Abstract
Purpose
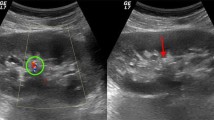
To compare the effectiveness of B-Mode and color-Doppler ultrasound imaging features, including “twinkling-artifact” with unenhanced CT for detecting millimetrical nephrolithiasis.
Methods
397 patients were examined for suspected urolithiasis with US and CT were included. US findings such as echogenic focuses, posterior acoustic shadowing and twinkling artifact were examined for their ability to detect millimetricalcalculies (greatest diameter ≤5 mm) using CT findings as the gold-standard. The accuracy of US for measuring stone size was also investigated.
Results
219 millimetriccalculies in 164 cases were detected by CT. The sensitivity and positive-predictive-values for the detection of microcalculies were 76.7 and 94.9 %, 85.8 and 88.3 %, 40.6 and 97.8 %, 68.9 and 94.4 %, and 38.4 and 97.7 % for the presence of B-Mode echogenity, twinkling-artifact, B-Mode echogenity with acoustic shadowing, B-Mode echogenity with twinkling-artifact, B-Mode echogenity with acoustic shadowing and twinkling-artifact, respectively. No significant difference between US and CT was observed in quantification of nephrolithiasis sizes (p = 913).
Conclusion
Twinkling-artifact based color-Doppler US is preferable for the sensitive detection of millimetrical nephrolithiasis; however, the high false-positive value of this technique, which can lead to an overestimation of the stone number, has to be considered.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bultitude M, Rees J. Management of renal colic. BMJ. 2012;345:e5499.
Romero V, Akpinar H, Assimos DG. Kidney stones: a global picture of prevalence, incidence, and associated risk factors. Rev Urol. 2010;12:e86–96.
Kielar AZ, Shabana W, Vakili M, et al. Prospective evaluation of Doppler sonography to detect the twinkling artifact versus unenhanced computed tomography for identifying urinary tract calculi. J Ultrasound Med. 2012;31:1619–25.
King W 3rd, Kimme-Smith C, Winter J. Renal stone shadowing: an investigation of contributing factors. Radiology. 1985;154:191–6.
Vrtiska TJ, Hattery RR, King BF, et al. Role of ultrasound in medical management of patients with renal stone disease. Urol Radiol. 1992;14:131–8.
Fowler KA, Locken JA, Duchesne JH, et al. US for detecting renal calculi with nonenhanced CT as a reference standard. Radiology. 2002;222:109–13.
Ulusan S, Koc Z, Tokmak N. Accuracy of sonography for detecting renal stone: comparison with CT. J Clin Ultrasound. 2007;35:256–61.
Thoeny HC, Tuma J, Hess B. Diagnostic imaging of calculi in the upper urinary tract—sonography vs. computerized tomography. Ther Umsch. 2003;60:73–8.
Haroun AA, Hadidy AM, Mithqal AM, et al. The role of B-mode ultrasonography in the detection of urolithiasis in patients with acute renal colic. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2010;21:488–93.
Rahmouni A, Bargoin R, Herment A, et al. Color Doppler twinkling artifact in hyperechoic regions. Radiology. 1996;199:269–71.
Aytac SK, Ozcan H. Effect of color Doppler system on the twinkling sign associated with urinary tract calculi. J Clin Ultrasound. 1999;27:433–9.
Lee JY, Kim SH, Cho JY, et al. Color and power Doppler twinkling artifacts from urinary stones: clinical observations and phantom studies. AJR. 2001;176:1441–5.
Logias F, Manca EM, Carta P, et al. Twinkling artifact in kidney stone disease. G Ital Nefrol. 2005;22:503–7.
Turrin A, Minola P, Costa F, et al. Diagnostic value of colour Doppler twinkling artefact in sites negative for stones on B mode renal sonography. Urol Res. 2007;35:313–7.
Fujii Y, Kino M, Kimata T, et al. Significance of twinkling artifact on ultrasound in the diagnosis of cystine urolithiasis. Pediatr Int. 2013;55:e49–51.
Sorensen MD, Harper JD, Hsi RS, et al. B-mode ultrasound versus color Doppler twinkling artifact in detecting kidney stones. J Endourol. 2013;27:149–53.
Kamaya A, Tuthill T, Rubin JM. Twinkling artifact on color Doppler sonography: dependence on machine parameters and underlying cause. AJR. 2003;180:215–22.
Kimme-Smith C, Perrella RR, Kaveggia LP, et al. Detection of renal stones with real-time sonography: effect of transducers and scanning parameters. AJR. 1991;157:975–80.
Memarsadeghi M, Heinz-Peer G, Helbich TH, et al. Unenhanced multi-detector row CT in patients suspected of having urinary stone disease: effect of section width on diagnosis. Radiology. 2005;235:530–6.
Cook JH 3rd, Lytton B. Intraoperative localization of renal calculi during nephrolithotomy by ultrasound scanning. J Urol. 1977;117:543–6.
Pollack HM, Arger PH, Goldberg BB, et al. Ultrasonic detection of nonopaque renal calculi. Radiology. 1978;127:233–7.
Ray AA, Ghiculete D, Pace KT, et al. Limitations to ultrasound in the detection and measurement of urinary tract calculi. Urology. 2010;76:295–300.
Middleton WD, Dodds WJ, Lawson TL, et al. Renal calculi: sensitivity for detection with US. Radiology. 1988;167:239–44.
Choyke PL, Pahira JH, Davros WJ, et al. Renal calculi after shock wave lithotripsy: uS evaluation with an in vitro phantom. Radiology. 1989;170:39–44.
Alan C, Kocoglu H, Kosar S, et al. Role of twinkling artifact in characterization of urinary calculi. Actas Urol Esp. 2011;35:396–402.
Shabana W, Bude RO, Rubin JM. Comparison between color Doppler twinkling artifact and acoustic shadowing for renal calculus detection: an in vitro study. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2009;35:339–50.
Dillman JR, Kappil M, Weadock WJ, et al. Sonographic twinkling artifact for renal calculus detection: correlation with CT. Radiology. 2011;259:911–6.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have nothing to disclose and they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008 (5). Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Informed consent
Additional informed consent was obtained from all patients for which identifying information is included in this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Yavuz, A., Ceken, K., Alimoglu, E. et al. The reliability of color doppler “twinkling” artifact for diagnosing millimetrical nephrolithiasis: comparison with B-Mode US and CT scanning results. J Med Ultrasonics 42, 215–222 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-014-0599-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-014-0599-8