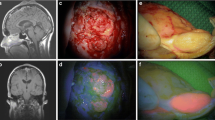
Abstract
5-Aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA)–fluorescence-guided resection is well established in many neuro-oncologic centers. Different classifications of 5-ALA-induced fluorescence have been reported. The aim of the systematic analysis was to evaluate the frequency of graduations, definitions, and designations of 5-ALA-induced fluorescence qualities. A systematic database search of PubMed was performed to identify studies reporting (1) on 5-ALA fluorescence-guided either spinal or cranial surgery, (2) on qualitative estimation and/or categorization of 5-ALA-induced fluorescence, (3) in English, and (4) were published as peer-reviewed original studies. Totally, 93 studies were identified. Different classification systems of 5-ALA-induced fluorescence were found. Over 60 % of the included studies used a dichotomized categorization of 5-ALA-induced fluorescence and 27.5 % of studies distinguished two different intensities of 5-ALA fluorescent tissue in addition to non-fluorescing tissue. More than 50 % of studies explicitly defined criteria for categorization of 5-ALA-induced fluorescence. The major limitation of the present analysis might be that it mainly comprises data from retrospective, uncontrolled, non-randomized trials. However, a precise definition of each 5-ALA-induced fluorescence quality is essential. Although dichotomized classification is the most common and simple graduation system, it may not be suitable for every clinical or scientific task. A three-level 5-ALA-induced fluorescence classification with precise definition of each fluorescence quality and their correlation with histological features would be more useful and reproducible in these cases.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldave G, Tejada S, Pay E, Marigil M, Bejarano B, Idoate MA, Diez-Valle R (2013) Prognostic value of residual fluorescent tissue in glioblastoma patients after gross total resection in 5-aminolevulinic acid-guided surgery. Neurosurgery 72:915–920, discussion 920–911
Arita H, Kinoshita M, Kagawa N, Fujimoto Y, Kishima H, Hashimoto N, Yoshimine T (2012) (1)(1)C-methionine uptake and intraoperative 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced fluorescence as separate index markers of cell density in glioma: a stereotactic image-histological analysis. Cancer 118:1619–1627
Barbagallo GM, Certo F, Heiss K, Albanese V (2014) 5-ALA fluorescence-assisted surgery in pediatric brain tumors: report of three cases and review of the literature. Br J Neurosurg 28:750–754
Beez T, Sarikaya-Seiwert S, Steiger HJ, Hanggi D (2014) Fluorescence-guided surgery with 5-aminolevulinic acid for resection of brain tumors in children—a technical report. Acta Neurochir 156:597–604
Bekelis K, Valdes PA, Erkmen K, Leblond F, Kim A, Wilson BC, Harris BT, Paulsen KD, Roberts DW (2011) Quantitative and qualitative 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced protoporphyrin IX fluorescence in skull base meningiomas. Neurosurg Focus 30:E8
Belloch JP, Rovira V, Llacer JL, Riesgo PA, Cremades A (2014) Fluorescence-guided surgery in high grade gliomas using an exoscope system. Acta Neurochir 156:653–660
Brokinkel B, Schober O, Ewelt C, Heindel W, Hargus G, Stummer W, Holling M, Wolfer J (2013) Cerebellar anaplastic astrocytoma in an adult with neurofibromatosis type 1: case report and review of literature. J Neurol Surg A Cen Eur Neurosurg 74(Suppl 1):e203–e206
Cage TA, Pekmezci M, Prados M, Berger MS (2013) Subependymal spread of recurrent glioblastoma detected with the intraoperative use of 5-aminolevulinic acid: case report. J Neurosurg 118:1220–1223
