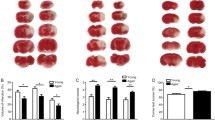
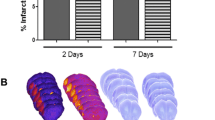
Abstract
Age is the principal nonmodifiable risk factor for stroke. Over the past 10 years, suitable models for stroke in aged rats have been established. At genetic and cellular level there are significant differences in behavioral, cytological and genomics responses to injury in old animals as compared with the young ones. Behaviorally, the aged rats have the capacity to recover after cortical infarcts albeit to a lower extent than the younger counterparts. Similarly, the increased vulnerability of the aged brain to stroke, together with a decreased interhemisphere synchrony after stroke, assessed by different experimental methods (MRI, fMRI, in vivo microscopy, EEG) leads to unfavorable recovery of physical and cognitive functions in aged people and may have a prognostic value for the recovery of stroke patients. Furthermore, in elderly, comorbidities like diabetes or arterial hypertension are associated with higher risk of stroke, increased mortality and disability, and poorer functional status and quality of life. Aging brain reacts strongly to ischemia–reperfusion injury with an early inflammatory response. The process of cellular senescence can be an important additional contributor to chronic post-stroke by creating a “primed” inflammatory environment in the brain. Overall, these pro-inflammatory reactions promote early scar formation associated with tissue fibrosis and reduce functional recovery. A better understanding of molecular factors and signaling pathways underlying the contribution of comorbidities to stroke-induced pathological sequelae, may be translated into successful treatment or prevention therapies for age-associated diseases which would improve lifespan and quality of life.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- CX3CL1:
-
Fractalkine
- CX3CR1:
-
Fractalkine receptor
- DTI:
-
Diffusion tensor imaging
- DWI:
-
Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging
- EEG:
-
Electroencephalography
- fMRI:
-
Functional magnetic resonance imaging
- IL-1:
-
Interleukin-1
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- MCA:
-
Middle cerebral artery
- MCAO:
-
Middle cerebral artery occlusion
- mNSS:
-
Modified neurological severity score
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- PWI:
-
Perfusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging
- SHR:
-
Spontaneously hypertensive rat model
- SHRSP:
-
Spontaneously Hypertensive Stroke Prone rat
- (TNF-α):
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- WKY:
-
Wistar–Kyoto rats
References
Amor F, Puentes D, Baker P, van der Valk (2010) Inflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Immunology 129:154
Andersen MB, Zimmer J, Sams-Dodd F (1999) Specific behavioral effects related to age and cerebral ischemia in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 62:673–682
Arumugam TV, Phillips TM et al (2010) Age and energy intake interact to modify cell stress pathways and stroke outcome. Annals of neurology 67(1):41–52
Ay H, Koroshetz WJ, Vangel M, Benner T, Melinosky C, Zhu M, Menezes N, Lopez CJ, Sorensen AG (2005) Conversion of ischemic brain tissue into infarction increases with age. Stroke 36:2632
Bachstetter AD, Morganti JM et al (2011) Fractalkine and CX 3 CR1 regulate hippocampal neurogenesis in adult and aged rats. Neurobiol Aging 32(11):2030–2044
Badan I, Buchhold B, Hamm A, Gratz M, Walker LC, Platt D, Kessler Ch, Popa-Wagner A (2003) Accelerated glial reactivity to stroke in aged rats correlates with reduced functional recovery. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 23:845–854
Benderro GF, LaManna JC (2011) Hypoxia-induced angiogenesis is delayed in aging mouse brain. Brain Res 1389:50–60
Bergerat A, Decano J, Wu CJ, Choi H, Nesvizhskii AI, Moran AM, Ruiz-Opazo N, Steffen M, Herrera VL (2011) Prestroke proteomic changes in cerebral microvessels in stroke-prone, transgenic[hCETP]-Hyperlipidemic, Dahl salt-sensitive hypertensive rats. Mol Med 17:588–598
Biber K, Neumann H et al (2007) Neuronal ‘On’ and ‘Off’ signals control microglia. Trends Neurosci 30:596–602
Brown AW, Marlowe KJ, Bjelke B (2003) Age effect on motor recovery in a post-acute animal stroke model. Neurobiol Aging 24:607–614
