Abstract
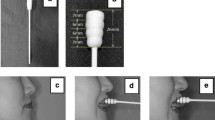
It is clinically important to evaluate tongue function in terms of rehabilitation of swallowing and eating ability. We have developed a disposable tongue pressure measurement device designed for clinical use. In this study we used this device to determine standard values of maximum tongue pressure in adult Japanese. Eight hundred fifty-three subjects (408 male, 445 female; 20–79 years) were selected for this study. All participants had no history of dysphagia and maintained occlusal contact in the premolar and molar regions with their own teeth. A balloon-type disposable oral probe was used to measure tongue pressure by asking subjects to compress it onto the palate for 7 s with maximum voluntary effort. Values were recorded three times for each subject, and the mean values were defined as maximum tongue pressure. Although maximum tongue pressure was higher for males than for females in the 20-49-year age groups, there was no significant difference between males and females in the 50-79-year age groups. The maximum tongue pressure of the seventies age group was significantly lower than that of the twenties to fifties age groups. It may be concluded that maximum tongue pressures were reduced with primary aging. Males may become weaker with age at a faster rate than females; however, further decreases in strength were in parallel for male and female subjects.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feinberg MJ, Knebl J, Tully J, Segall L. Aspiration and the elderly. Dysphagia 1990;5:61–71.
Hudson HM, Daubert CR, Mills RH. The interdependency of protein-energy malnutrition, aging, and dysphagia. Dysphagia 2000;15:31–38.
Marik PK, Kaplan D. Aspiration pneumonia and dysphagia in the elderly. Chest 2003;124:328–336.
Leopold NA, Kagel MC. Swallowing, ingestion and dysphagia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1983;64:371–373.
Robbins J, Levine R, Wood J, Roecker EB, Luschei E. Age effects on lingual pressure generation as a risk factor for dysphagia. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 1995;50:M257–M262.
Ono T, Hori K, Nokubi T. Pattern of tongue pressure on hard palate during swallowing. Dysphagia 2004;19:259–264.
Yoshida M, Kikutani T, Tsuga K, Utanohara Y, Hayashi R, Akagawa Y. Decreased tongue pressure reflects symptom dysphagia. Dysphagia 2006;21:1–5.
Shaker R, Cook IJS, Dodds WJ, Hogan WJ. Pressure-flow dynamics of the oral phase of swallowing. Dysphagia 1988;3:79–84.
Nagao K, Kitaoka N, Kawano F, Komoda J, Ichikawa T. Influence of changes in occlusal vertical dimension on tongue pressure to palate during swallowing. Prosthodont Res Pract 2002;1:16–23.
Nicosia MA, Hind JA, Roecker EB, Carnes M, Doyle J, Dengel GA, Robbins J. Age effects on the temporal evolution of isometric and swallowing pressure. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2000;55:M634–M640.
Hayashi R, Tsuga K, Hosokawa R, Yoshida M, Sato Y, Akagawa Y. Novel handy probe for tongue pressure measuremaent. Int J Prosthodont 2002;15:385–388.
Yoshikawa M, Yoshida M, Nagasaki T, Tanimoto K, Tsuga K, Akagawa Y, Komatsu T. Aspects of swallowing in healthy dentate elderly persons older than 80 years. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2005;60:M506–M509.
Kawashima K, Motohashi Y, Fujishima I. Prevalence of dysphagia among community-dwelling elderly individuals as estimated using a questionnaire for dysphagia screening. Dysphagia 2004;19:266–271.
Oguchi K, Saitoh E, Mizuno M, Baba M, Okui M, Suzuki M. The repetitive saliva swallowing test (RSST) as a screening test of functional dysphagia (1) normal values of RSST. Jpn J Rehabil Med 2000;37:375–382.
Tamura F, Mizukami M, Ayano R, Mukai Y. Analysis of feeding function and jaw stability in bedridden elderly. Dysphagia 2002;17:235–241.
Eichner K. Über eine Gruppeneintelung des Lückengebisses für die Prothetik. Dtsch Zahnärztl Z 1955;10:1831–1834.
Palmer JB. Evaluation of swallowing disorders. In: Grabois M, Garrison SJ, Hart KA, Lehmkuhl LD (eds.), Physical Medicine, Rehabilitation: The Complete Approach. Maiden MA: Blackwell, 1999, pp 277–290.
Breakthrough. Iowa oral performance instrument: Reference manual. Oakdale IA: Breakthrough, 1992.
Youmans SR, Stierwalt JAG. Measures of tongue function related to normal swallowing. Dysphagia 2006;21:102–111.
Crow HC, Ship JA. Tongue strength and endurance in different aged individuals. J Gerontol Biol Sci Med Sci 1996;51:247–250.
Doherty TJ. The influence of aging and sex on skeletal muscle mass and strength. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 2001;4:503–508.
Hiiemae KM, Palmer JB. Tongue movements in feeding and speech. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 2003;14:413–429.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a Grant-in-Aid of the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (tyoujyu-14-020) and a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research of Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Utanohara, Y., Hayashi, R., Yoshikawa, M. et al. Standard Values of Maximum Tongue Pressure Taken Using Newly Developed Disposable Tongue Pressure Measurement Device. Dysphagia 23, 286–290 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-007-9142-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-007-9142-z