Chae MP, Song SW, Park SH, Park CK (2012) Experience with 5-aminolevulinic acid in fluorescence-guided resection of a deep sylvian meningioma. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 52:558–560
Coburger J, Engelke J, Scheuerle A, Thal DR, Hlavac M, Wirtz CR, Konig R (2014) Tumor detection with 5-aminolevulinic acid fluorescence and Gd-DTPA-enhanced intraoperative MRI at the border of contrast-enhancing lesions: a prospective study based on histopathological assessment. Neurosurg Focus 36:E3
Coluccia D, Fandino J, Fujioka M, Cordovi S, Muroi C, Landolt H (2010) Intraoperative 5-aminolevulinic-acid-induced fluorescence in meningiomas. Acta Neurochir 152:1711–1719
Cornelius JF, Slotty PJ, Kamp MA, Schneiderhan TM, Steiger HJ, El-Khatib M (2014) Impact of 5-aminolevulinic acid fluorescence-guided surgery on the extent of resection of meningiomas—with special regard to high-grade tumors. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther 11:481–490
Cornelius JF, Slotty PJ, Stoffels G, Galldiks N, Langen KJ, Steiger HJ (2013) 5-aminolevulinic acid and (18)F-FET-PET as metabolic imaging tools for surgery of a recurrent skull base meningioma. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base 74:211–216
Della Puppa A, Ciccarino P, Lombardi G, Rolma G, Cecchin D, Rossetto M (2014) 5-Aminolevulinic acid fluorescence in high grade glioma surgery: surgical outcome, intraoperative findings, and fluorescence patterns. BioMed Res Int 2014:232561
Della Puppa A, De Pellegrin S, d’Avella E, Gioffre G, Rossetto M, Gerardi A, Lombardi G, Manara R, Munari M, Saladini M, Scienza R (2013) 5-aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA) fluorescence guided surgery of high-grade gliomas in eloquent areas assisted by functional mapping. Our experience and review of the literature. Acta Neurochir 155:965–972, discussion 972
Della Puppa A, Gioffre G, Gardiman MP, Frasson C, Cecchin D, Scienza R, Persano L (2014) Intra-operative 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA)-induced fluorescence of medulloblastoma: phenotypic variability and CD133(+) expression according to different fluorescence patterns. Neurol Sci 35:99–102
Della Puppa A, Rustemi O, Gioffre G, Scienza R (2015) Approaching a brainstem high-grade glioma (HGG) with the assistance of 5-aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA) technology: a new strategy for an old surgical challenge. Neurol Sci 36:797–799
Della Puppa A, Rustemi O, Gioffre G, Troncon I, Lombardi G, Rolma G, Sergi M, Munari M, Cecchin D, Gardiman MP, Scienza R (2014) Predictive value of intraoperative 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced fluorescence for detecting bone invasion in meningioma surgery. J Neurosurg 120:840–845
Diez Valle R, Slof J, Galvan J, Arza C, Romariz C, Vidal C, researchers Vs (2014) Observational, retrospective study of the effectiveness of 5-aminolevulinic acid in malignant glioma surgery in Spain (the VISIONA study). Neurologia 29:131–138
Diez Valle R, Tejada Solis S, Idoate Gastearena MA, Garcia de Eulate R, Dominguez Echavarri P, Aristu Mendiroz J (2011) Surgery guided by 5-aminolevulinic fluorescence in glioblastoma: volumetric analysis of extent of resection in single-center experience. J Neuro-Oncol 102:105–113
Eicker S, Sarikaya-Seiwert S, Borkhardt A, Gierga K, Turowski B, Heiroth HJ, Steiger HJ, Stummer W (2011) ALA-induced porphyrin accumulation in medulloblastoma and its use for fluorescence-guided surgery. Cen Eur Neurosurg 72:101–103
Eicker SO, Floeth FW, Kamp M, Steiger HJ, Hanggi D (2013) The impact of fluorescence guidance on spinal intradural tumour surgery. Eur Spine J 22:1394–1401
Eljamel MS (2009) Which intracranial lesions would be suitable for 5-aminolevulenic acid-induced fluorescence-guided identification, localization, or resection? A prospective study of 114 consecutive intracranial lesions. Clin Neurosurg 56:93–97
