Abstract
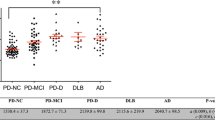
Impaired renal function is regarded as a risk factor for vascular disease, and is associated with an increasing pulse wave velocity. Both renal dysfunction and arterial stiffness are associated with cognitive impairment and dementia. However, there have been few studies that have evaluated the relationship between albuminuria and arterial stiffness and Alzheimer’s disease (AD). We investigated renal dysfunction and arterial stiffness in AD, as compared to normal controls, patients with subjective memory impairment (SMI), and patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI). Case–control comparisons were made between 29 patients with AD, 27 with MCI, 14 with SMI, and 25 healthy controls. All patients underwent clinical and neuropsychological assessments. The urine albumin/creatinine ratio and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) were determined. Pulse wave velocity and the ankle-brachial index were used to evaluate arterial stiffness. The urine albumin/creatinine ratio and eGFR were significantly different in patients with AD, compared with the results from cognitive normal controls. The pulse wave velocity was increased and the ankle-brachial index was decreased in AD. The eGFR was well correlated with other indices and decreasing eGFR was independently associated with cognitive decline. In conclusion, albuminuria, a decreased glomerular filtration rate, an increased pulse wave velocity, and a decreased ankle-brachial index were associated with AD. These finding suggests that impaired renal functions and arterial stiffness are related to AD, in which a vascular mechanism plays a prominent role in the cognitive dysfunction associated with the disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang QL, Koenig W, Raum E, Stegmaier C, Brenner H, Rothenbacher D (2009) Epidemiology of chronic kidney disease: results from a population of older adults in Germany. Prev Med 48(2):122–127
Currie G, Delles C (2013) Proteinuria and its relation to cardiovascular disease. Int J Nephrol Renovasc Dis 7:13–24
Ninomiya T (2013) Risk of stroke in kidney disease. Contrib Nephrol 179:58–66
Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY (2004) Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med 351(13):1296–1305
Elias MF, Dore GA, Davey A (2013) Kidney disease and cognitive function. Contrib Nephrol 179:42–57
Seliger SL, Siscovick DS, Stehman-Breen CO, Gillen DL, Fitzpatrick A, Bleyer A, Kuller LH (2004) Moderate renal impairment and risk of dementia among older adults: the Cardiovascular Health Cognition Study. J Am Soc Nephrol 15(7):1904–1911
Helmer C, Stengel B, Metzger M, Froissart M, Massy ZA, Tzourio C, Berr C, Dartigues JF (2011) Chronic kidney disease, cognitive decline, and incident dementia: the 3C study. Neurology 77(23):2043–2051
Sasaki Y, Marioni R, Kasai M, Ishii H, Yamaguchi S, Meguro K (2011) Chronic kidney disease: a risk factor for dementia onset: a population-based study. The Osaki-Tajiri Project. J Am Geriatr Soc 59(7):1175–1181
Barzilay JI, Fitzpatrick AL, Luchsinger J, Yasar S, Bernick C, Jenny NS, Kuller LH (2008) Albuminuria and dementia in the elderly: a community study. Am J Kidney Dis 52(2):216–226
Weiner DE, Bartolomei K, Scott T, Price LL, Griffith JL, Rosenberg I, Levey AS, Folstein MF, Sarnak MJ (2009) Albuminuria, cognitive functioning, and white matter hyperintensities in homebound elders. Am J Kidney Dis 53(3):438–447
Jassal SK, Kritz-Silverstein D, Barrett-Connor E (2010) A prospective study of albuminuria and cognitive function in older adults: the Rancho Bernardo study. Am J Epidemiol 171(3):277–286
Buchman AS, Tanne D, Boyle PA, Shah RC, Leurgans SE, Bennett DA (2009) Kidney function is associated with the rate of cognitive decline in the elderly. Neurology 73(12):920–927
Higuchi M, Chen R, Abbott RD, Bell C, Launer L, Ross GW, Petrovitch H, Masaki K (2015) Mid-life proteinuria and late-life cognitive function and dementia in elderly men: the Honolulu-Asia Aging Study. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 29(3):200–205
Yoon HE, Shin DI, Kim SJ, Koh ES, Hwang HS, Chung S, Shin SJ (2013) Brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity predicts decline in renal function and cardiovascular events in early stages of chronic kidney disease. Int J Med Sci 10(11):1430–1436
Chen FA, Yang CY, Yang WC, Chen JY, Ng YY, Li SY, Liu WS, Cheng ST, Wang YJ, Lin CC (2012) Ankle-brachial index is a powerful predictor of renal outcome and cardiovascular events in patients with chronic kidney disease. ScientificWorldJournal 2012:238494. doi:10.1100/2012/238494
Zhong W (2011) Pulse wave velocity in association with cognitive function. N Am J Med Sci 4(4):212–216
Hanon O, Haulon S, Lenoir H, Seux ML, Rigaud AS, Safar M, Girerd X, Forette F (2005) Relationship between arterial stiffness and cognitive function in elderly subjects with complaints of memory loss. Stroke 36(10):2193–2197
Waldstein SR, Rice SC, Thayer JF, Najjar SS, Scuteri A, Zonderman AB (2008) Pulse pressure and pulse wave velocity are related to cognitive decline in the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging. Hypertension 51(1):99–104
McKhann GM, Knopman DS, Chertkow H, Hyman BT, Jack CR Jr, Kawas CH, Klunk WE, Koroshetz WJ, Manly JJ, Mayeux R, Mohs RC, Morris JC, Rossor MN, Scheltens P, Carrillo MC, Thies B, Weintraub S, Phelps CH (2011) The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 7(3):263–269
American Psychiatric Association (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th edn. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
Petersen RC, Smith GE, Waring SC, Ivnik RJ, Tangalos EG, Kokmen E (1999) Mild cognitive impairment: clinical characterization and outcome. Arch Neurol 56(3):303–308
Stewart R (2012) Subjective cognitive impairment. Curr Opin Psychiatry 25(6):445–450
Kang YW, Na DL (2003) Seoul neuropsychological screening battery. Human Consulting Co, Incheon
Levey AS, Bosch JP, Lewis JB, Greene T, Rogers N, Roth D (1999) A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine: a new prediction equation. Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Group. Ann Intern Med 130(6):461–470
Hashimoto J, Aikawa T, Imai Y (2008) Large artery stiffening as a link between cerebral lacunar infarction and renal albuminuria. Am J Hypertens 21(12):1304–1309
Lambers Heerspink HJ, Brantsma AH, de Zeeuw D, Bakker SJ, de Jong PE, Gansevoort RT, PREVEND Study Group (2008) Albuminuria assessed from first-morning-void urine samples versus 24-hour urine collections as a predictor of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Am J Epidemiol 168(8):897–905
Witte MM, Trzepacz P, Case M, Yu P, Hochstetler H, Quinlivan M, Sundell K, Henley D (2014) Association between clinical measures and florbetapir F18 PET neuroimaging in mild or moderate Alzheimer’s disease dementia. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 26(3):214–220
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest or financial support to report.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, YS., Kim, JS., Park, JW. et al. Arterial stiffness and impaired renal function in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol Sci 37, 451–457 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-015-2434-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-015-2434-4