Abstract
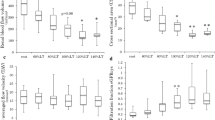
About 30% of diabetic patients develop progressive renal failure. We studied albumin, IgG, and transferrin excretion during exercise in diabetic children without signs of nephropathy to investigate proteinuria under these conditions: 39 patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and 21 healthy children undertook a bicycle exercise test. Albuminuria measured by nephelometry was calculated as the albumin excretion rate (AER) and albumin-to-creatinine ratio before and after exercise. The diabetic group was divided into three subgroups according to disease duration (DI<5 years, DII 5–10 years, DIII>10 years). No significant difference in metabolic control (hemoglobin A1c) was detected between the diabetic groups (median hemoglobin A1c: DI 7.2%, DII 7.6%, DIII 8.6%). There was no increase in AER in the healthy children after exercise. Before exercise the diabetic groups had an AER similar to controls. No significant increase in albuminuria after exercise was seen in group DI. Both groups with a disease duration of more than 5 years had a significant increase in albuminuria [median before/after: DII 7.8/16.7 (P<0.05), DIII 0/57.9 (P<0.05) ώg/min per 1.73 m2). Of these patients, 43% also had a measurable urinary excretion of IgG and transferrin, indicating structural glomerular damage. There was no correlation of albuminuria and parameters of metabolic control or renal function. We conclude that in diabetic children an exercise test unveils albuminuria in certain patients, while their AER may be normal at rest.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Österby R (1992) Glomerular structural changes in type 1 (insulin dependent) diabetes mellitus: causes consequences and prevention. Diabetologia 35:803–812
Mogensen CE, Christensen CK, Vittinghus E (1983) The stages in diabetic renal disease. Diabetes 32:64–78
Mogensen CE, Christensen CK (1984) Predicting diabetic nephropathy in insulin-dependent patients. N Engl J Med 311:89–93
Viberti GC, Hill RD, Jarrett RJ, Argyropouloos A, Mahmud U, Keen H (1982) Microalbuminuria as a predictor of clinical nephropathy in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Lancet I:1430–1432
Houser MT (1987) Characterization of recumbent, ambulatory, and post-exercise proteinuria in the adolescent. Pediatr Res 21:442–446
Poortmans JR, Brauman H, Staroukine M, Verniory A, Decaestecker C, Leclerq R (1988) Indirect evidence of glomerular/tubular mixed-type post-exercise proteinuria in healthy humans. Am J Physiol 254:F277-F283
Feldt-Rasmussen B, Baker L, Deckert T (1985) Exercise as a provocative test in early renal disease in type 1 diabetes: albuminuric, systemic and haemodynamic response. Diabetologia 28:389–396
Davies AG, Postlethwaite RJ, Price DA, Burn JL, Houltan CA, Fielding BA (1984) Urinary albumin excretion in school children. Arch Dis Child 59:625–630
Ehrich JHH, Foelmer HG, Krull F, Winnecken HJ, Wurster U (1984) Aussagen, Fehlerquellen und Grenzen der Proteindiagnostik im Urin. II. Normalwerte und Klassifikation pathologischer Proteinurien. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd 132:144–150
Mogensen CE, Vittinghus E (1975) Urinary albumin excretion during exercise in juvenile diabetes. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 35:295–300
Jefferson IG, Greene SA, Smith MA, Smith RF, Griffin NKG, Baum JD (1985) Urine albumin to creatinine ratio — response to exercise in diabetes. Arch Dis Child 60:305–309
Huttunen N-P, Käär M-L, Puuka R, Äkerblom HK (1981) Exercise induced proteinuria in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 21: 495–497
Houser MT (1984) Assessment of proteinuria using random urine samples. J Pediatr 104:845–848
Dahlquist G, Aperia A, Broberger O, Persson B, Wilton P (1983) Renal function in relation to metabolic control in children with diabetes of different duration. Acta Paediatr Scand 72:903–909
Ellis D, Becker DJ, Daneman D, Lobes L, Drash AL (1983) Proteinuria in children with insulin-dependent diabetes: relationship to duration of disease, metabolic control and retinal changes. J Pediatr 102:672–680
Gibb DM, Dalton NR, Barratt MT (1989) Measurement of glomerular filtration rate in children with insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Clin Chim Acta 182:131–139
Nakamura Y, Myers BD (1988) Charge selectivity of proteinuria in diabetic glomerulopathy. Diabetes 37(9):1202–1211
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krüger, M., Gordjani, N. & Burghard, R. Postexercise albuminuria in children with different duration of type-1 diabetes mellitus. Pediatr Nephrol 10, 594–597 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004670050168
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004670050168