Eljamel S, Petersen M, Valentine R, Buist R, Goodman C, Moseley H, Eljamel S (2013) Comparison of intraoperative fluorescence and MRI image guided neuronavigation in malignant brain tumours, a prospective controlled study. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther 10:356–361
Ewelt C, Floeth FW, Felsberg J, Steiger HJ, Sabel M, Langen KJ, Stoffels G, Stummer W (2011) Finding the anaplastic focus in diffuse gliomas: the value of Gd-DTPA enhanced MRI, FET-PET, and intraoperative, ALA-derived tissue fluorescence. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 113:541–547
Ewelt C, Nemes A, Senner V, Wolfer J, Brokinkel B, Stummer W, Holling M (2015) Fluorescence in neurosurgery: its diagnostic and therapeutic use. Review of the literature. J Photochem Photobiol B 148:302–309
Ewelt C, Stummer W, Klink B, Felsberg J, Steiger HJ, Sabel M (2010) Cordectomy as final treatment option for diffuse intramedullary malignant glioma using 5-ALA fluorescence-guided resection. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 112:357–361
Eyupoglu IY, Hore N, Savaskan NE, Grummich P, Roessler K, Buchfelder M, Ganslandt O (2012) Improving the extent of malignant glioma resection by dual intraoperative visualization approach. PLoS One 7:e44885
Floeth FW, Sabel M, Ewelt C, Stummer W, Felsberg J, Reifenberger G, Steiger HJ, Stoffels G, Coenen HH, Langen KJ (2011) Comparison of (18)F-FET PET and 5-ALA fluorescence in cerebral gliomas. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 38:731–741
Hayashi Y, Nakada M, Tanaka S, Uchiyama N, Hayashi Y, Kita D, Hamada J (2010) Implication of 5-aminolevulinic acid fluorescence of the ventricular wall for postoperative communicating hydrocephalus associated with cerebrospinal fluid dissemination in patients with glioblastoma multiforme: a report of 7 cases. J Neurosurg 112:1015–1019
Hefti M, Holenstein F, Albert I, Looser H, Luginbuehl V (2011) Susceptibility to 5-aminolevulinic acid based photodynamic therapy in WHO I meningioma cells corresponds to ferrochelatase activity. Photochem Photobiol 87:235–241
Hefti M, von Campe G, Moschopulos M, Siegner A, Looser H, Landolt H (2008) 5-aminolevulinic acid induced protoporphyrin IX fluorescence in high-grade glioma surgery: a one-year experience at a single institution. Swiss Med Wkly 138:180–185
Idoate MA, Diez Valle R, Echeveste J, Tejada S (2011) Pathological characterization of the glioblastoma border as shown during surgery using 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced fluorescence. Neuropathology 31:575–582
Inoue T, Endo T, Nagamatsu K, Watanabe M, Tominaga T (2013) 5-aminolevulinic acid fluorescence-guided resection of intramedullary ependymoma: report of 9 cases. Neurosurgery 72:ons159–ons168, discussion ons168
Ishihara R, Katayama Y, Watanabe T, Yoshino A, Fukushima T, Sakatani K (2007) Quantitative spectroscopic analysis of 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced protoporphyrin IX fluorescence intensity in diffusely infiltrating astrocytomas. Neurol Med Chir 47:53–57, discussion 57
Kajimoto Y, Kuroiwa T, Miyatake S, Ichioka T, Miyashita M, Tanaka H, Tsuji M (2007) Use of 5-aminolevulinic acid in fluorescence-guided resection of meningioma with high risk of recurrence. Case report. J Neurosurg 106:1070–1074
Kamp MA, Dibue M, Niemann L, Reichelt DC, Felsberg J, Steiger HJ, Szelenyi A, Rapp M, Sabel M (2012) Proof of principle: supramarginal resection of cerebral metastases in eloquent brain areas. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 154:1981–1986