Buchhold B, Mogoanta L, Suofu Y, Hamm A, Walker L, Kessler C, Popa-Wagner A (2007) Environmental enrichment improves functional and neuropathological indices following stroke in young and aged rats. Restorative Neurol Neurosci 25:1–18
Buga AM, Sascau M, Pisoschi C, Herndon JG, Kessler C, Popa-Wagner A (2008) The genomic response of the ipsilateral and contralateral cortex to stroke in aged rats. J Cell Mol Med 12(6B):2731–2753
Buga AM, Scholz CJ, Kumar S, Herndon JG, Alexandru D, Cojocaru GR, Dandekar T, Popa-Wagner A (2012) Identification of new therapeutic targets by genome-wide analysis of gene expression in the ipsilateral cortex of aged rats after stroke. PLoS ONE 7(12):e50985. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0050985
Cai J, Liu T (2012) Inflammatory cause of metabolic syndrome via brain stress and NF-κB. Aging 4:98–115
Canese R, Fortuna S, Lorenzini P, Podo F, Michalek H (1998) Transient global brain ischemia in young and aged rats: differences in severity and progression, but not localization, of lesions evaluated by magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Res Mater Phys Biol Med 7:8–34
Canese R, Lorenzini P, Fortuna S, Volpe MT, Giannini M, Podo F, Michalek H (2004) Age-dependent MRI-detected lesions at early stages of transient global ischemia in rat brain. MAGMA 17:109–116
Chen Y, Sun F-Y (2007) Age-related decrease of striatal neurogenesis is associated with apoptosis of neural precursors and newborn neurons in rat brain after ischemia. Brain Res 166:9–19
Chitnis T, Imitola J et al (2007) Elevated neuronal expression of CD200 protects Wlds mice from inflammation-mediated neurodegeneration. Am J Pathol 170:1695–1712
Cipriani R, Villa P et al (2011) CX3CL1 is neuroprotective in permanent focal cerebral ischemia in rodents. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 31:16327–16335
Cox FF, Carney D et al (2012) CD200 fusion protein decreases microglial activation in the hippocampus of aged rats. Brain Behav Immun 26:789–796
Damani MR, Zhao L et al (2011) Age-related alterations in the dynamic behavior of microglia. Aging Cell 10:263–276
Davies L, Hayes KC, Shi R (2006) Recombinant human TNFalpha induces concentration-dependent and reversible alterations in the electrophysiological properties of axons in mammalian spinal cord. J Neurotrauma 23:1261–1273
de Haas AH, van Weering HR et al (2007) Neuronal chemokines: versatile messengers in central nervous system cell interaction. Mol Neurobiol 36:137–151
Denes A, Ferenczi S et al (2008) Role of CX3CR1 (fractalkine receptor) in brain damage and inflammation induced by focal cerebral ischemia in mouse. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab Off J Int Soc Cereb Blood Flow Metab 28:1707–1721
Dentesano G, Straccia M et al (2012) Inhibition of CD200R1 expression by C/EBP beta may constitute an effort to revascularize and oxygenate the tissue in reactive microglial cells. J Neuroinflamm 9:165
Dhabhar FS, Saul AN et al (2010) Short-term stress enhances cellular immunity and increases early resistance to squamous cell carcinoma. Brain Behav Immun 24:127–137
Dhungana H, Malm T et al (2013) Aging aggravates ischemic stroke-induced brain damage in mice with chronic peripheral infection. Aging cell doi. doi:10.1111/acel.12106
DiNapoli VA, Huber JD, Houser K, Li X, Rosen CL (2008) Early disruptions of the blood–brain barrier may contribute to exacerbated neuronal damage and prolonged functional recovery following stroke in aged rats. Neurobiol Aging 29:753–764
Ding G, Jiang Q, Li L, Zhang L, Zhang Z, Lu M, Li Q, Gu S, Ewing J, Chopp M (2011) Longitudinal magnetic resonance imaging of sildenafil treatment of embolic stroke in aged rats. Stroke 42:3537–3541
Dunn KM, Renic M, Flasch AK, Harder DR, Falck J, Roman RJ (2008) Elevated production of 20-HETE in the cerebral vasculature contributes to severity of ischemic stroke and oxidative stress in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 295:H2455–H2465
Farkas E, Obrenovitch TP, Institóris Á, Bari F (2011) Effects of early aging and cerebral hypoperfusion on spreading depression in rats. Neurobiol Aging 32:1707–1715
