Abstract
Objectives
This in vitro study was established to examine whether visfatin thought to be a link between periodontitis and obesity is produced by periodontal ligament (PDL) cells and, if so, whether its synthesis is modulated by microbial and/or biomechanical signals.
Materials and methods
PDL cells seeded on BioFlex® plates were exposed to the oral pathogen Fusobacterium nucleatum ATCC 25586 and/or subjected to biomechanical strain for up to 3 days. Gene expression of visfatin and toll-like receptors (TLR) 2 and 4 was analyzed by RT-PCR, visfatin protein synthesis by ELISA and immunocytochemistry, and NFκB nuclear translocation by immunofluorescence.
Results
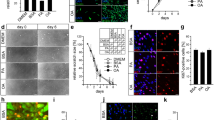
F. nucleatum upregulated the visfatin expression in a dose- and time-dependent fashion. Preincubation with neutralizing antibodies against TLR2 and TLR4 caused a significant inhibition of the F. nucleatum-upregulated visfatin expression at 1 day. F. nucleatum stimulated the NFκB nuclear translocation. Biomechanical loading reduced the stimulatory effects of F. nucleatum on visfatin expression at 1 and 3 days and also abrogated the F. nucleatum-induced NFκB nuclear translocation at 60 min. Biomechanical loading inhibited significantly the expression of TLR2 and TLR4 at 3 days. The regulatory effects of F. nucleatum and/or biomechanical loading on visfatin expression were also observed at protein level.
Conclusions
PDL cells produce visfatin, and this production is enhanced by F. nucleatum. Biomechanical loading seems to be protective against the effects of F. nucleatum on visfatin expression.
Clinical relevance
Visfatin produced by periodontal tissues could play a major role in the pathogenesis of periodontitis and the interactions with obesity and other systemic diseases.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pihlstrom BL, Michalowicz BS, Johnson NW (2005) Periodontal diseases. Lancet 366:1809–1820
Sbordone L, Bortolaia C (2003) Oral microbial biofilms and plaque-related diseases: microbial communities and their role in the shift from oral health to disease. Clin Oral Investig 7:181–188
Seymour GJ, Ford PJ, Cullinan MP, Leishman S, Yamazaki K (2007) Relationship between periodontal infections and systemic disease. Clin Microbiol Infect 13(Suppl 4):3–10
Naveh GR, Lev-Tov Chattah N, Zaslansky P, Shahar R, Weiner S (2012) Tooth-PDL-bone complex: response to compressive loads encountered during mastication—a review. Arch Oral Biol 57(12):1575–1584
McCulloch CA, Lekic P, McKee MD (2000) Role of physical forces in regulating the form and function of the periodontal ligament. Periodontol 24:56–72
Harrel SK, Nunn ME (2001) The effect of occlusal discrepancies on periodontitis. II. Relationship of occlusal treatment to the progression of periodontal disease. J Periodontol 72:495–505
Nunn ME, Harrel SK (2001) The effect of occlusal discrepancies on periodontitis. I. Relationship of initial occlusal discrepancies to initial clinical parameters. J Periodontol 72:485–494
Wennström JL, Stokland BL, Nyman S, Thilander B (1993) Periodontal tissue response to orthodontic movement of teeth with infrabony pockets. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 103:313–319
Bildt MM, Bloemen M, Kuijpers-Jagtman AM, Von den Hoff JW (2009) Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in gingival crevicular fluid during orthodontic tooth movement. Eur J Orthod 31:529–535
Ren Y, Vissink A (2008) Cytokines in crevicular fluid and orthodontic tooth movement. Eur J Oral Sci 116:89–97
Goto KT, Kajiya H, Nemoto T, Tsutsumi T, Tsuzuki T, Sato H, Okabe K (2011) Hyperocclusion stimulates osteoclastogenesis via CCL2 expression. J Dent Res 90:793–798
Chaffee BW, Weston SJ (2010) Association between chronic periodontal disease and obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Periodontol 81:1708–1724
Johnson AR, Justin Milner J, Makowski L (2012) The inflammation highway: metabolism accelerates inflammatory traffic in obesity. Immunol Rev 249:218–238
Rasouli N, Kern PA (2008) Adipocytokines and the metabolic complications of obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:64–73