Kamp MA, Felsberg J, Sadat H, Kuzibaev J, Steiger HJ, Rapp M, Reifenberger G, Dibue M, Sabel M (2014) 5-ALA-induced fluorescence behavior of reactive tissue changes following glioblastoma treatment with radiation and chemotherapy. Acta Neurochir
Kamp MA, Grosser P, Felsberg J, Slotty PJ, Steiger HJ, Reifenberger G, Sabel M (2012) 5-aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA)-induced fluorescence in intracerebral metastases: a retrospective study. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 154:223–228, discussion 228
Kotowski M, Naggara O, Darsaut TE, Nolet S, Gevry G, Kouznetsov E, Raymond J (2013) Safety and occlusion rates of surgical treatment of unruptured intracranial aneurysms: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature from 1990 to 2011. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 84:42–48
Marbacher S, Klinger E, Schwyzer L, Fischer I, Nevzati E, Diepers M, Roelcke U, Fathi AR, Coluccia D, Fandino J (2014) Use of fluorescence to guide resection or biopsy of primary brain tumors and brain metastases. Neurosurg Focus 36:E10
Millesi M, Kiesel B, Woehrer A, Hainfellner JA, Novak K, Martinez-Moreno M, Wolfsberger S, Knosp E, Widhalm G (2014) Analysis of 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced fluorescence in 55 different spinal tumors. Neurosurg Focus 36:E11
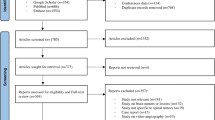
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Group P (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ 339:b2535
Moiyadi A, Shetty P (2014) Navigable intraoperative ultrasound and fluorescence-guided resections are complementary in resection control of malignant gliomas: one size does not fit all. J Neurol Surg A Cen Eur Neurosurg 75:434–441
Montcel B, Mahieu-Williame L, Armoiry X, Meyronet D, Guyotat J (2013) Two-peaked 5-ALA-induced PpIX fluorescence emission spectrum distinguishes glioblastomas from low grade gliomas and infiltrative component of glioblastomas. Biomed Opt Express 4:548–558
Moriuchi S, Yamada K, Dehara M, Teramoto Y, Soda T, Imakita M, Taneda M (2011) Use of 5-aminolevulinic acid for the confirmation of deep-seated brain tumors during stereotactic biopsy. Report of 2 cases. J Neurosurg 115:278–280
Muroi C, Fandino J, Coluccia D, Berkmann S, Fathi AR, Landolt H (2013) 5-Aminolevulinic acid fluorescence-guided surgery for spinal meningioma. World Neurosurg 80(223):e221–e223
Nabavi A, Thurm H, Zountsas B, Pietsch T, Lanfermann H, Pichlmeier U, Mehdorn M, Group ALARGS (2009) Five-aminolevulinic acid for fluorescence-guided resection of recurrent malignant gliomas: a phase ii study. Neurosurgery 65:1070–1076, discussion 1076–1077
Noell S, Feigl GC, Naros G, Barking S, Tatagiba M and Ritz R (2015) Experiences in surgery of primary malignant brain tumours in the primary sensori-motor cortex practical recommendations and results of a single institution. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 136:41–50
Panciani PP, Fontanella M, Garbossa D, Agnoletti A, Ducati A, Lanotte M (2012) 5-aminolevulinic acid and neuronavigation in high-grade glioma surgery: results of a combined approach. Neurocirugia 23:23–28
Panciani PP, Fontanella M, Schatlo B, Garbossa D, Agnoletti A, Ducati A, Lanotte M (2012) Fluorescence and image guided resection in high grade glioma. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 114:37–41
Piccirillo SG, Dietz S, Madhu B, Griffiths J, Price SJ, Collins VP, Watts C (2012) Fluorescence-guided surgical sampling of glioblastoma identifies phenotypically distinct tumour-initiating cell populations in the tumour mass and margin. Br J Cancer 107:462–468
Pichlmeier U, Bink A, Schackert G, Stummer W, Group ALAGS (2008) Resection and survival in glioblastoma multiforme: an RTOG recursive partitioning analysis of ALA study patients. Neuro-Oncology 10:1025–1034
