Abstract
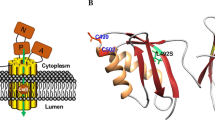
This study aimed to understand the pathogenesis of a new mtDNA-related etiology of Leigh snydrome. We identified the T9176G mutation as the molecular basis of Leigh syndrome in a child and looked for alterations in cellular ATP production. We then modeled the new mtDNA mutation in E. coli and analyzed ATP synthesis, hydrolysis, and the ability of the mutated enzyme to pump protons. Our results suggest that the T9176G change results in a novel, fully assembled enzyme which inhibits the holoenzyme probably by blocking the proton pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carrozzo, R., Murray, J., Capuano, O. et al. A novel mtDNA mutation in the ATPase6 gene studied by E. coli modeling. Neurol Sci 21 (Suppl 3), S983–S984 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100720070016
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100720070016