Abstract
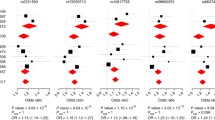
The chromosomal region 10p13 has been linked to paucibacillary leprosy in two independent studies. The MRC1 gene, encoding the human mannose receptor (MR), is located in the 10p13 region and non-synonymous SNPs in exon 7 of the gene have been suggested as leprosy susceptibility factors. We determined that G396S is the only non-synonymous exon 7-encoded polymorphism in 396 unrelated Vietnamese subjects. This SNP was genotyped in 490 simplex and 90 multiplex leprosy families comprising 704 patients (47% paucibacillary; 53% multibacillary). We observed significant under-transmission of the serine allele of the G396S polymorphism with leprosy per se (P = 0.036) and multibacillary leprosy (P = 0.034). In a sample of 384 Brazilian leprosy cases (51% paucibacillary; 49% multibacillary) and 399 healthy controls, we observed significant association of the glycine allele of the G396S polymorphism with leprosy per se (P = 0.016) and multibacillary leprosy (P = 0.023). In addition, we observed a significant association of exon 7 encoded amino acid haplotypes with leprosy per se (P = 0.012) and multibacillary leprosy (P = 0.004). Next, we tested HEK293 cells over-expressing MR constructs (293-MR) with three exon 7 haplotypes of MRC1 for their ability to bind and internalize ovalbumin and zymosan, two classical MR ligands. No difference in uptake was measured between the variants. In addition, 293-MR failed to bind and internalize viable Mycobacterium leprae and BCG. We propose that the MR–M. leprae interaction is modulated by an accessory host molecule of unknown identity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcais A, Alter A, Antoni G, Orlova M, Van Thuc N, Singh M, Vanderborght PR, Katoch K, Mira MT, Thai VH, Huong NT, Ba NN, Moraes M, Mehra N, Schurr E, Abel L (2007) Stepwise replication identifies a low-producing lymphotoxin-[alpha] allele as a major risk factor for early-onset leprosy. Nat Genet 39:517–522
Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ (2005) Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 21:263–265
Bell P, Chaturvedi S, Gelfand C, Huang C, Kochersperger M, Kopla R, Modica F, Pohl M, Varde S, Zhao R, Zhao X, Boyce-Jacino M, Yassen A (2002) SNPstream UHT: ultra-high throughput SNP genotyping for pharmacogenomics and drug discovery. Biotechniques (Suppl 70–2, 74, 76–7)
Boskovic J, Arnold JN, Stilion R, Gordon S, Sim RB, Rivera-Calzada A, Wienke D, Isacke CM, Martinez-Pomares L, Llorca O (2006) Structural model for the mannose receptor family uncovered by electron microscopy of Endo180 and the mannose receptor. J Biol Chem 281:8780–8787
Chakravartti M, Vogel F (1973) A twin study on leprosy. In: Becker PE, Lenz W, Vogel F, Wendt GG (eds) Topics in human genetics, vol 1. Georg Thieme, Stuttgart, pp 1–123
Cooke G, Hill A (2008) Tuberculosis, leprosy and other mycobacterial diseases. In: Kaslow RA, McNicholl JM, Hill AVS (eds) Genetic susceptibility to infectious diseases. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 333–351
Ezekowitz RA, Sastry K, Bailly P, Warner A (1990) Molecular characterization of the human macrophage mannose receptor: demonstration of multiple carbohydrate recognition-like domains and phagocytosis of yeasts in Cos-1 cells. J Exp Med 172:1785–1794
Fan J, Oliphant A, Shen R, Kermani B, Garcia F, Gunderson K, Hansen M, Steemers F, Butler S, Deloukas P, Galver L, Hunt S, McBride C, Bibikova M, Rubano T, Chen J, Wickham E, Doucet D, Chang W, Campbell D, Zhang B, Kruglyak S, Bentley D, Haas J, Rigault P, Zhou L, Stuelpnagel J, Chee M (2003) Highly parallel SNP genotyping. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 68:69–78
Griffin TJ, Smith LM (2000) Single-nucleotide polymorphism analysis by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Trends Biotechnol 18:77–84
Groger M, Holnthoner W, Maurer D, Lechleitner S, Wolff K, Mayr BB, Lubitz W, Petzelbauer P (2000) Dermal microvascular endothelial cells express the 180-kDa macrophage mannose receptor in situ and in vitro. J Immunol 165:5428–5434
Hattori T, Konno S, Hizawa N, Isada A, Takahashi A, Shimizu K, Shimizu K, Gao P, Beaty TH, Barnes KC, Huang SK, Nishimura M (2009) Genetic variants in the mannose receptor gene (MRC1) are associated with asthma in two independent populations. Immunogenetics. doi:10.1007/s00251-009-0403-x
Hill AV (2006) Aspects of genetic susceptibility to human infectious diseases. Annu Rev Genet 40:469–486
Horvath S, Xu X, Laird NM (2001) The family based association test method: strategies for studying general genotype–phenotype associations. Eur J Hum Genet 9:301–306
Kabha K, Nissimov L, Athamna A, Keisari Y, Parolis H, Parolis LA, Grue RM, Schlepper-Schafer J, Ezekowitz AR, Ohman DE (1995) Relationships among capsular structure, phagocytosis, and mouse virulence in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect Immun 63:847–852
Kang PB, Azad AK, Torrelles JB, Kaufman TM, Beharka A, Tibesar E, DesJardin LE, Schlesinger LS (2005) The human macrophage mannose receptor directs Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipoarabinomannan-mediated phagosome biogenesis. J Exp Med 202:987–999
Lake SL, Blacker D, Laird NM (2000) Family-based tests of association in the presence of linkage. Am J Hum Genet 67:1515–1525