Piquer J, Llacer JL, Rovira V, Riesgo P, Rodriguez R, Cremades A (2014) Fluorescence-guided surgery and biopsy in gliomas with an exoscope system. Biomed Res Int 2014:207974
Preuss M, Renner C, Krupp W, Christiansen H, Fischer L, Merkenschlager A, Kiess W, Muller W, Manzo N, Meixensberger J, Nestler U (2013) The use of 5-aminolevulinic acid fluorescence guidance in resection of pediatric brain tumors. Childs Nerv Syst 29:1263–1267
Rampazzo E, Della Puppa A, Frasson C, Battilana G, Bianco S, Scienza R, Basso G, Persano L (2014) Phenotypic and functional characterization of Glioblastoma cancer stem cells identified through 5-aminolevulinic acid-assisted surgery [corrected]. J Neuro-Oncol 116:505–513
Rapp M, Kamp M, Steiger HJ, Sabel M (2013) Endoscopic-assisted visualization of 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced fluorescence in malignant glioma surgery: a technical note. World Neurosurg
Ritz R, Feigl GC, Schuhmann MU, Ehrhardt A, Danz S, Noell S, Bornemann A, Tatagiba MS (2011) Use of 5-ALA fluorescence guided endoscopic biopsy of a deep-seated primary malignant brain tumor. J Neurosurg 114:1410–1413
Roberts DW, Valdes PA, Harris BT, Fontaine KM, Hartov A, Fan X, Ji S, Lollis SS, Pogue BW, Leblond F, Tosteson TD, Wilson BC, Paulsen KD (2011) Coregistered fluorescence-enhanced tumor resection of malignant glioma: relationships between delta-aminolevulinic acid-induced protoporphyrin IX fluorescence, magnetic resonance imaging enhancement, and neuropathological parameters. Clinical article. J Neurosurg 114:595–603
Roessler K, Becherer A, Donat M, Cejna M, Zachenhofer I (2012) Intraoperative tissue fluorescence using 5-aminolevolinic acid (5-ALA) is more sensitive than contrast MRI or amino acid positron emission tomography ((18)F-FET PET) in glioblastoma surgery. Neurol Res 34:314–317
Ruge JR, Liu J (2009) Use of 5-aminolevulinic acid for visualization and resection of a benign pediatric brain tumor. J Neurosurg Pediatr 4:484–486
Sanai N, Snyder LA, Honea NJ, Coons SW, Eschbacher JM, Smith KA, Spetzler RF (2011) Intraoperative confocal microscopy in the visualization of 5-aminolevulinic acid fluorescence in low-grade gliomas. J Neurosurg 115:740–748
Schucht P, Beck J, Abu-Isa J, Andereggen L, Murek M, Seidel K, Stieglitz L, Raabe A (2012) Gross total resection rates in contemporary glioblastoma surgery: results of an institutional protocol combining 5-aminolevulinic acid intraoperative fluorescence imaging and brain mapping. Neurosurgery 71:927–935, discussion 935–926
Schucht P, Beck J, Vajtai I, Raabe A (2011) Paradoxical fluorescence after administration of 5-aminolevulinic acid for resection of a cerebral melanoma metastasis. Acta Neurochir 153:1497–1499
Schucht P, Knittel S, Slotboom J, Seidel K, Murek M, Jilch A, Raabe A, Beck J (2014) 5-ALA complete resections go beyond MR contrast enhancement: shift corrected volumetric analysis of the extent of resection in surgery for glioblastoma. Acta Neurochir 156:305–312, discussion 312
Schucht P, Murek M, Jilch A, Seidel K, Hewer E, Wiest R, Raabe A, Beck J (2013) Early re-do surgery for glioblastoma is a feasible and safe strategy to achieve complete resection of enhancing tumor. PLoS One 8:e79846
Schucht P, Seidel K, Beck J, Murek M, Jilch A, Wiest R, Fung C, Raabe A (2014) Intraoperative monopolar mapping during 5-ALA-guided resections of glioblastomas adjacent to motor eloquent areas: evaluation of resection rates and neurological outcome. Neurosurg Focus 37:E16
Shimizu S, Utsuki S, Sato K, Oka H, Fujii K, Mii K (2006) Photodynamic diagnosis in surgery for spinal ependymoma. Case illustration. J Neurosurg Spine 5:380
