Abstract
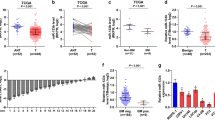
The invasion and metastasis of tumors are triggered by an epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT), which is regulated by microRNAs (miRNAs). EMT also promotes malignant tumor progression and the maintenance of the stem cell property, which endows cancer cells with the capabilities of self-renewal and immortalized proliferation. The transcriptional repressor zinc-finger E-box binding homeobox 2 (ZEB2), as an EMT activator, might be an important promoter of metastasis in some tumors. Here, we report that ZEB2 directly represses the transcription of miR-145, which is a strong repressor of EMT. In turn, ZEB2 is also a direct target of miR-145. Further, our findings show that the downregulation of ZEB2 not only represses invasion, migration, EMT, and the stemness of prostate cancer (PCa) cells, but also suppresses the capability of PC-3 cells to invade bone in vivo. Importantly, the expression level of ZEB2 as revealed by immunohistochemical analysis is positively correlated to bone metastasis, the serum free PSA level, the total PSA level, and the Gleason score in PCa patients and is negatively correlated with miR-145 expression in primary PCa specimens. Thus, our findings demonstrate a double-negative feedback loop between ZEB2 and miR-145 and indicate that the ZEB2/miR-145 double-negative feedback loop plays a significant role in the control of EMT and stem cell properties during the bone metastasis of PCa cells. These results suggest that the double-negative feedback loop between ZEB2 and miR-145 contributes to PCa progression and metastasis and might have therapeutic relevance for the bone metastasis of PCa.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adammek M, Greve B, Kassens N, Schneider C, Bruggemann K, Schuring AN, Starzinski-Powitz A, Kiesel L, Gotte M (2013) MicroRNA miR-145 inhibits proliferation, invasiveness, and stem cell phenotype of an in vitro endometriosis model by targeting multiple cytoskeletal elements and pluripotency factors. Fertil Steril 99:1346–1355
Ahn YH, Gibbons DL, Chakravarti D, Creighton CJ, Rizvi ZH, Adams HP, Pertsemlidis A, Gregory PA, Wright JA, Goodall GJ, Flores ER, Kurie JM (2012) ZEB1 drives prometastatic actin cytoskeletal remodeling by downregulating miR-34a expression. J Clin Invest 122:3170–3183
Ambros V (2004) The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431:350–355
Barrallo-Gimeno A, Nieto MA (2005) The Snail genes as inducers of cell movement and survival: implications in development and cancer. Development 132:3151–3161
Barrandon Y, Green H (1987) Three clonal types of keratinocyte with different capacities for multiplication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 84:2302–2306
Berx G, Raspe E, Christofori G, Thiery JP, Sleeman JP (2007) Pre-EMTing metastasis? Recapitulation of morphogenetic processes in cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis 24:587–597
Brabletz T (2012) miR-34 and SNAIL: another double-negative feedback loop controlling cellular plasticity/EMT governed by p53. Cell Cycle 11:215–216
Bracken CP, Gregory PA, Kolesnikoff N, Bert AG, Wang J, Shannon MF, Goodall GJ (2008) A double-negative feedback loop between ZEB1-SIP1 and the microRNA-200 family regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res 68:7846–7854
Casas E, Kim J, Bendesky A, Ohno-Machado L, Wolfe CJ, Yang J (2011) Snail2 is an essential mediator of Twist1-induced epithelial mesenchymal transition and metastasis. Cancer Res 71:245–254
Castilla MA, Moreno-Bueno G, Romero-Perez L, Van De Vijver K, Biscuola M, Lopez-Garcia MA, Prat J, Matias-Guiu X, Cano A, Oliva E, Palacios J (2011) Micro-RNA signature of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in endometrial carcinosarcoma. J Pathol 223:72–80