Le Cabec V, Emorine LJ, Toesca I, Cougoule C, Maridonneau-Parini I (2005) The human macrophage mannose receptor is not a professional phagocytic receptor. J Leukoc Biol 77:934–943
Miller EN, Jamieson SE, Joberty C, Fakiola M, Hudson D, Peacock CS, Cordell HJ, Shaw MA, Lins-Lainson Z, Shaw JJ, Ramos F, Silveira F, Blackwell JM (2004) Genome-wide scans for leprosy and tuberculosis susceptibility genes in Brazilians. Genes Immun 5:63–67
Mira MT, Alcais A, Van Thuc N, Thai VH, Huong NT, Ba NN, Verner A, Hudson TJ, Abel L, Schurr E (2003) Chromosome 6q25 is linked to susceptibility to leprosy in a Vietnamese population. Nat Genet 33:412–415
Mira MT, Alcais A, Van Thuc N, Moraes MO, Di Flumeri C, Hong Thai V, Chi Phuong M, Thu Huong N, Ngoc Ba N, Xuan Khoa P, Sarno EN, Alter A, Montpetit A, Moraes ME, Moraes JR, Dore C, Gallant CJ, Lepage P, Verner A, van de Vosse E, Hudson TJ, Abel L, Schurr E (2004) Susceptibility to leprosy is associated with PARK2 and PACRG. Nature 427:636–640
Nigou J, Zelle-Rieser C, Gilleron M, Thurnher M, Puzo G (2001) Mannosylated lipoarabinomannans inhibit IL-12 production by human dendritic cells: evidence for a negative signal delivered through the mannose receptor. J Immunol 166:7477–7485
Ridley DS, Jopling WH (1966) Classification of leprosy according to immunity. A five-group system. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis 34:255–273
Schlesinger LS (1993) Macrophage phagocytosis of virulent but not attenuated strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is mediated by mannose receptors in addition to complement receptors. J Immunol 150:2920–2930
Schlesinger LS, Hull SR, Kaufman TM (1994) Binding of the terminal mannosyl units of lipoarabinomannan from a virulent strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to human macrophages. J Immunol 152:4070–4079
Schlesinger LS, Kaufman TM, Iyer S, Hull SR, Marchiando LK (1996) Differences in mannose receptor-mediated uptake of lipoarabinomannan from virulent and attenuated strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by human macrophages. J Immunol 157:4568–4575
Shimada K, Takimoto H, Yano I, Kumazawa Y (2006) Involvement of mannose receptor in glycopeptidolipid-mediated inhibition of phagosome-lysosome fusion. Microbiol Immunol 50:243–251
Siddiqui MR, Meisner S, Tosh K, Balakrishnan K, Ghei S, Fisher SE, Golding M, Shanker Narayan NP, Sitaraman T, Sengupta U, Pitchappan R, Hill AVS (2001) A major susceptibility locus for leprosy in India maps to chromosome 10p13. Nat Genet 27:439–441
Taylor ME, Bezouska K, Drickamer K (1992) Contribution to ligand binding by multiple carbohydrate-recognition domains in the macrophage mannose receptor. J Biol Chem 267:1719–1726
Tosh K, Meisner S, Siddiqui MÂR, Balakrishnan K, Ghei S, Golding M, Sengupta U, Pitchappan Ramasamy ÂM, Hill Adrian ÂVÂS (2002) A region of chromosome 20 is linked to leprosy susceptibility in a south Indian population. J Infect Dis 186:1190–1193
Tregouet DA, Garelle V (2007) A new JAVA interface implementation of THESIAS: testing haplotype effects in association studies. Bioinformatics 23:1038–1039
Wallace C, Fitness J, Hennig B, Sichali L, Mwaungulu L, Ponnighaus JM, Warndorff DK, Clayton D, Fine PEM, Hill AVS (2004) Linkage analysis of susceptibility to leprosy type using an IBD regression method. Genes Immun 5:221–225
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to all patients and their families who participated in this study. We thank J.L. Casanova, M. Behr and K. Morgan for helpful discussions and A. Montpetit and A. Bélisle for assistance with high-throughput genotyping. Fresh nu/nu mouse derived M. leprae were supplied by Dr. R. Truman and Dr. L. Adams of the National Hansen’s Disease Program Laboratory Research Branch, Baton Rouge, LA. Funding for this service was provided by the American Leprosy Missions. We thank Dr. J.J. He (Indiana University, IN) for providing the MRC1 cDNA. This study was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) to E.S. and MAGRALEPRE from l’Ordre de Malte to Al.A. The Laboratory of Human Genetics of Infectious Diseases is supported by grants from The Rockefeller University Center for Clinical and Translational Science grant number 5UL1RR024143-03 and The Rockefeller University. An.A. holds a graduate studentship from the Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC). Al.A. and L.A. are supported by the Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, Programme de Recherche Fondamentale en Microbiologie Maladies Infectieuses et Parasitaires (PRFMMIP), and the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR) of the Ministère Français de l’Éducation Nationale de la Recherche et de la Technologie. E.S. is a Chercheur National du Fonds de la Recherche en Santé du Québec and an International Research Scholar of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
A. Alter, L. de Léséleuc contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
439_2009_775_MOESM2_ESM.doc
Identification of coding SNPs with minor allele frequencies >5% in MRC1 by direct sequencing in 23 unrelated Vietnamese individuals (DOC 36 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alter, A., de Léséleuc, L., Van Thuc, N. et al. Genetic and functional analysis of common MRC1 exon 7 polymorphisms in leprosy susceptibility. Hum Genet 127, 337–348 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-009-0775-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-009-0775-x