Song SW, Kim YH, Park SH, Park CK (2013) 5-aminolevulinic acid fluorescence discriminates the histological grade of extraventricular neurocytoma. Brain Tumor Res Treat 1:45–49
Stockhammer F, Misch M, Horn P, Koch A, Fonyuy N, Plotkin M (2009) Association of F18-fluoro-ethyl-tyrosin uptake and 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced fluorescence in gliomas. Acta Neurochir 151:1377–1383
Stummer W, Kamp MA (2009) The importance of surgical resection in malignant glioma. Curr Opin Neurol 22:645–649
Stummer W, Novotny A, Stepp H, Goetz C, Bise K, Reulen HJ (2000) Fluorescence-guided resection of glioblastoma multiforme by using 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced porphyrins: a prospective study in 52 consecutive patients. J Neurosurg 93:1003–1013
Stummer W, Pichlmeier U, Meinel T, Wiestler OD, Zanella F, Reulen HJ, Group AL-GS (2006) Fluorescence-guided surgery with 5-aminolevulinic acid for resection of malignant glioma: a randomised controlled multicentre phase III trial. Lancet Oncol 7:392–401
Stummer W, Reulen HJ, Meinel T, Pichlmeier U, Schumacher W, Tonn JC, Rohde V, Oppel F, Turowski B, Woiciechowsky C, Franz K, Pietsch T, Group AL-GS (2008) Extent of resection and survival in glioblastoma multiforme: identification of and adjustment for bias. Neurosurgery 62:564–576, discussion 564–576
Stummer W, Rodrigues F, Schucht P, Preuss M, Wiewrodt D, Nestler U, Stein M, Artero JM, Platania N, Skjoth-Rasmussen J, Della Puppa A, Caird J, Cortnum S, Eljamel S, Ewald C, Gonzalez-Garcia L, Martin AJ, Melada A, Peraud A, Brentrup A, Santarius T, Steiner HH, European ALAPBTSG (2014) Predicting the “usefulness” of 5-ALA-derived tumor fluorescence for fluorescence-guided resections in pediatric brain tumors: a European survey. Acta Neurochir 156:2315–2324
Stummer W, Stocker S, Novotny A, Heimann A, Sauer O, Kempski O, Plesnila N, Wietzorrek J, Reulen HJ (1998) In vitro and in vivo porphyrin accumulation by C6 glioma cells after exposure to 5-aminolevulinic acid. J Photochem Photobiol B 45:160–169
Stummer W, Stocker S, Wagner S, Stepp H, Fritsch C, Goetz C, Goetz AE, Kiefmann R, Reulen HJ (1998) Intraoperative detection of malignant gliomas by 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced porphyrin fluorescence. Neurosurgery 42:518–525, discussion 525–516
Stummer W, Tonn JC, Goetz C, Ullrich W, Stepp H, Bink A, Pietsch T, Pichlmeier U (2014) 5-Aminolevulinic acid-derived tumor fluorescence: the diagnostic accuracy of visible fluorescence qualities as corroborated by spectrometry and histology and postoperative imaging. Neurosurgery 74:310–319, discussion 319–320
Stummer W, van den Bent MJ, Westphal M (2011) Cytoreductive surgery of glioblastoma as the key to successful adjuvant therapies: new arguments in an old discussion. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 153:1211–1218
Suero Molina EJ, Ardon H, Schroeteler J, Klingenhofer M, Holling M, Wolfer J, Fischer B, Stummer W, Ewelt C (2013) Aquaporin-4 in glioma and metastatic tissues harboring 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced porphyrin fluorescence. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 115:2075–2081
Tamura Y, Kuroiwa T, Kajimoto Y, Miki Y, Miyatake S, Tsuji M (2007) Endoscopic identification and biopsy sampling of an intraventricular malignant glioma using a 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced protoporphyrin IX fluorescence imaging system. Technical note. J Neurosurg 106:507–510
Tanaka S, Nakada M, Hayashi Y, Nakada S, Sawada-Kitamura S, Furuyama N, Suzuki T, Kamide T, Hayashi Y, Yano S, Hamada J (2011) Epithelioid glioblastoma changed to typical glioblastoma: the methylation status of MGMT promoter and 5-ALA fluorescence. Brain Tumor Pathol 28:59–64
