Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to investigate postoperative changes in spinal sagittal alignment and postural balance in patients with hip-spine syndrome (HSS) and to verify whether any significant correlation exists between these changes and improvement of low back pain (LBP) symptoms following total hip replacement (THR) surgery.
Methods
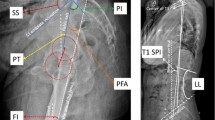
Twenty-eight consecutive patients with HSS undergoing unilateral THR were prospectively enrolled. Whole spine X-rays were obtained before surgery and 6 months after surgery. The following parameters were measured: cervical lordosis, thoracic kyphosis, lumbar lordosis, pelvic incidence (PI), pelvic tilt (PT), sacral slope (SS), and sagittal vertical axis (C7 SVA). Patients underwent pre- and postoperative postural balance assessment (950-460 BioSwayTM system; clinical test of sensory integration—CTSIB, limit of stability test—LOS) and patient reported outcome measures assessment (Short Form-36, SF-36, Oswestry Disability Index, ODI, Visual Analog Scale, VAS and Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Arthritis Index, WOMAC).
Results
Mean age of the patients was 61.7 ± 6.4. Median (interquartile range, IQR) pre-operative PI and PT were 50.0 (35.0, 60.0) and 11.0 (7.0, 23.0), respectively; lumbar lordosis was 49.0 (41.0, 68.0) and SVA 5.0 (−11.0, 41.0). No significant changes in sagittal alignment were observed postoperatively. Median LBP VAS decreased from 6.0 (5.0, 7.0) to 3.0 (2.0, 4.0) and ODI from 54.0 (39.0, 64.0) to 34.0 (26.0, 48.0) (p < 0.001). Median CTSIB improved from 1.22 (1.07, 1.45) to 1.01 (0.80, 1.19) and LOS from 46.0 (42.0, 58.0) to 37.0 (32.0, 39.0) postoperatively. No significant correlation was noted between postoperative changes in spinal sagittal alignment or postural balance and improvement of LBP VAS and ODI scores.
Conclusions
Our study demonstrated an improvement in LBP levels (VAS and ODI) and postural balance in patients with HSS following THR surgery. No significant changes have been noted in radiographic spinal sagittal alignment postoperatively. The improvement in LBP levels does not correlate with post-operative changes in spinopelvic alignment or postural balance.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson GB (1999) Epidemiological features of chronic low-back pain. Lancet 354:581–585. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(99)01312-4 (London, England)
Offierski CM, MacNab I (1983) Hip-spine syndrome. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 8:316–321
Schwab F, Lafage V, Boyce R et al (2006) Gravity line analysis in adult volunteers: age-related correlation with spinal parameters, pelvic parameters, and foot position. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 31:E959–E967. doi:10.1097/01.brs.0000248126.96737.0f
Lamartina C, Berjano P (2014) Classification of sagittal imbalance based on spinal alignment and compensatory mechanisms. Eur Spine J 23:1177–1189. doi:10.1007/s00586-014-3227-9
Buckland AJ, Vigdorchik J, Schwab FJ et al (2015) Acetabular anteversion changes due to spinal deformity correction: bridging the gap between hip and spine surgeons. J Bone Joint Surg Am 97:1913–1920. doi:10.2106/JBJS.O.00276
Lazennec J-Y, Brusson A, Rousseau M-A (2011) Hip-spine relations and sagittal balance clinical consequences. Eur Spine J 20(Suppl 5):686–698. doi:10.1007/s00586-011-1937-9
Weng W-J, Wang W-J, Wu M-D et al (2015) Characteristics of sagittal spine-pelvis-leg alignment in patients with severe hip osteoarthritis. Eur Spine J 24:1228–1236. doi:10.1007/s00586-014-3700-5
Ben-Galim P, Ben-Galim T, Rand N et al (2007) Hip-spine syndrome: the effect of total hip replacement surgery on low back pain in severe osteoarthritis of the hip. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 32:2099–2102. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e318145a3c5
Radcliff KE, Orozco F, Molby N et al (2013) Change in spinal alignment after total hip arthroplasty. Orthop Surg 5:261–265. doi:10.1111/os.12076
Nashner LM, McCollum G (1985) The organization of human postural movements: a formal basis and experimental synthesis. Behav Brain Sci 8:135. doi:10.1017/S0140525X00020008
Bisson EJ, McEwen D, Lajoie Y, Bilodeau M (2011) Effects of ankle and hip muscle fatigue on postural sway and attentional demands during unipedal stance. Gait Posture 33:83–87. doi:10.1016/j.gaitpost.2010.10.001
Roussouly P, Nnadi C (2010) Sagittal plane deformity: an overview of interpretation and management. Eur Spine J 19:1824–1836. doi:10.1007/s00586-010-1476-9
Barrey C, Roussouly P, Perrin G, Le Huec J-C (2011) Sagittal balance disorders in severe degenerative spine. Can we identify the compensatory mechanisms? Eur Spine J 20(Suppl 5):626–633. doi:10.1007/s00586-011-1930-3
Acknowledgments
No funding was received by the authors to support this work. We would like to acknowledge the staff and resident doctors of the Gazi University Medical School, Department of Orthopedic Surgery and Traumatology, for their help and support in data collection and all patients who accepted to take part to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eyvazov, K., Eyvazov, B., Basar, S. et al. Effects of total hip arthroplasty on spinal sagittal alignment and static balance: a prospective study on 28 patients. Eur Spine J 25, 3615–3621 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-016-4696-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-016-4696-9