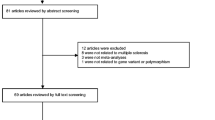
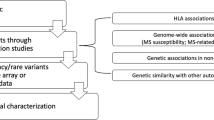
Abstract
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a common complex neurodegenerative disease of the central nervous system. It develops with autoimmune inflammation and demyelination. Genome-wide association studies (GWASs) serve as a powerful tool for investigating the genetic architecture of MS and are generally used to identify the genetic factors of disease susceptibility, clinical phenotypes, and treatment response. This review considers the main achievements and challenges of using GWAS to identify the genes involved in MS. It also describes hypothesis-driven studies with extensive genome coverage of the selected regions, complementary to GWASs. To date, over 100 MS risk loci have been identified by the combination of both approaches; 40 of them were found in at least two GWASs and meet genome-wide significance threshold (p ≤ 5 × 10−8) in at least one GWAS, whereas the threshold for the rest of GWASs was set in our review at p < 1 × 10−5. Yet, MS risk loci identified to date explain only a part of the total heritability, and the reasons of “missing heritability” are discussed. The functions of MS-associated genes are described briefly; the majority of them encode immune-response proteins involved in the main stages of MS pathogenesis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aulchenko YS, Hoppenbrouwers IA, Ramagopalan SV et al (2008) Genetic variation in the KIF1B locus influences susceptibility to multiple sclerosis. Nat Genet 40:1402–1403. doi:10.1038/ng.251
Australia and New Zealand Multiple Sclerosis Genetics Consortium (ANZgene), Bahlo M et al (2009) Genome-wide association study identifies new multiple sclerosis susceptibility loci on chromosomes 12 and 20. Nat Genet 41:824–828. doi:10.1038/ng.396
Bahreini SA, Jabalameli MR, Saadatnia M, Zahednasab H (2010) The role of non-HLA single nucleotide polymorphisms in multiple sclerosis susceptibility. J Neuroimmunol 229:5–15
Ban M, Stewart GJ, Bennetts BH, Heard R, Simmons R, Maranian M, Compston A, Sawcer SJ (2002) A genome screen for linkage in Australian sibling-pairs with multiple sclerosis. Genes Immun 3:464–469
Baranzini SE, Wang J, Gibson RA et al (2009) Genome-wide association analysis of susceptibility and clinical phenotype in multiple sclerosis. Hum Mol Genet 18:767–778. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddn388
Bomprezzi R, Kovanen PE, Martin R (2003) New approaches to investigating heterogeneity in complex traits. J Med Genet 40:553–559. doi:10.1136/jmg.40.8.553
Bradl M, Lassmann H (2009) Progressive multiple sclerosis. Semin Immunopathol 31:455–465
Browne P, Chandraratna D, Angood C, Tremlett H, Baker C, Taylor BV, Thompson AJ (2014) Atlas of Multiple Sclerosis 2013: a growing global problem with widespread inequity. Neurology 83:1022–1024
Burdett T, Hall PN, Hasting E, Hindorff LA, Junkins HA, Klemm AK, MacArthur J, Manolio TA, Morales J, Parkinson H, Welter D (2015) The NHGRI-EBI Catalog of published genome-wide association studies. http://www.ebi.ac.uk/gwas. Accessed 17 April 2015
Bush WS, Moore JH (2012) Chapter 11: Genome-wide association studies. PLoS Comput Biol 8:e1002822. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002822
Comabella M, Craig DW, Carmiña-Tato M et al (2008) Identification of a novel risk locus for multiple sclerosis at 13q31.3 by a pooled genome-wide scan of 500,000 single nucleotide polymorphisms. PLoS One 3:e3490. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0003490
Compston DA, Batchelor JR, McDonald WI (1976) B-lymphocyte alloantigens associated with multiple sclerosis. Lancet 2:1261–1265. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(76)92027-4
Cotsapas C, Hafler DA (2013) Immune-mediated disease genetics: the shared basis of pathogenesis. Trends Immunol 34:22–26
Cree BA (2014) Multiple sclerosis genetics. Handb Clin Neurol 122:193–209
Cunningham C (2013) Microglia and neurodegeneration: the role of systemic inflammation. Glia 61:71–90. doi:10.1002/glia.22350
De Jager PL, Jia X, Wang J et al (2009a) Meta-analysis of genome scans and replication identify CD6, IRF8 and TNFRSF1A as new multiple sclerosis susceptibility loci. Nat Genet 41:776–782. doi:10.1038/ng.401.Meta-analysis
De Jager PL, Baecher-Allan C, Maier LM et al (2009b) The role of the CD58 locus in multiple sclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:5264–5269. doi:10.1073/pnas.0813310106