Chaffer CL, Weinberg RA (2011) A perspective on cancer cell metastasis. Science 331:1559–1564
Chaffer CL, Brennan JP, Slavin JL, Blick T, Thompson EW, Williams ED (2006) Mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition facilitates bladder cancer metastasis: role of fibroblast growth factor receptor-2. Cancer Res 66:11271–11278
Chivukula RR, Mendell JT (2009) Abate and switch: miR-145 in stem cell differentiation. Cell 137:606–608
Chng ZZ, Teo A, Pedersen RA, Vallier L (2010) SIP1 mediates cell-fate decisions between neuroectoderm and mesendoderm in human pluripotent stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 6:59–70
Chu PY, Hu FW, Yu CC, Tsai LL, Yu CH, Wu BC, Chen YW, Huang PI, Lo WL (2013) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition transcription factor ZEB1/ZEB2 co-expression predicts poor prognosis and maintains tumor-initiating properties in head and neck cancer. Oral Oncol 49:34–41
Cioce M, Ganci F, Canu V, Sacconi A, Mori F, Canino C, Korita E, Casini B, Alessandrini G, Cambria A, Carosi MA, Blandino R, Panebianco V, Facciolo F, Visca P, Volinia S, Muti P, Strano S, Croce CM, Pass HI, Blandino G (2013) Protumorigenic effects of mir-145 loss in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Oncogene (in press)
Dai YH, Tang YP, Zhu HY, Lv L, Chu Y, Zhou YQ, Huo JR (2012) ZEB2 promotes the metastasis of gastric cancer and modulates epithelial mesenchymal transition of gastric cancer cells. Dig Dis Sci 57:1253–1260
Dang H, Ding W, Emerson D, Rountree CB (2011) Snail1 induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and tumor initiating stem cell characteristics. BMC Cancer 11:396
Drewa T (2010) Re: Minja J. Pfeiffer, Jack A. Schalken. Stem cell characteristics in prostate cancer cell lines. Eur Urol 57:246-255
Fan L, Wu Q, Xing XJ, Wei YL, Shao ZW (2012) MicroRNA-145 targets vascular endothelial growth factor and inhibits invasion and metastasis of osteosarcoma cells. Acta Bioch Bioph Sin 44:407–414
Fang Y, Wei J, Cao J, Zhao H, Liao B, Qiu S, Wang D, Luo J, Chen W (2013) Protein expression of ZEB2 in renal cell carcinoma and its prognostic significance in patient survival. PLoS One 8:e62558
Frank SR, Schroeder M, Fernandez P, Taubert S, Amati B (2001) Binding of c-Myc to chromatin mediates mitogen-induced acetylation of histone H4 and gene activation. Genes Dev 15:2069–2082
Gao D, Vahdat LT, Wong S, Chang JC, Mittal V (2012) Microenvironmental regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in cancer. Cancer Res 72:4883–4889
Gao P, Xing AY, Zhou GY, Zhang TG, Zhang JP, Gao C, Li H, Shi DB (2013) The molecular mechanism of microRNA-145 to suppress invasion-metastasis cascade in gastric cancer. Oncogene 32:491–501
Gasparotto D, Polesel J, Marzotto A, Colladel R, Piccinin S, Modena P, Grizzo A, Sulfaro S, Serraino D, Barzan L, Doglioni C, Maestro R (2011) Overexpression of TWIST2 correlates with poor prognosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Oncotarget 2:1165–1175
Guan H, Song L, Cai J, Huang Y, Wu J, Yuan J, Li J, Li M (2011) Sphingosine kinase 1 regulates the Akt/FOXO3a/Bim pathway and contributes to apoptosis resistance in glioma cells. PLoS One 6:e19946
Gunasinghe NP, Wells A, Thompson EW, Hugo HJ (2012) Mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET) as a mechanism for metastatic colonisation in breast cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 31:469–478
Guo W, Ren D, Chen X, Tu X, Huang S, Wang M, Song L, Zou X, Peng X (2013) HEF1 promotes epithelial mesenchymal transition and bone invasion in prostate cancer under the regulation of microRNA-145. J Cell Biochem 114:1606–1615
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144:646–674