Conde J, Scotece M, Gómez R, López V, Gómez-Reino JJ, Lago F, Gualillo O (2011) Adipokines: biofactors from white adipose tissue. A complex hub among inflammation, metabolism, and immunity. Biofactors 37:413–420
Inadera H (2008) The usefulness of circulating adipokine levels for the assessment of obesity-related health problems. Int J Med Sci 5:248–262
Preshaw PM, Foster N, Taylor JJ (2007) Cross-susceptibility between periodontal disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus: an immunobiological perspective. Periodontol 2000 45:138-157
Kanda N, Hau CS, Tada Y, Tatsuta A, Sato S, Watanabe S (2011) Visfatin enhances CXCL8, CXCL10, and CCL20 production in human keratinocytes. Endocrinology 152:3155–3164
Lee WJ, Wu CS, Lin H, Lee IT, Wu CM, Tseng JJ, Chou MM, Sheu WH (2009) Visfatin-induced expression of inflammatory mediators in human endothelial cells through the NF-kappaB pathway. Int J Obes (Lond) 33:465–472
Moschen AR, Kaser A, Enrich B, Mosheimer B, Theurl M, Niederegger H, Tilg H (2007) Visfatin, an adipocytokine with proinflammatory and immunomodulating properties. J Immunol 178:1748–1758
Taşkesen D, Kirel B, Us T (2012) Serum visfatin levels, adiposity and glucose metabolism in obese adolescents. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol 4:76–81
Chang YH, Chang DM, Lin KC, Shin SJ, Lee YJ (2011) Visfatin in overweight/obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular diseases: a meta-analysis and systemic review. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 27:515–527
Zhang LQ, Heruth DP, Ye SQ (2011) Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase in Human Diseases. J Bioanal Biomed 3:13–25
Saddi-Rosa P, Oliveira CS, Giuffrida FM, Reis AF (2010) Visfatin, glucose metabolism and vascular disease: a review of evidence. Diabetol Metab Syndr 2:21
Chen MP, Chung FM, Chang DM, Tsai JC, Huang HF, Shin SJ, Lee YJ (2006) Elevated plasma level of visfatin/pre-B cell colony-enhancing factor in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:295–299
Haider DG, Schindler K, Schaller G, Prager G, Wolzt M, Ludvik B (2006) Increased plasma visfatin concentrations in morbidly obese subjects are reduced after gastric banding. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:1578–1581
Berndt J, Klöting N, Kralisch S, Kovacs P, Fasshauer M, Schön MR, Stumvoll M, Blüher M (2005) Plasma visfatin concentrations and fat depot-specific mRNA expression in humans. Diabetes 54:2911–2916
Pradeep AR, Raghavendra NM, Prasad MV, Kathariya R, Patel SP, Sharma A (2011) Gingival crevicular fluid and serum visfatin concentration: their relationship in periodontal health and disease. J Periodontol 82:1314–1319
Pradeep AR, Raghavendra NM, Sharma A, Patel SP, Raju A, Kathariya R, Rao NS, Naik SB (2012) Association of serum and crevicular visfatin levels in periodontal health and disease with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Periodontol 83:629–634
Raghavendra NM, Pradeep AR, Kathariya R, Sharma A, Rao NS, Naik SB (2012) Effect of non-surgical periodontal therapy on gingival crevicular fluid and serum visfatin concentration in periodontal health and disease. Dis Markers 32:383–388
Nokhbehsaim M, Deschner B, Winter J, Reimann S, Bourauel C, Jepsen S, Jäger A, Deschner J (2010) Contribution of orthodontic load to inflammation-mediated periodontal destruction. J Orofac Orthop 71:390–402
Nokhbehsaim M, Deschner B, Bourauel C, Reimann S, Winter J, Rath B, Jäger A, Jepsen S, Deschner J (2011) Interactions of enamel matrix derivative and biomechanical loading in periodontal regenerative healing. J Periodontol 82:1725–1734
Nokhbehsaim M, Deschner B, Winter J, Bourauel C, Rath B, Jäger A, Jepsen S, Deschner J (2011) Interactions of regenerative, inflammatory and biomechanical signals on bone morphogenetic protein-2 in periodontal ligament cells. J Periodontal Res 46:374–381
Nokhbehsaim M, Deschner B, Winter J, Bourauel C, Jäger A, Jepsen S, Deschner J (2012) Anti-inflammatory effects of EMD in the presence of biomechanical loading and interleukin-1β in vitro. Clin Oral Investig 16:275–283
Lee KJ, Shin YA, Lee KY, Jun TW, Song W (2010) Aerobic exercise training-induced decrease in plasma visfatin and insulin resistance in obese female adolescents. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 20:275–281