De Jager PL, Chibnik LB, Cui J, Reischl J, Lehr S et al (2009c) Integration of genetic risk factors into a clinical algorithm for multiple sclerosis susceptibility: a weighted genetic risk score. Lancet Neurol 8:1111–1119. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70275-3
Denic A, Wootla B, Rodriguez M (2013) CD8(+) T cells in multiple sclerosis. Expert Opin Ther Targets 17:1053–1066
Dore-Duffy P, Washington R, Dragovic L (1993) Expression of endothelial cell activation antigens in microvessels from patients with multiple sclerosis. Adv Exp Med Biol 331:243–248
Ebers GC, Kukay K, Bulman DE et al (1996) A full genome search in multiple sclerosis. Nat Genet 13:472–476. doi:10.1038/ng0896-472
Favorov AV, Andreewski TV, Sudomoina MA, Favorova OO, Parmigiani G, Ochs MF (2005) A Markov chain Monte Carlo technique for identification of combinations of allelic variants underlying complex diseases in humans. Genetics 171:2113–2121. doi:10.1534/genetics.105.048090
Favorova OO, Andreewski TV, Boiko AN et al (2002) The chemokine receptor CCR5 deletion mutation is associated with MS in HLA-DR4-positive Russians. Neurology 59:1652–1655. doi:10.1212/01.WNL.0000035626.92372.0A
Favorova OO, Favorov AV, Boiko AN, Andreewski TV, Sudomoina MA, Alekseenkov AD, Kulakova OG, Gusev EI, Parmigiani G, Ochs MF (2006) Three allele combinations associated with multiple sclerosis. BMC Med Genet 7:63. doi:10.1186/1471-2350-7-63
GAMES, Transatlantic Multiple Sclerosis Genetics Cooperative (2003) A meta-analysis of whole genome linkage screens in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 143:39–46
Goodin DS, Khankhanian P (2014) Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)-strings: an alternative method for assessing genetic associations. PLoS One 9:e90034
Gourraud PA, International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics Consortium (IMSGC) (2011) When is the absence of evidence, evidence of absence? Use of equivalence-based analyses in genetic epidemiology and a conclusion for the KIF1B rs10492972*C allelic association in multiple sclerosis. Genet Epidemiol 35:568–571. doi:10.1002/gepi.20592
Gourraud PA, McElroy JP, Caillier SJ, Johnson BA, Santaniello A, Hauser SL, Oksenberg JR (2011) Aggregation of multiple sclerosis genetic risk variants in multiple and single case families. Ann Neurol 69:65–74
Gourraud PA, Harbo HF, Hauser SL, Baranzini SE (2012) The genetics of multiple sclerosis: an up-to-date review. Immunol Rev 248:87–103. doi:10.1111/j.1600-065X.2012.01134.x
Gourraud PA, Sdika M, Khankhanian P, Henry RG, Beheshtian A, Matthews PM, Hauser SL, Oksenberg JR, Pelletier D, Baranzini SE (2013) A genome-wide association study of brain lesion distribution in multiple sclerosis. Brain 136:1012–1024
Goverman J (2009) Autoimmune T cell responses in the central nervous system. Nat Rev Immunol 9:393–407. doi:10.1038/nri2550
Gregory SG, Schmidt S, Seth P et al (2007) Interleukin 7 receptor alpha chain (IL7R) shows allelic and functional association with multiple sclerosis. Nat Genet 39:1083–1091. doi:10.1038/ng2103
Gregory AP, Dendrou CA, Attfield KE et al (2012) TNF receptor 1 genetic risk mirrors outcome of anti-TNF therapy in multiple sclerosis. Nature 488:508–511. doi:10.1038/nature11307
Guerini FR, Ferrante P, Losciale L, Caputo D, Lombardi ML, Pirozzi G, Luongo V, Sudomoina MA, Andreewski TV, Alekseenkov AD, Boiko AN, Gusev EI, Favorova OO (2003) Myelin basic protein gene is associated with MS in DR4- and DR5-positive Italians and Russians. Neurology 61:520–526
Hedegaard CJ, Krakauer M, Bendtzen K et al (2008) T helper cell type 1 (Th1), Th2 and Th17 responses to myelin basic protein and disease activity in multiple sclerosis. Immunology 125:161–169. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.02837.x
Hermanowski J, Bouzigon E, Forabosco P, Ng MY, Fisher SA, Lewis CM (2007) Meta-analysis of genome-wide linkage studies for multiple sclerosis, using an extended GSMA method. Eur J Hum Genet 15:703–710. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201818
Hindorff LA, Sethupathy P, Junkins HA et al (2009) Potential etiologic and functional implications of genome-wide association loci for human diseases and traits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:9362–9367. doi:10.1073/pnas.0903103106