Hu F, Wang C, Guo S, Sun W, Mi D, Gao Y, Zhang J, Zhu T, Yang S (2011) DeltaEF1 promotes osteolytic metastasis of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells by regulating MMP-1 expression. Biochim Biophys Acta 1809:200–210
Hu J, Guo H, Li H, Liu Y, Liu J, Chen L, Zhang J, Zhang N (2012) MiR-145 regulates epithelial to mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells by targeting Oct4. PLoS One 7:e45965
Huang S, Guo W, Tang Y, Ren D, Zou X, Peng X (2012) miR-143 and miR-145 inhibit stem cell characteristics of PC-3 prostate cancer cells. Oncol Rep 28:1831–1837
Hugo H, Ackland ML, Blick T, Lawrence MG, Clements JA, Williams ED, Thompson EW (2007) Epithelial–mesenchymal and mesenchymal–epithelial transitions in carcinoma progression. J Cell Physiol 213:374–383
Ibrahim AF, Weirauch U, Thomas M, Grunweller A, Hartmann RK, Aigner A (2011) MicroRNA replacement therapy for miR-145 and miR-33a is efficacious in a model of colon carcinoma. Cancer Res 71:5214–5224
Iliopoulos D, Lindahl-Allen M, Polytarchou C, Hirsch HA, Tsichlis PN, Struhl K (2010) Loss of miR-200 inhibition of Suz12 leads to polycomb-mediated repression required for the formation and maintenance of cancer stem cells. Mol Cell 39:761–772
Janga SC, Vallabhaneni S (2011) MicroRNAs as post-transcriptional machines and their interplay with cellular networks. Adv Exp Med Biol 722:59–74
Kong DJ, Banerjee S, Ahmad A, Li YW, Wang ZW, Sethi S, Sarkar FH (2010) Epithelial to mesenchymal transition is mechanistically linked with stem cell signatures in prostate cancer cells. PLoS One 5:e12445
Koopmansch B, Berx G, Foidart JM, Gilles C, Winkler R (2013) Interplay between KLF4 and ZEB2/SIP1 in the regulation of E-cadherin expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 431:652–657
Korpal M, Lee ES, Hu G, Kang Y (2008) The miR-200 family inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer cell migration by direct targeting of E-cadherin transcriptional repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. J Biol Chem 283:14910–14914
Kurrey NK, Jalgaonkar SP, Joglekar AV, Ghanate AD, Chaskar PD, Doiphode RY, Bapat SA (2009) Snail and slug mediate radioresistance and chemoresistance by antagonizing p53-mediated apoptosis and acquiring a stem-like phenotype in ovarian cancer cells. Stem Cells 27:2059–2068
Lemma S, Karihtala P, Haapasaari KM, Jantunen E, Soini Y, Bloigu R, Pasanen AK, Turpeenniemi-Hujanen T, Kuittinen O (2013) Biological roles and prognostic values of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition-mediating transcription factors Twist, ZEB1 and Slug in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Histopathology 62:326–333
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(T)(-Delta Delta C) method. Methods 25:402–408
Menssen A, Epanchintsev A, Lodygin D, Rezaei N, Jung P, Verdoodt B, Diebold J, Hermeking H (2007) c-MYC delays prometaphase by direct transactivation of MAD2 and BubR1: identification of mechanisms underlying c-MYC-induced DNA damage and chromosomal instability. Cell Cycle 6:339–352
Mo YY, Beck WT (1999) Association of human DNA topoisomerase IIalpha with mitotic chromosomes in mammalian cells is independent of its catalytic activity. Exp Cell Res 252:50–62
Moes M, Le Bechec A, Crespo I, Laurini C, Halavatyi A, Vetter G, Sol A del, Friederich E (2012) A novel network integrating a miRNA-203/SNAI1 feedback loop which regulates epithelial to mesenchymal transition. PLoS One 7:e35440
Monteiro J, Fodde R (2010) Cancer stemness and metastasis: therapeutic consequences and perspectives. Eur J Cancer 46:1198–1203
Nicoloso MS, Spizzo R, Shimizu M, Rossi S, Calin GA (2009) MicroRNAs—the micro steering wheel of tumour metastases. Nat Rev Cancer 9:293–302
