Abstract
Aim
To validate Liano score as a prognostic scoring system in acute renal failure (ARF): a prospective study in Indian patients.
Patients and methods
Prospective study including 100 patients over a period of 1 year, from March 2006 to July 2007. Inclusion criteria were patients with no previous renal disease or any systemic disease known to affect the kidney and who presented with acute rise (hours to days) in serum creatinine. Exclusion criteria were patients with preexisting chronic renal failure, age younger than 12 years and ultrasound of the abdomen showing contracted kidneys.
Results and conclusions
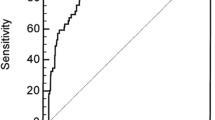
In this study there were 68 males and 32 females. Peak incidence by age was in the fifth decade. There was no increased mortality in any age group (p = 0.278). A total of 19 patients had pre-renal ARF, 74 patients had intrinsic ARF, of which 46 were acute tubular necrosis (ATN); 7 patients had obstructive ARF. A total of 21 patients had Liano score greater than 0.9, of which 18 patients died and 3 were discharged against medical advice in a critical condition (and died later at home). Calculated sensitivity was 62.1%, specificity was 100% and positive predictive value was 100%. Sensitivity and specificity when calculated separately for intrinsic renal ARF (after excluding post renal ARF) were 60.7% and 100%, respectively. There was statistically significant correlation between Liano score and mortality (p < 0.001).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nolan CR, Anderson RJ. Hospital-acquired acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1998;9:710–8.
McCarthy JT. Prognosis of patients with acute renal failure in the intensive-care unit: a tale of two eras. Mayo Clin Proc. 1996;71:117–26.
Brivet FG, Kleinknecht DJ, Loirat P, Landais PJ. Acute renal failure in intensive care units–causes, outcome, and prognostic factors of hospital mortality; a prospective, multicenter study. French study group on acute renal failure. Crit Care Med. 1996;24:192–8.
Hamel MB, Phillips RS, Davis RB, Desbiens N, Connors AF Jr, Teno JM, et al. Outcomes and cost-effectiveness of initiating dialysis and continuing aggressive care in seriously ill hospitalized adults. SUPPORT investigators. Study to understand prognoses and preferences for outcomes and risks of treatments. Ann Intern Med. 1997;127:195–202.
MacKay K, Moss AH. To dialyze or not to dialyze: an ethical and evidence-based approach to the patient with acute renal failure in the intensive care unit. Adv Ren Replace Ther. 1997;4:288–96.
Groeneveld AB, Tran DD, van der Meulen J, Nauta JJ, Thijs LG. Acute renal failure in the medical intensive care unit: predisposing, complicating factors and outcome. Nephron. 1991;59:602–10.
Sural S, Sharma RK, Singhal MK, Kher V, Gupta A, Arora P, et al. Acute renal failure in an intensive care unit in India—prognostic factors and outcome. J Nephrol. 1999;12:390–4.
Ahlström A, Kuitunen A, Peltonen S, Hynninen M, Tallgren M, Aaltonen J, et al. Comparison of 2 acute renal failure severity scores to general scoring systems in the critically ill. Am J Kidney Dis. 2006;48:262–8.
Uchino S, Bellomo R, Morimatsu H, Morgera S, Schetz M, Tan I, et al. Beginning and ending supportive therapy for the kidney (B.E.S.T. Kidney) investigators. External validation of severity scoring systems for acute renal failure using a multinational database. Crit Care Med. 2005;33:1961–7.
Liaño F, Gallego A, Pascual J, García-Martín F, Teruel JL, Marcén R, et al. Prognosis of acute tubular necrosis: an extended prospectively contrasted study. Nephron. 1993;63:21–31.
Schäfer JH, Maurer A, Jochimsen F, Emde C, Wegscheider K, Arntz HR, et al. Outcome prediction models on admission in a medical intensive care unit: do they predict individual outcome? Crit Care Med. 1990;18:1111–8.
Knaus WA, Draper EA, Wagner DP, Zimmerman JE. APACHE II: a severity of disease classification system. Crit Care Med. 1985;13:818–29.
Le Gall JR, Lemeshow S, Saulnier F. A new simplified acute physiology score (SAPS II) based on a European/North American multicenter study. JAMA. 1993;270(24):2957–63. Erratum in: JAMA 1994;271:1321.
Lemeshow S, Le Gall JR. Modeling the severity of illness of ICU patients. A systems update. JAMA. 1994;272:1049–55.
Auriant I, Vinatier I, Thaler F, Tourneur M, Loirat P. Simplified acute physiology score II for measuring severity of illness in intermediate care units. Crit Care Med. 1998;26:1368–71.
Maher ER, Robinson KN, Scoble JE, Farrimond JG, Browne DR, Sweny P, et al. Prognosis of critically-ill patients with acute renal failure: APACHE II score and other predictive factors. Q J Med. 1989;72:857–66.
Beck DH, Taylor BL, Millar B, Smith GB. Prediction of outcome from intensive care: a prospective cohort study comparing acute physiology and chronic health evaluation II and III prognostic systems in a United Kingdom intensive care unit. Crit Care Med. 1997;25:9–15.
Liaño F, Gallego A, Pascual J, García-Martín F, Teruel JL, Marcén R, et al. Prognosis of acute tubular necrosis: an extended prospectively contrasted study. Nephron. 1993;63:21–31.
Liaño F, Pascual J. Acute renal failure, critical illness and the artificial kidney: can we predict outcome? Blood Purif. 1997;15:346–53.
Liaño F. Severity of acute renal failure: the need of measurement. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1994;9 Suppl 4:229–38.
Liaño F, Pascual J. Epidemiology of acute renal failure: a prospective, multicenter, community-based study. Madrid Acute Renal Failure Study Group. Kidney Int. 1996;50:811–8.
Uchino S, Bellomo R, Kellum JA, Morimatsu H, Morgera S, Schetz MR, et al. Beginning and ending supportive therapy for the kidney (B.E.S.T. Kidney) investigators writing committee. Patient and kidney survival by dialysis modality in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. Int J Artif Organs. 2007;30:281–92.
Lins RL, Elseviers MM, Daelemans R, Arnouts P, Billiouw JM, Couttenye M, et al. Re-evaluation and modification of the Stuivenberg Hospital acute renal failure (SHARF) scoring system for the prognosis of acute renal failure: an independent multicentre, prospective study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004;19:2282–8. Epub 2004 July 20.
Abosaif NY, Tolba YA, Heap M, Russell J, El Nahas AM. The outcome of acute renal failure in the intensive care unit according to RIFLE: model application, sensitivity, and predictability. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005;46:1038–48.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Varricatt, V.P., Rau, N.R., Attur, R.P. et al. Validation of Liano score in acute renal failure: a prospective study in Indian patients. Clin Exp Nephrol 13, 33–37 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-008-0073-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-008-0073-2