Abstract
Background
Membranous glomerulopathy, though typically a disease of adults, does occur in children. Antiphospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R) autoantibodies have recently been implicated as a causative agent in most cases of adult primary (idiopathic) membranous glomerulopathy. PLA2R staining of renal biopsies in two recent large case series of adults with primary membranous glomerulopathy showed a sensitivity of approximately 75 % for detecting primary membranous glomerulopathy. To our knowledge, this is the largest study of its kind to assess PLA2R staining in a pediatric population.
Methods
Forty-one consecutive cases of pediatric membranous glomerulopathy were identified from our database, and clinical follow-up was performed to confirm primary membranous glomerulopathy. Twenty-two patients met inclusion criteria and are the subject of this report.
Results
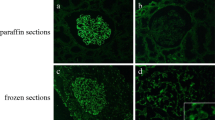
Granular, capillary loop immunofluorescence staining for immunoglobulin G (IgG) was present in 100 % of patients, and C3 staining was present in 77 %. PLA2R staining was identified in ten patients, providing a sensitivity of 45 % [confidence interval (CI) 25–67 %]. Bovine serum albumin staining was performed in all PLA2R-negative cases and showed no positivity. Morphologic findings associated with negative PLA2R staining included segmental membranous lesions, mesangial and subendothelial deposits, C1q and “full-house” staining, and lower-stage lesions by electron microscopy. At 38 months’ average follow-up, all patients were still considered as having primary membranous glomerulopathy, with none developing a clinically detectable secondary etiology.
Conclusions
PLA2R staining sensitivity is much lower in the pediatric than the adult primary membranous glomerulopathy population. This finding suggests a more diverse and currently incompletely described set of etiologies for this disease in this group.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bell ET (1950) Renal diseases. Lea & Febiger, Philadelphia
Jones DB (1957) Nephrotic glomerulonephritis. Am J Pathol 33:313–329
Movat HZ, McGregor DD (1959) The fine structure of the glomerulus in membranous glomerulonephritis (lipoid nephrosis) in adults. Am J Clin Pathol 32:100–127
Mellors RC, Ortega LG, Holman HR (1957) Role of gammaglobulins in pathogenesis of renal lesions in systemic lupus erythematosus and chronic membranous glomerulonephriris, with an observation of the lupus erythematosus cell reaction. J Exp Med 1065:191–202
Heymann W, Hackel DB, Harwood S, Wilson SGF, Hunter JL (2000) Production of nephrotic syndrome in rats by Freund’s adjuvants and rat kidney suspensions. J Am Soc Nephrol 10:183–188
Makker SP, Singh AK (1984) Characterization of the antigen (gp600) of heymann nephritis. Lab Investig 50:287–293
Beck LH, Bonegio RG, Lambeau G, Beck DM, Powell DW, Cummins TD, Klein JB, Salant DJ (2009) M-type phospholipase A2 receptor as target antigen in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. N Engl J Med 361:11–21
Qin W, Beck LH Jr, Zeng C, Chen Z, Li S, Zuo K, Salant DJ, Liu Z (2011) Anti-phospholipase A2 receptor antibody in membranous nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 22:1137–1143
Debiec H, Martin L, Jouanneau C, Dautin G, Mesnard L, Rondeau E, Mousson C, Ronco P (2011) Autoantibodies specific for the phospholipase A2 receptor in recurrent and De Novo membranous nephropathy. Am J Transplant 11:2144–2152
Larsen CP, Messias NC, Silva FG, Messias E, Walker PD (2013) Determination of primary versus secondary membranous glomerulopathy utilizing phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R1) staining in renal biopsies. Mod Pathol 26:709–715
Churg J, Habib R, White RH (1970) Pathology of the nephrotic syndrome in children: a report for the International Study of Kidney Disease in Children. Lancet 760:1299–1302
A report for the International Study of Kidney Disease in Children (1978) Nephrotic syndrome in children: prediction of histopathology from clinical and laboratory characteristics at time of diagnosis. Kidney Int 13:159–165
Markowitz GS (2001) Membranous glomerulopathy: emphasis on secondary forms and disease variants. Adv Anat Pathol 8:119–125
Beck LH Jr (2012) Childhood membranous nephropathy and dietary antigens. Am J Kidney Dis 59:174–176
Debiec H, Lefeu F, Kemper MJ, Niaudet P, Deschênes G, Remuzzi G, Ulinski T, Ronco P (2011) Early-childhood membranous nephropathy due to cationic bovine serum albumin. N Engl J Med 364:2101–2110
Debiec H, Guigonis V, Mougenot B, Decobert F, Haymann J, Bensman A, Deschenes G, Ronco PM (2002) Antenatal membranous glomerulonephritis due to anti-neutral endopeptidase antibodies. N Engl J Med 346:2053–2060
Walker PD, Cavallo T, Bonsib SM (2004) Practice guidelines for the renal biopsy. Mod Pathol 17:1555–1563
Walker PD (2009) The renal biopsy. Arch Pathol Lab Med 133:181–188
Ehrenreich T, Churg J (1968) Pathology of membranous nephropathy. Pathol Annu 2:145–186
Jennette JC, Iskandar SS, Dalldorf FG (1983) Pathologic differentiation between lupus and nonlupus membranous glomerulopathy. Kidney Int 24:377–385
Debiec H, Ronco P (2011) PLA2R autoantibodies and PLA2R glomerular deposits in membranous nephropathy. N Engl J Med 364:689–690
Menon S, Valentini R (2010) Membranous nephropathy in children: clinical presentation and therapeutic approach. Pediatr Nephrol 25:1419–1428
Waldman M, Austin HA III (2009) Controversies in the treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Nat Rev Nephrol 5:469–479
Valentini RP, Mattoo TK, Kapur G, Imam A (2009) Membranous glomerulonephritis: treatment response and outcome in children. Pediatr Nephrol 24:301–308
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Robert Yerton, Steve Strong, and Cindy Smith for their valuable technical aid and I-Shen Wen and Tina Priddy for their administrative support. The abstract to this work was presented at the USCAP 102nd Annual Meeting (2013), Baltimore, MD, USA (Mod Pathol 26: 383–396; doi:10.1038/modpathol.2013.16).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cossey, L.N., Walker, P.D. & Larsen, C.P. Phospholipase A2 receptor staining in pediatric idiopathic membranous glomerulopathy. Pediatr Nephrol 28, 2307–2311 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-013-2574-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-013-2574-9