rhipicephalus sanguineus. Vet Parasitol 151(2–4):351–354
Rongsriyam Y, Trongtokit Y, Komalamisra N, Sinchaipanich N, Apiwathnasorn C, Mitrejet A (2006) Formulation of tablets from the crude extract of Rhinacanthus nasutus (Thai local plant) against Aedes aegypti and Culex quinquefasciatus larvae: a preliminary study. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 37(2):265–271
Sahare KN, Anandhraman V, Meshram VG, Meshram SU, Reddy MV, Tumane PM, Goswami K (2008) Anti-microfilarial activity of methanolic extract of Vitex negundo and Aegle marmelos and their phytochemical analysis. Ind J Exp Bio 46:128–131
Saleem A, Husheem M, Hrknen P, Pihlaja K (2002) Inhibition of cancer cell growth by crude extract and the phenolics of Terminalia chebula retz. fruit. J Ethnopharmacol 81:327–336
Sawhney AN, Khan MR, Ndaalio G, Nkunya MHH, Wavers H (1978) Studies on the rationale of African traditional medicine. Part II. Preliminary screening of medicinal plants for Anti- Gonoccoci activity. Pak J Sci Ind Res 21:189–192
Shuaibu MN, Wuyep PT, Yanagi T, Hirayama K, Ichinose A, Tanaka T, Kouno I (2008a) Trypanocidal activity of extracts and compounds from the stem bark of Anogeissus leiocarpus and Terminalia avicennoides. Parasitol Res 102(4):697–703
Shuaibu MN, Pandey K, Wuyep PA, Yanagi T, Hirayama K, Ichinose A, Tanaka T, Kouno I (2008b) Castalagin from Anogeissus leiocarpus mediates the killing of Leishmania in vitro. Parasitol Res 103:1333–1338
Silva TM, Batista MM, Camara CA, Agra MF (2005) Molluscicidal activity of some Brazilian Solanum spp. (Solanaceae) against Biomphalaria glabrata. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 99:419–425
Sivapriya M, Srinivas L (2007) Isolation and purification of a novel antioxidant protein from thewater extract of Sundakai (Solanum torvum) seeds. Food Chem 104:510–517
Sohni YR, Kaimal P, Bhatt RM (1995) The antiamoebic effect of a crude drug formulation of herbal extracts against Entamoeba histolytica in vitro and in vivo. J Ethnopharmacol 45:43–52
Srivastava R, Ghosh S, Mandal DB, Azhahianambi P, Singhal PS, Pandey NN, Swarup D (2008) Efficacy of Azadirachta indica extracts against Boophilus microplus. Parasitol Res 104(1):149–153
Tandon V, Pal P, Roy B, Rao HS, Reddy KS (1997) In vitro anthelmintic activity of root-tuber extract of Flemingia vestita, an indigenous plant in Shillong, India. Parasitol Res 835:492–498
Vedavathi S, Mrudula V, Sudhakar A (1997) Tribal medicine of Chittoor district, AndhraPradesh, India, vols. 48–49. Herbal Folklore Research Center, Tirupati
Waller PJ (2003) The future of anthelmintics in sustainable parasite control programs for livestock. Helminthologia 40:97–102
Wiart C, Mogana S, Califa S, Mahan M, Ismael S, Bucle M, Narayana AK, Sulaiman M (2004) Antimicrobial screening of plants used for traditional medicine in the state of Perak, Peninsular Malaysia. Fitoterapia 75:68–73
Wu TS, Hsu HC, Wu PL, Teng CM, Wu YC (1998) Rhinacanthin-Q, a naphthoquinone from Rhinacanthus nasutus and its biological activity. Phytochem 49:2001–2003
Zahir AA, Rahuman AA, Kamaraj C, Bagavan A, Elango G, Sangaran A, Kumar BS (2009) Laboratory determination of efficacy of indigenous plant extracts for parasites control. Parasitol Res 105:453–461
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to C. Abdul Hakeem College Management, Dr. S. Mohammed Yousuff, Principal, Dr. K. Abdul Subhan, HOD of Zoology Department, and Dr. Sait Sahul Hameed, Reader in Zoology, for their help and suggestion. The authors wish to thank Dr. A. Sangaran, Department of Parasitology, Madras Veterinary College, Tamil Nadu Veterinary and Animal Sciences University, Chennai, India for identification of parasites.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamaraj, C., Rahuman, A.A., Bagavan, A. et al. Evaluation of medicinal plant extracts against blood-sucking parasites. Parasitol Res 106, 1403–1412 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-1816-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-1816-z