Tejada-Solis S, Aldave-Orzaiz G, Pay-Valverde E, Marigil-Sanchez M, Idoate-Gastearena MA, Diez-Valle R (2012) Prognostic value of ventricular wall fluorescence during 5-aminolevulinic-guided surgery for glioblastoma. Acta Neurochir 154:1997–2002, discussion 2002
Tsugu A, Ishizaka H, Mizokami Y, Osada T, Baba T, Yoshiyama M, Nishiyama J, Matsumae M (2011) Impact of the combination of 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced fluorescence with intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging-guided surgery for glioma. World Neurosurg 76:120–127
Tykocki T, Michalik R, Bonicki W, Nauman P (2012) Fluorescence-guided resection of primary and recurrent malignant gliomas with 5-aminolevulinic acid. Preliminary results. Neurol Neurochir Pol 46:47–51
Utsuki S, Miyoshi N, Oka H, Miyajima Y, Shimizu S, Suzuki S, Fujii K (2007) Fluorescence-guided resection of metastatic brain tumors using a 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced protoporphyrin IX: pathological study. Brain Tumor Pathol 24:53–55
Utsuki S, Oka H, Kijima C, Miyajima Y, Hagiwara H, Fujii K (2011) Utility of intraoperative fluorescent diagnosis of residual hemangioblastoma using 5-aminolevulinic acid. Neurol India 59:612–615
Utsuki S, Oka H, Sato S, Shimizu S, Suzuki S, Tanizaki Y, Kondo K, Miyajima Y, Fujii K (2007) Histological examination of false positive tissue resection using 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced fluorescence guidance. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 47:210–213, discussion 213–214
Valdes PA, Bekelis K, Harris BT, Wilson BC, Leblond F, Kim A, Simmons NE, Erkmen K, Paulsen KD, Roberts DW (2014) 5-Aminolevulinic acid-induced protoporphyrin IX fluorescence in meningioma: qualitative and quantitative measurements in vivo. Neurosurgery 10(Suppl 1):74–82, discussion 82–73
Valdes PA, Kim A, Brantsch M, Niu C, Moses ZB, Tosteson TD, Wilson BC, Paulsen KD, Roberts DW, Harris BT (2011) Delta-aminolevulinic acid-induced protoporphyrin IX concentration correlates with histopathologic markers of malignancy in human gliomas: the need for quantitative fluorescence-guided resection to identify regions of increasing malignancy. Neuro-Oncology 13:846–856
Valdes PA, Kim A, Leblond F, Conde OM, Harris BT, Paulsen KD, Wilson BC, Roberts DW (2011) Combined fluorescence and reflectance spectroscopy for in vivo quantification of cancer biomarkers in low- and high-grade glioma surgery. J Biomed Opt 16:116007
Valdes PA, Leblond F, Kim A, Harris BT, Wilson BC, Fan X, Tosteson TD, Hartov A, Ji S, Erkmen K, Simmons NE, Paulsen KD, Roberts DW (2011) Quantitative fluorescence in intracranial tumor: implications for ALA-induced PpIX as an intraoperative biomarker. J Neurosurg 115:11–17
Valdes PA, Moses ZB, Kim A, Belden CJ, Wilson BC, Paulsen KD, Roberts DW, Harris BT (2012) Gadolinium- and 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced protoporphyrin IX levels in human gliomas: an ex vivo quantitative study to correlate protoporphyrin IX levels and blood–brain barrier breakdown. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 71:806–813
Voellger B, Klein J, Mawrin C, Firsching R (2014) 5-aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA) fluorescence in infectious disease of the brain. Acta Neurochir 156:1977–1978
von Campe G, Moschopulos M, Hefti M (2012) 5-Aminolevulinic acid-induced protoporphyrin IX fluorescence as immediate intraoperative indicator to improve the safety of malignant or high-grade brain tumor diagnosis in frameless stereotactic biopsies. Acta Neurochir 154:585–588, discussion 588
Wachter D, Kallenberg K, Wrede A, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Behm T, Rohde V (2012) Fluorescence-guided operation in recurrent glioblastoma multiforme treated with bevacizumab-fluorescence of the noncontrast enhancing tumor tissue? J Neurol Surg A Cen Eur Neurosurg 73:401–406