Okugawa Y, Inoue Y, Tanaka K, Kawamura M, Saigusa S, Toiyama Y, Ohi M, Uchida K, Mohri Y, Kusunoki M (2013) Smad interacting protein 1 (SIP1) is associated with peritoneal carcinomatosis in intestinal type gastric cancer. Clin Exp Metastas 30:417–429
Oliveira MV de, Pereira Gomes EP, Pereira CS, Souza LR de, Barros LO, Mendes DC, Guimarães AL, De Paula AM (2013) Prognostic value of microvessel density and p53 expression on the locoregional metastasis and survival of the patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 21:444–451
Olmeda D, Moreno-Bueno G, Flores JM, Fabra A, Portillo F, Cano A (2007) SNAI1 is required for tumor growth and lymph node metastasis of human breast carcinoma MDA-MB-231 cells. Cancer Res 67:11721–11731
Oztas E, Avci ME, Ozcan A, Sayan AE, Tulchinsky E, Yagci T (2010) Novel monoclonal antibodies detect Smad-interacting protein 1 (SIP1) in the cytoplasm of human cells from multiple tumor tissue arrays. Exp Mol Pathol 89:182–189
Peinado H, Olmeda D, Cano A (2007) Snail, Zeb and bHLH factors in tumour progression: an alliance against the epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer 7:415–428
Peng X, Guo W, Liu T, Wang X, Tu X, Xiong D, Chen S, Lai Y, Du H, Chen G, Liu G, Tang Y, Huang S, Zou X (2011) Identification of miRs-143 and-145 that is associated with bone metastasis of prostate cancer and involved in the regulation of EMT. PLoS One 6:e20341
Pfeiffer MJ, Schalken JA (2010) Stem cell characteristics in prostate cancer cell lines. Eur Urol 57:246–254
Pirozzi G, Tirino V, Camerlingo R, Franco R, La Rocca A, Liguori E, Martucci N, Paino F, Normanno N, Rocco G (2011) Epithelial to mesenchymal transition by TGFbeta-1 induction increases stemness characteristics in primary non small cell lung cancer cell line. PLoS One 6:e21548
Polyak K, Weinberg RA (2009) Transitions between epithelial and mesenchymal states: acquisition of malignant and stem cell traits. Nat Rev Cancer 9:265–273
Polytarchou C, Iliopoulos D, Struhl K (2012) An integrated transcriptional regulatory circuit that reinforces the breast cancer stem cell state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:14470–14475
Qiao B, Johnson NW, Chen X, Li R, Tao Q, Gao J (2011) Disclosure of a stem cell phenotype in an oral squamous cell carcinoma cell line induced by BMP-4 via an epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncol Rep 26:455–461
Rosen JM, Jordan CT (2009) The increasing complexity of the cancer stem cell paradigm. Science 324:1670–1673
Sanchez-Tillo E, Siles L, Barrios O de, Cuatrecasas M, Vaquero EC, Castells A, Postigo A (2011) Expanding roles of ZEB factors in tumorigenesis and tumor progression. Am J Cancer Res 1:897–912
Sethi S, Macoska J, Chen W, Sarkar FH (2010) Molecular signature of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in human prostate cancer bone metastasis. Am J Transl Res 3:90–99
Shackleton M, Quintana E, Fearon ER, Morrison SJ (2009) Heterogeneity in cancer: cancer stem cells versus clonal evolution. Cell 138:822–829
Shimono Y, Zabala M, Cho RW, Lobo N, Dalerba P, Qian D, Diehn M, Liu H, Panula SP, Chiao E, Dirbas FM, Somlo G, Pera RA, Lao K, Clarke MF (2009) Downregulation of miRNA-200c links breast cancer stem cells with normal stem cells. Cell 138:592–603
Siemens H, Jackstadt R, Hunten S, Kaller M, Menssen A, Gotz U, Hermeking H (2011) miR-34 and SNAIL form a double-negative feedback loop to regulate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Cell Cycle 10:4256–4271
Teng Y, Mei Y, Hawthorn L, Cowell JK (2013) WASF3 regulates miR-200 inactivation by ZEB1 through suppression of KISS1 leading to increased invasiveness in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 33:203–211
Thiery JP, Sleeman JP (2006) Complex networks orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:131–142