Hohlfeld R (2008) Neurotrophic cross-talk between the nervous and immune systems: relevance for repair strategies in multiple sclerosis? J Neurol Sci 265:93–96. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2007.03.012
Holman DW, Klein RS, Ransohoff RM (2011) The blood–brain barrier, chemokines and multiple sclerosis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1812:220–230
http://www.genecards.org. Accessed 20 April 2015
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene. Accessed 20 April 2015
http://amigo.geneontology.org/amigo/landing. Accessed 25 April 2015
http://revigo.irb.hr/. Accessed 25 April 2015
International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics Consortium (2013) Network-based multiple sclerosis pathway analysis with GWAS data from 15,000 cases and 30,000 controls. Am J Hum Genet 92:854–865. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.04.019
International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics Consortium (IMSGC), Bush WS, Sawcer SJ, de Jager PL, Oksenberg JR, McCauley JL, Pericak-Vance MA, Haines JL (2010) Evidence for polygenic susceptibility to multiple sclerosis—the shape of things to come. Am J Hum Genet 86:621–625. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.02.027
International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics Consortium (IMSGC), Beecham AH, Patsopoulos NA, Xifara DK et al (2013) Analysis of immune-related loci identifies 48 new susceptibility variants for multiple sclerosis. Nat Genet 45:1353–1360. doi:10.1038/ng.2770
International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics Consortium, David A, Hafler MD, Compston A et al (2007) Risk alleles for multiple sclerosis identified by a genomewide study. N Engl J Med 357:2373–2383. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1407764
International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics Consortium, Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium, Sawcer S et al (2011) Genetic risk and a primary role for cell-mediated immune mechanisms in multiple sclerosis. Nature 476:214–219. doi:10.1038/nature10251
International Schizophrenia Consortium, Purcell SM, Wray NR, Stone JL et al (2009) Common polygenic variation contributes to risk of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Nature 460:748–752. doi:10.1038/nature08185
Isobe N, Madireddy L, Khankhanian P, Matsushita T, Caillier SJ, Moré JM, Gourraud PA, McCauley JL, Beecham AH, International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics Consortium, Piccio L, Herbert J, Khan O, Cohen J, Stone L, Santaniello A, Cree BA, Onengut-Gumuscu S, Rich SS, Hauser SL, Sawcer S, Oksenberg JR (2015) An ImmunoChip study of multiple sclerosis risk in African Americans. Brain 138:1518–1530
Iwanowski P, Losy J (2015) Immunological differences between classical phenotypes of multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 349:10–14
Jafari N, Broer L, van Duijn CM, Janssens AC, Hintzen RQ (2011) Perspectives on the use of multiple sclerosis risk genes for prediction. PLoS One 6:e26493. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0026493
Jakkula E, Leppä V, Sulonen AM et al (2010) Genome-wide association study in a high-risk isolate for multiple sclerosis reveals associated variants in STAT3 gene. Am J Hum Genet 86:285–291. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.01.017
Kaufman DW, Reshef S, Golub HL, Peucker M, Corwin MJ, Goodin DS, Knappertz V, Pleimes D, Cutter G (2014) Survival in commercially insured multiple sclerosis patients and comparator subjects in the US. Mult Scler Relat Disord 3:364–371. doi:10.1016/j.msard.2013.12.003
Khankhanian P, Gourraud PA, Lizee A, Goodin DS (2015) Haplotype-based approach to known MS-associated regions increases the amount of explained risk. J Med Genet 52:587–594
Kilpinen H, Barrett JC (2013) How next-generation sequencing is transforming complex disease genetics. Trends Genet 29:23–30
Kleinewietfeld M, Hafler DA (2014) Regulatory T cells in autoimmune neuroinflammation. Immunol Rev 259:231–244. doi:10.1111/imr.12169
Kuhle J, Disanto G, Dobson R, Adiutori R et al (2015) Conversion from clinically isolated syndrome to multiple sclerosis: a large multicentre study. Mult Scler 21:1013–1024. doi:10.1177/1352458514568827
Lambert CA, Tishkoff SA (2009) Genetic structure in African populations: implications for human demographic history. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 74:395–402
