Abstract
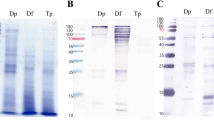
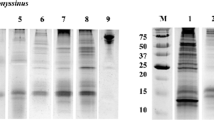
Although specific IgE to the storage mite Acarus siro is often detected, there are no detailed studies on IgE reactivity to A. siro in Korea. This study was undertaken to investigate the cross-reactivity to the mite species Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus, Dermatophagoides farinae, Tyrophagus putrescentiae, and A. siro in Korean mite allergic patients. Specific IgE values were determined for the four mite species and a competitive inhibition test was performed for mite extracts using the ImmunoCAP system. The IgE value to D. farinae was the highest among the four mite species tested. There was a strong correlation in the IgE value between house dust mites (D. pteronyssinus and D. farinae) and between storage mites (A. siro and T. putrescentiae). IgE reactivity to A. siro was inhibited by D. farinae and T. putrescentiae extract. Dermatophagoides farinae extract was the strongest inhibitor of IgE binding to A. siro extract, indicating that IgE reactivity to A. siro extract is a cross-reaction caused by sensitization to D. farinae. Strong IgE reactive components were observed in D. farinae and T. putrescentiae extract by SDS-PAGE and IgE immunoblotting. However, no strong IgE-binding component was observed for A. siro. Dermatophagoides farinae is the main source of mite allergens that cause sensitization in Korea. Serum IgE from some of the house dust mite-sensitized patients showed positive responses to storage mite allergens by cross-reaction. Therefore, it is necessary to pay special attention to the diagnosis of mite allergies.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arlian LG, Morgan MS, Vyszenski-Moher DL, Sharra D (2009) Cross-reactivity between storage and dust mites and between mites and shrimp. Exp App Acarol 47:159–172
Barber D, Arias J, Boquete M, Cardona V, Carrillo T, Gala G, Gamboa P, Garcia-Robaina JC, Hernandez D, Sanz ML, Tabar AI, Vidal C, Ipsen H, de la Torre F, Lombardero M (2012) Analysis of mite allergic patients in a diverse territory by improved diagnostic tools. Clin Exp Allergy 42:1129–1138
Blainey AD, Topping MD, Ollier S, Davies RJ (1989) Allergic respiratory disease in grain workers: the role of storage mites. J Allergy Clin Immunol 84:296–303
Brazis P, Serra M, Selles A, Dethiouxt F, Biourge V, Puigdement A (2008) Evaluation of storage mite contamination of commercial dry dog food. Vet Dermatol 19:209–214
Caraballo L, Acevedo N (2011) Allergy in the tropics: the impact of cross-reactivity between mites and ascaris. Front Biosci (Elite Ed) 3:51–64
Cuthbert OD, Brostoff J, Wraith DG, Brighton WD (1979) ‘Barn allergy’: asthma and rhinitis due to storage mites. Clin Allergy 9:229–236
Dunn JA, Thind BB, Danks C, Chambers J (2008) Rapid method for the detection of storage mites in cereals: feasibility of an ELISA based approach. Bull Entomol Res 98:207–213
Dutau G (2002) House dust mites; new food allergens. Revue Francaised’ Allergologieetd’ Immunologie Clinique 42:171–177
Eriksson TL, Whitley P, Johansson E, van Hage-Hamsten M, Gafvelin G (1999) Identification and characterization of two allergens from the dust mite Acarus siro, homologous with fatty acid-binding proteins. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 119:275–281
Han CY, Bahn JM, Kim JG, Kim HS, Kim GC, Park GH, Gang CD, Cho JH (1999) The allergenicity of the storage mites (Tyrophagus putrescentiae and Acarus siro) in patients with allergic rhinitis. Korean J Otolaryngol 42:1392–1399
Huang CH, Liew LM, Mah KW, Kuo IC, Lee BW, Chua KY (2006) Characterization of glutathione S-transferase from dust mite, Der p 8 and its immunoglobulin E cross-reactivity with cockroach glutathione S-transferase. Clin Exp Allergy 36:369–376