Dahl TB, Holm S, Aukrust P, Halvorsen B (2012) Visfatin/NAMPT: a multifaceted molecule with diverse roles in physiology and pathophysiology. Annu Rev Nutr 32:229–243
Li Y, Zhang Y, Dorweiler B, Cui D, Wang T, Woo CW, Brunkan CS, Wolberger C, Imai S, Tabas I (2008) Extracellular Nampt promotes macrophage survival via a nonenzymatic interleukin-6/STAT3 signaling mechanism. J Biol Chem 283:34833–34843
Jia SH, Li Y, Parodo J, Kapus A, Fan L, Rotstein OD, Marshall JC (2004) Pre-B cell colony-enhancing factor inhibits neutrophil apoptosis in experimental inflammation and clinical sepsis. J Clin Invest 113:1318–1327
Signat B, Roques C, Poulet P, Duffaut D (2011) Fusobacterium nucleatum in periodontal health and disease. Curr Issues Mol Biol 13:25–36
He J, Huang W, Pan Z, Cui H, Qi G, Zhou X, Chen H (2011) Quantitative analysis of microbiota in saliva, supragingival, and subgingival plaque of Chinese adults with chronic periodontitis. Clin Oral Investig 16(6):1579–8
Dabija-Wolter G, Cimpan MR, Costea DE, Johannessen AC, Sørnes S, Neppelberg E, Al-Haroni M, Skaug N, Bakken V (2009) Fusobacterium nucleatum enters normal human oral fibroblasts in vitro. J Periodontol 80:1174–1183
Ji S, Shin JE, Kim YS, Oh JE, Min BM, Choi Y (2009) Toll-like receptor 2 and NALP2 mediate induction of human beta-defensins by Fusobacterium nucleatum in gingival epithelial cells. Infect Immun 77:1044–1052
Han YW, Shi W, Huang GT, Kinder Haake S, Park NH, Kuramitsu H, Genco RJ (2000) Interactions between periodontal bacteria and human oral epithelial cells: Fusobacterium nucleatum adheres to and invades epithelial cells. Infect Immun 68:3140–3146
Saito A, Inagaki S, Kimizuka R, Okuda K, Hosaka Y, Nakagawa T, Ishihara K (2008) Fusobacterium nucleatum enhances invasion of human gingival epithelial and aortic endothelial cells by Porphyromonas gingivalis. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 54:349–355
Agarwal S, Long P, Seyedain A, Piesco N, Shree A, Gassner R (2003) A central role for the nuclear factor-kappaB pathway in anti-inflammatory and proinflammatory actions of mechanical strain. FASEB J 17:899–901
Long P, Hu J, Piesco N, Buckley M, Agarwal S (2001) Low magnitude of tensile strain inhibits IL-1beta-dependent induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines and induces synthesis of IL-10 in human periodontal ligament cells in vitro. J Dent Res 80:1416–1420
Doyle SL, O'Neill LA (2006) Toll-like receptors: from the discovery of NFkappaB to new insights into transcriptional regulations in innate immunity. Biochem Pharmacol 72:1102–1113
Yoshimura A, Kaneko T, Kato Y, Golenbock DT, Hara Y (2002) Lipopolysaccharides from periodontopathic bacteria Porphyromonas gingivalis and Capnocytophaga ochracea are antagonists for human toll-like receptor 4. Infect Immun 70:218–225
Eick S, Straube A, Guentsch A, Pfister W, Jentsch H (2011) Comparison of real-time polymerase chain reaction and DNA-strip technology in microbiological evaluation of periodontitis treatment. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 69:12–20
Ziegler A, Keilig L, Kawarizadeh A, Jäger A, Bourauel C (2005) Numerical simulation of the biomechanical behaviour of multi-rooted teeth. Eur J Orthod 27:333–339
Toms SR, Dakin GJ, Lemons JE, Eberhardt AW (2002) Quasi-linear viscoelastic behavior of the human periodontal ligament. J Biomech 35:1411–1415
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant from São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP: 2010/07771-4, 2011/13752-5), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES: 2385-11-2), the German Research Foundation (DFG: KFO208/TP4), and the Medical Faculty of the University of Bonn. We would like to thank Ms. Ramona Hömig, Dr. Susanne Reimann, and Prof. Werner Götz for their great support.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nogueira, A.V.B., Nokhbehsaim, M., Eick, S. et al. Regulation of visfatin by microbial and biomechanical signals in PDL cells. Clin Oral Invest 18, 171–178 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-013-0935-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-013-0935-1