Lassmann H, Brück W, Lucchinetti CF (2007) The immunopathology of multiple sclerosis: an overview. Brain Pathol 17:210–218
Leray E, Vukusic S, Debouverie M, Clanet M et al (2015) Excess mortality in patients with multiple sclerosis starts at 20 years from clinical onset: data from a large-scale French observational study. PLoS One 10:e0132033. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0132033
Li Y, Willer C, Sanna S, Abecasis G (2009) Genotype imputation. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 10:387–406. doi:10.1146/annurev.genom.9.081307.164242
Lill CM (2014) Recent advances and future challenges in the genetics of multiple sclerosis. Front Neurol 5:130
Lin R, Charlesworth J, van der Mei I, Taylor BV (2012) The genetics of multiple sclerosis. Pract Neurol 12:279–288
Lovett-Racke AE, Yang Y, Racke MK (2011) Th1 versus Th17: are T cell cytokines relevant in multiple sclerosis? Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1812:246–251. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.05.012
Lu YF, Goldstein DB, Angrist M, Cavalleri G (2014) Personalized medicine and human genetic diversity. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 4:a008581
Lundmark F, Duvefelt K, Iacobaeus E et al (2007) Variation in interleukin 7 receptor alpha chain (IL7R) influences risk of multiple sclerosis. Nat Genet 39:1108–1113. doi:10.1038/ng2106
Lvovs D, Favorova OO, Favorov AV (2012) A polygenic approach to the study of polygenic diseases. Acta Naturae 4:59–71
Maier LM, Anderson DE, Severson CA, Baecher-Allan C, Healy B, Liu DV, Wittrup KD, De Jager PL, Hafler DA (2009) Soluble IL-2RA levels in multiple sclerosis subjects and the effect of soluble IL-2RA on immune responses. J Immunol 182:1541–1547
Manolio TA, Collins FS, Cox NJ et al (2009) Finding the missing heritability of complex diseases. Nature 461:747–753. doi:10.1038/nature08494
Marian AJ (2012) Molecular genetic studies of complex phenotypes. Transl Res 159:64–79. doi:10.1016/j.trsl.2011.08.001
Marigorta UM, Lao O, Casals F et al (2011) Recent human evolution has shaped geographical differences in susceptibility to disease. BMC Genom 12:55. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-12-55
Marrie RA, Elliott L, Marriott J, Cossoy M, Blanchard J, Leung S, Yu N (2015) Effect of comorbidity on mortality in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 85:240–247. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000001718
Martinelli-Boneschi F, Esposito F, Brambilla P et al (2012) A genome-wide association study in progressive multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 18:1384–1394. doi:10.1177/1352458512439118
Matesanz F, González-Pérez A, Lucas M, et al. (2012) Genome-wide association study of multiple sclerosis confirms a novel locus at 5p13.1. PLoS One 7:e36140. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0036140
Matsushita T, Madireddy L, Sprenger T, Khankhanian P, Magon S, Naegelin Y, Caverzasi E, Lindberg RL, Kappos L, Hauser SL, Oksenberg JR, Henry R, Pelletier D, Baranzini SE (2015) Genetic associations with brain cortical thickness in multiple sclerosis. Genes Brain Behav 14:217–227
Naito S, Namerow N, Mickey MR, Terasaki PI (1972) Multiple sclerosis: association with HL-A3. Tissue Antigens 2:1–4
Nischwitz S, Cepok S, Kroner A et al (2010) Evidence for VAV2 and ZNF433 as susceptibility genes for multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 227:162–166. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2010.06.003
Nylander A, Hafler DA (2012) Multiple sclerosis. J Clin Invest 122:1180–1188
Oksenberg JR (2013) Decoding multiple sclerosis: an update on genomics and future directions. Expert Rev Neurother 13:11–19. doi:10.1586/14737175.2013.865867
Oksenberg JR, Baranzini SE, Sawcer S, Hauser SL (2008) The genetics of multiple sclerosis: sNPs to pathways to pathogenesis. Nat Rev Genet 9:516–526
Ortiz GG, Pacheco-Moisés FP, Macías-Islas MÁ, Flores-Alvarado LJ, Mireles-Ramírez MA, González-Renovato ED, Hernández-Navarro VE, Sánchez-López AL, Alatorre-Jiménez MA (2014) Role of the blood–brain barrier in multiple sclerosis. Arch Med Res 45:687–697
Parkes M, Cortes A, van Heel DA, Brown MA (2013) Genetic insights into common pathways and complex relationships among immune-mediated diseases. Nat Rev Genet 14:661–673. doi:10.1038/nrg3502