Tikhmyanova N, Golemis EA (2011) NEDD9 and BCAR1 negatively regulate E-cadherin membrane localization, and promote E-cadherin degradation. PLoS One 6:e22102
Tudor D, Locke M, Owen-Jones E, Mackenzie IC (2004) Intrinsic patterns of behavior of epithelial stem cells. Eur Soc Dermatol Res 9:208-214
Visvader JE, Lindeman GJ (2008) Cancer stem cells in solid tumours: accumulating evidence and unresolved questions. Nat Rev Cancer 8:755–768
Wang SC, Makino K, Su LK, Pao AY, Kim JS, Hung MC (2001) Ultraviolet irradiation induces BRCA2 protein depletion through a p53-independent and protein synthesis-dependent pathway. Cancer Res 61:2838–2842
Wellner U, Schubert J, Burk UC, Schmalhofer O, Zhu F, Sonntag A, Waldvogel B, Vannier C, Darling D, Zur Hausen A, Brunton VG, Morton J, Sansom O, Schuler J, Stemmler MP, Herzberger C, Hopt U, Keck T, Brabletz S, Brabletz T (2009) The EMT-activator ZEB1 promotes tumorigenicity by repressing stemness-inhibiting microRNAs. Nat Cell Biol 11:1487–1495
Wu CY, Hung JJ, Wu KJ (2012) Linkage between Twist1 and Bmi1: molecular mechanism of cancer metastasis/stemness and clinical implications. Clin Exp Pharmacol 39:668–673
Wu TT, Sikes RA, Cui Q, Thalmann GN, Kao C, Murphy CF, Yang H, Zhau HE, Balian G, Chung LW (1998) Establishing human prostate cancer cell xenografts in bone: induction of osteoblastic reaction by prostate-specific antigen-producing tumors in athymic and SCID/bg mice using LNCaP and lineage-derived metastatic sublines. Int J Cancer 77:887–894
Xu N, Papagiannakopoulos T, Pan G, Thomson JA, Kosik KS (2009) MicroRNA-145 regulates OCT4, SOX2, and KLF4 and represses pluripotency in human embryonic stem cells. Cell 137:647–658
Yang M, Burton DW, Geller J, Hillegonds DJ, Hastings RH, Deftos LJ, Hoffman RM (2006) The bisphosphonate olpadronate inhibits skeletal prostate cancer progression in a green fluorescent protein nude mouse model. Clin Cancer Res 12:2602–2606
Yang XW, Zhang LJ, Huang XH, Chen LZ, Su Q, Zeng WT, Li W, Wang Q (2013) miR-145 suppresses cell invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma cells: miR-145 targets ADAM17. Hepatol Res 44:551–559
Ying SY, Lin SL (2006) Current perspectives in intronic micro RNAs (miRNAs). J Biomed Sci 13:5–15
Yu CC, Chang YC (2013) Enhancement of cancer stem-like and epithelial-mesenchymal transdifferentiation property in oral epithelial cells with long-term nicotine exposure: reversal by targeting SNAIL. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 266:459–469
Zhang H, Pu J, Qi T, Qi M, Yang C, Li S, Huang K, Zheng L, Tong Q (2012) MicroRNA-145 inhibits the growth, invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis of neuroblastoma cells through targeting hypoxia-inducible factor 2 alpha. Oncogene 33:387–397
Zheng L, Pu J, Qi T, Qi M, Li D, Xiang X, Huang K, Tong Q (2013) miRNA-145 targets v-ets erythroblastosis virus E26 oncogene homolog 1 to suppress the invasion, metastasis, and angiogenesis of gastric cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res 11:182–193
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dong Ren and Min Wang contributed equally to this work.
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81272938) and the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangzhou, China (no. 11C22060772).
No potential conflicts of interest are declared.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, D., Wang, M., Guo, W. et al. Double-negative feedback loop between ZEB2 and miR-145 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stem cell properties in prostate cancer cells. Cell Tissue Res 358, 763–778 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-014-2001-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-014-2001-y