Ingram CG, Symington IS, Jeffrey IG, Cuthbert OD (1979) Bronchial provocation studies in farmers allergic to storage mites. Lancet 2:1330–1332
Jeong KY, Hong CS, Yong TS (2006a) Allergenic tropomyosins and their cross-reactivity. Protein Pept Lett 13:835–845
Jeong KY, Lee IY, Lee J, Ree HI, Hong CS, Yong TS (2006b) Effectiveness of education for control of house dust mites and cockroaches in Seoul, Korea. Korean J Parasitol 44:73–79
Jeong KY, Lee H, Lee JS, Lee J, Lee IY, Ree HI, Hong CS, Yong TS (2007) Molecular cloning and the allergenic characterization of tropomyosin from Tyrophagus putrescentiae. Protein Pept Lett 14:431–436
Jeong KY, Choi SY, Lee JH, Lee IY, Yong TS, Lee JS, Hong CS, Park JW (2012a) Standardization of house dust mite extracts in Korea. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res 4:346–350
Jeong KY, Park JW, Hong CS (2012b) House dust mite allergy in Korea: the most important inhalant allergen in current and future. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res 4:313–325
Lee WK, Choi WY (1980) Studies on the mites (Order Acarina) in Korea: I. Suborder sacroptiformes. Kisaengchunghak Chapchi 18:119–144
Melnyk JP, Scott-Dupree A, Marcone MF, Hill A (2010) Identification of cheese mite species inoculated on Mimolette and Milbenkase cheese through cryogenic scanning electron microscopy. J Dairy Sci 93:3461–3468
Molina C, Aiache JM, Tourreau A, Jeanneret A (1975) Enqueteepidemiologique et immunologique chez les fromagers. Revue Francaised’ Allergologieetd’ Immunologie Clinique 15:89–91
Ownby DR, Bailey J (1986) Comparison of MAST with radioallergosorbent and skin tests for diagnosis of allergy in children. Am J Dis Child 140:45–48
Park JW, Ko SH, Yong TS, Ree HI, Jeoung BJ, Hong CS (1999) Cross-reactivity of Tyrophagus putrescentiae with Dermatophagoides farinae and Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus in urban areas. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 83:533–539
Parsons AC (1924) Report on bakers’ dermatitis. Br J Dermatol Syphilis 36:193–200
Pytelkova J, Lepsik M, Sanda M, Talacko P, Maresova L, Mares M (2012) Enzymatic activity and immunoreactivity of Aca s 4, an alpha-amylase allergen from the storage mite Acarus siro. BMC Biochem 13:3
Ree HI, Jeon SH, Lee IY, Hong CS, Lee DK (1997) Fauna and geographical distribution of house dust mites in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 35:9–17
Revsbech P, Dueholm M (1990) Storage mite allergy among bakers. Allergy 45:204–208
Van der Heide S, Niemeijer NR, Hovenga H, de Monchy JG, Dubois AE, Kauffman HF (1998) Prevalence of sensitization to the storage mites Acarus siro, Tyrophagus putrescentiae, and Lepidoglyphus destructor in allergic patients with different degrees of sensitization to the house-dust mite Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus. Allergy 53:426–430
Zheng YW, Chen S, Lai XX, Gjesing B, Zhong NS, Spangfor MD (2012) Indoor mite allergen levels, specific IgE prevalence and IgE cross-inhibition pattern among asthmatic children in Haikou, southern China. Chin Med J 125:3059–3063
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Grant (No. C0010179) from the Business for Cooperative R&D between Industry, Academy, and Research Institute funded by the Korea Small and Medium Business Administration in 2012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Son, M., Jeong, K.Y., Kim, B.J. et al. IgE reactivity to Acarus siro extract in Korean dust mite allergic patients. Exp Appl Acarol 63, 57–64 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-013-9759-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-013-9759-6