Whitson WJ, Valdes PA, Harris BT, Paulsen KD, Roberts DW (2011) Confocal microscopy for the histological fluorescence pattern of a recurrent atypical meningioma: case report. Neurosurgery 68:E1768–E1772, discussion E1772-1763
Widhalm G, Kiesel B, Woehrer A, Traub-Weidinger T, Preusser M, Marosi C, Prayer D, Hainfellner JA, Knosp E, Wolfsberger S (2013) 5-Aminolevulinic acid induced fluorescence is a powerful intraoperative marker for precise histopathological grading of gliomas with non-significant contrast-enhancement. PLoS One 8:e76988
Widhalm G, Minchev G, Woehrer A, Preusser M, Kiesel B, Furtner J, Mert A, Di Ieva A, Tomanek B, Prayer D, Marosi C, Hainfellner JA, Knosp E, Wolfsberger S (2012) Strong 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced fluorescence is a novel intraoperative marker for representative tissue samples in stereotactic brain tumor biopsies. Neurosurg Rev 35:381–391, discussion 391
Widhalm G, Wolfsberger S, Minchev G, Woehrer A, Krssak M, Czech T, Prayer D, Asenbaum S, Hainfellner JA, Knosp E (2010) 5-Aminolevulinic acid is a promising marker for detection of anaplastic foci in diffusely infiltrating gliomas with nonsignificant contrast enhancement. Cancer 116:1545–1552
Yamaguchi F, Takahashi H, Teramoto A (2007) Photodiagnosis for frameless stereotactic biopsy of brain tumor. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther 4:71–75
Zhao SG, Chen XF, Wang LG, Yang G, Han DY, Teng L, Yang MC, Wang DY, Shi C, Liu YH, Zheng BJ, Shi CB, Gao X, Rainov NG (2013) Increased expression of ABCB6 enhances protoporphyrin IX accumulation and photodynamic effect in human glioma. Ann Surg Oncol 20:4379–4388
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest statement
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest (such as honoraria; educational grants; participation in speakers’ bureaus; membership, employment, consultancies, stock ownership, or other equity interest; and expert testimony or patent-licensing arrangements) or non-financial interest (such as personal or professional relationships, affiliations, knowledge, or beliefs) in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Funding
The present study was not funded.
Additional information
Comments
Kazunori Arita, Kagoshima, Japan
Authors collected 378 studies from the PubMed database and finally analyzed 93 studies reporting qualitative estimation of 5-aminolevulinic acid–fluorescence (5-AIF). The quality of the studies was evaluated according to modified STROBE scale. Through their extensive review, they found the use of dichotomized categorization of 5-ALA-induced fluorescence in more than half of the reported studies. And they recommend a three-level 5-ALA-induced fluorescence classification for precise definition of each fluorescence quality and their correlation with histological features.
In these 93 studies, they analyzed, however, included wide variety in histopathology, malignancy, 5-ALA dose, elapsed time after oral intake, light source, wave length, and filter. We know that all these factors influence the 5-ALA fluorescence intensity and visibility.
Thus, future study should aim to establish a new classification system of fluorescence intensity considering these variances.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamp, M.A., Krause Molle, Z., Munoz-Bendix, C. et al. Various shades of red—a systematic analysis of qualitative estimation of ALA-derived fluorescence in neurosurgery. Neurosurg Rev 41, 3–18 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-016-0745-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-016-0745-4