Patsopoulos NA, Bayer Pharma MS Genetics Working Group, Steering Committees of Studies Evaluating IFN[beta]-1b and a CCR1-Antagonist, ANZgene Consortium, GeneMSA, International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics Consortium, Esposito F, Reischl J et al (2011) Genome-wide meta-analysis identifies novel multiple sclerosis susceptibility loci. Ann Neurol 70:897–912. doi:10.1002/ana.22609
Pavlopoulos GA, Oulas A, Iacucci E et al (2013) Unraveling genomic variation from next generation sequencing data. BioData Min 6:13. doi:10.1186/1756-0381-6-13
Pèer I, Yelensky R, Altshuler D, Daly MJ (2008) Estimation of the multiple testing burden for genomewide association studies of nearly all common variants. Genet Epidemiol 32:381–385. doi:10.1002/gepi.20303
Ramagopalan SV, Ebers GC (2009) Multiple sclerosis: major histocompatibility complexity and antigen presentation. Genome Med 1:105. doi:10.1186/gm105
Rasmussen HB, Kelly MA, Clausen J (2001) Genetic susceptibility to multiple sclerosis: detection of polymorphic nucleotides and an intron in the 3′ untranslated region of the major histocompatibility complex class II transactivator gene. Hum Immunol 62:371–377. doi:10.1016/S0198-8859(01)00215-4
Sadee W, Hartmann K, Seweryn M, Pietrzak M, Handelman SK, Rempala GA (2014) Missing heritability of common diseases and treatments outside the protein-coding exome. Hum Genet 133:1199–1215
Sanna S, Pitzalis M, Zoledziewska M et al (2010) Variants within the immunoregulatory CBLB gene are associated with multiple sclerosis. Nat Genet 42:495–497. doi:10.1038/ng.584
Sawcer S, Jones HB, Feakes R et al (1996) A genome screen in multiple sclerosis reveals susceptibility loci on chromosome 6p21 and 17q22. Nat Genet 13:464–468. doi:10.1038/ng0896-464
Sawcer S, Ban M, Maranian M et al (2005) A high-density screen for linkage in multiple sclerosis. Am J Hum Genet 77:454–467. doi:10.1086/444547
Sawcer S, Franklin RJ, Ban M (2014) Multiple sclerosis genetics. Lancet Neurol 13:700–709
Spencer CC, Su Z, Donnelly P, Marchini J (2009) Designing genome-wide association studies: sample size, power, imputation, and the choice of genotyping chip. PLoS Genet 5:e1000477. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000477
Stys PK (2005) General mechanisms of axonal damage and its prevention. J Neurol Sci 233:3–13
Supek F, Bošnjak M, Škunca N, Šmuc T (2011) Revigo summarizes and visualizes long lists of gene ontology terms. PLoS One 6:e21800. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0021800
Tauber SC, Nau R, Gerber J (2007) Systemic infections in multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Arch Physiol Biochem 113:124–130
The ENCODE Project Consortium, Bernstein BE, Birney E, Dunham I, Green ED, Gunter C, Snyder M (2012) An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature 489:57–74. doi:10.1038/nature11247
Visscher PM, Brown MA, McCarthy MI, Yang J (2012) Five years of GWAS discovery. Am J Hum Genet 90:7–24
von Büdingen H-C, Bar-Or A, Zamvil SS (2011) B cells in multiple sclerosis: connecting the dots. Curr Opin Immunol 23:713–720
Wang JH, Pappas D, De Jager PL et al (2011) Modeling the cumulative genetic risk for multiple sclerosis from genome-wide association data. Genome Med 3:3. doi:10.1186/gm217
Wang L, Mousavi P, Baranzini SE (2015) iPINBPA: an integrative network-based functional module discovery tool for genome-wide association studies. Pac Symp Biocomput 2015:255–266
Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium, Australo-Anglo-American Spondylitis Consortium (TASC), Burton PR et al (2007) Association scan of 14,500 nonsynonymous SNPs in four diseases identifies autoimmunity variants. Nat Genet 39:1329–1337. doi:10.1038/ng.2007.17
Zuk O, Hechter E, Sunyaev SR, Lander ES (2012) The mystery of missing heritability: genetic interactions create phantom heritability. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:1193–1198. doi:10.1073/pnas.1119675109
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (projects 13-04-40281-H, 13-04-40279-H, and 15-04-04866-A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bashinskaya, V.V., Kulakova, O.G., Boyko, A.N. et al. A review of genome-wide association studies for multiple sclerosis: classical and hypothesis-driven approaches. Hum Genet 134, 1143–1162 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-015-1601-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-015-1601-2