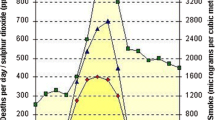
Abstract
Air quality assessment studies have either high sampling or analyses costs. In these studies the representation of a city by a single sampling point is still a serious problem, especially in the metropolitans of developing countries, because of the absence of equipments required for sampling at different locations. In this paper, the smoke data measurements of long years are used in the determination of the region for the representation of the city by drawing contours through the Kriging method. Then, the selection of the sampling site in this region is done on the basis of the criteria recommended by the EPA. By this way, the data taken from this sampling point are used for assessing the average city concentrations with lower sampling and analyses costs. This information is valuable for monitoring the air quality and defining environmental policies, although the local distribution and the extreme concentration values over the city are not measurable.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambient Air Quality Monitoring Program Quality System Development (1998) Quality assurance handbook for air pollution measurement systems. United States Office of Air Quality EPA Environmental Protection Planning and Standards May Agency Research Triangle Park, NC 27711 Part I, Introduction 4/22/98 Draft
Brown PJ, Le ND, Zidek JV (1994) Multivariate spatial interpolation and exposure to air pollutants. Can J Stat 22:489–509
Chilès JP, Delfiner P (1999) Geostatistics: modeling spatial uncertainty. Wiley, New York, p 696
Cowell D, Apsimon H (1996) Estimating the cost of damage to buildings by acidifying atmospheric pollution in Europe. Atmos Environ 30(17):2959–2968
Deutsch CV, Journel AG (1998) GSLIB: geostatistical software library and user’s guide. Oxford University Press, New York, p 369
Fenger J (1999) Urban air quality. Atmos Environ 33:4877–4900
Goldberg MS, Burnett RT, Valois MF, Flegel K, Bailar JC III, Brook J, Vincent R, Radon K (2003) Associations between ambient air pollution and mortality among persons with congestive heart failure. Environ Res 91:8–20
Hansen AC, Setle HK (2000) Air pollution and sick-leaves. Environ Resour Econ 16:31–50
Hudson G, Wackernagel H (1994) Mapping temperature using Kriging with external drift: theory and an example from Scotland. Int J Climatol 14:77–91
Krige DG (1951) A statistical approach to some basic mine valuation problems on the Witwatersrand. J Chem Metall Min Soc S Afr December:119–139
Matheron G (1971) The theory of regionalized variables and its applications. Les Cahiers du Centre de Morphologie Mathématique, Fascicule 5. Ecole Nationale Superieure des Mines de Paris, Fontainebleau, p 211
Mayer H (1999) Air pollution in cities. Atmos Environ 33:4029–4037
Odriozola JCA, Jimenez JD, Rubio JCM, Perez IJM, Ortiz MSP, Rodrigues PR (1998) Air pollution and mortality in Madrid, Spain: a time-series analysis. Arch Environ Health 71:543–549
Parekh Pravin P, Khwaja Haider A, Khan Adil R, Naqvi Ronaq R, Shah A, Sajjad A, Khan K, Hussain G (2001) Ambient air quality of two metropolitan cities of Pakistan and its health implications. Atmos Environ 35:5971–5978
Wackernagel H (2003) Multivariate geostatistics: an introduction with applications. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 387
http://www.epa.gov. 40 CFR 58, Appendix Air Quality Assurance Requirements for State and Local Air Monitoring Stations (SLAMS), Ambient Air Quality Surveillance
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor Gürdal Tuncel for helpful criticism of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bayraktar, H., Turalioglu, F.S. A Kriging-based approach for locating a sampling site—in the assessment of air quality. Stoch Environ Res Ris Assess 19, 301–305 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-005-0234-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-005-0234-8