Feigin VL, Lawes CMM, Bennett DA, Anderson CS (2003) Stroke epidemiology: a review of populationbased studies of incidence, prevalence, and case-fatality in the late 20th century. Lancet Neurol 2:43–53
Florian B, Vintilescu R, Balseanu AT, Buga AM, Grisk O, Walker LC, Kessler C, Popa-Wagner A (2008) Long-term hypothermia reduces infarct volume in aged rats after focal ischemia. Neurosci Lett 438:180–185
Fumagalli S, Perego C et al (2013) CX3CR1 deficiency induces an early protective inflammatory environment in ischemic mice. Glia 61:827–842
Futrell N (1991) An improved photochemical model of embolic cerebral infarction in rats. Stroke 22:225
Fyhrquist F, Saijonmaa O et al (2013) The roles of senescence and telomere shortening in cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Cardiol 10:274–283
Giraldi-Guimaraes A, de Freitas HT et al (2012) Bone marrow mononuclear cells and mannose receptor expression in focal cortical ischemia. Brain Res 1452:173–184
Gokcay F, Arsava EM, Baykaner T, Vangel M, Garg P, Wu O, Singhal AB, Furie KL, Sorensen AG, Ay H (2011) Age-dependent susceptibility to infarct growth in women. Stroke 42:947–951
Harb R, Whiteus C, Freitas C, Grutzendler J (2013) In vivo imaging of cerebral microvascular plasticity from birth to death. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 33:146–156
Iadecola C, Anrather J (2011) The immunology of stroke: from mechanisms to translation. Nat Med 17:796–808
Ito J, Nikolaev AR, Leeuwen C (2005) Spatial and temporal structure of phase synchronization of spontaneous alpha EEG activity. Biol Cybern 92:54–60
James ML, Andersen ND, Swaminathan M, Phillips-Bute B, Hanna JM, Smigla GR, Barfield ME, Bhattacharya SD, Williams JB, Gaca JG, Husain AM, Hughes GC (2013) Predictors of electrocerebral inactivity with deep hypothermia. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 53(2):285–286. doi:10.1016/j.jtcvs.2013.03.022
Jiang Q, Thiffault C, Kramer C, Ding L, Zhang L, Nejad-Davarani S, Li L, Arbab A, Lu M, Navia B, Victor S, Hong K, Li JQ, Wang SY, Li Y, Chopp M (2012) MRI detects brain reorganization after human umbilicaltissue-derived cells (hUTC) treatment of stroke in rat. PLoS ONE 7(8):e42845
Joseph C, Buga AM, Vintilescu R, Balseanu AT, Moldovan M, Junker H, Walker L, Lotze M, Popa-Wagner A (2012) Prolonged gaseous hypothermia prevents the upregulation of phagocytosis-specific protein Annexin 1 and causes low-amplitude EEG activity in the aged rat brain after cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 32:1632–1642
Kierdorf K, Prinz M (2013) Factors regulating microglia activation. Frontiers Cell Neurosci 7:44
Kraemer M, Schormann T, Hagemann G, Qi B, Witte OW et al (2004) Delayed shrinkage of the brain after ischemic stroke: preliminary observations with voxel-guided morphometry. J Neuroimaging 14:265–272
Kumari S, Anderson L, Farmer S, Mehta SL, Li PA (2012) Hyperglycemia alters mitochondrial fission and fusion proteins in mice subjected to cerebral ischemia and reperfusion.Transl Stroke Res 3:296–304
Lee JC, Cho GS, Choi BO, Kim HC, Kim YS, Kim WK (2006) Intracerebral hemorrhage-induced brain injury is aggravated in senescence-accelerated prone mice. Stroke 37:216
Lindner MD, Gribkoff VK, Donlan NA, Jones TA (2003) Long-lasting functional disabilities in middle-aged rats with small cerebral infarcts. J Neurosci 23(34):10913–10922
Lloyd-Jones D, Adams RJ et al (2010) Executive summary: heart disease and stroke statistics–2010 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 121:948–954
Lynch AM, Murphy KJ et al (2010) The impact of glial activation in the aging brain.Aging Dis 1: 262–278
Macri MA, D’Alessandro N, Di GC, Di IP, Di LS, Giuliani P, Bianchi G, Esposito E (2006) Regional changes in the metabolite profile after long-term hypoxia-ischemia in brains of young and aged rats: a quantitative proton MRS study. Neurobiol Aging 27:98
Macri MA, D’Alessandro N, Di Giulio C, Di Iorio P, Di Luzio S, Giuliani P, Esposito E, Pokoski M (2010) Region-specific effects on brain metabolites of hypoxia and hyperoxia overlaid on cerebral ischemia in young and old rats: a quantitative proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. J Biomed Sci 17:14
Manwani B, Liu F, Xu Y, Persky R, Li J, McCullough L (2011) Functional recovery in aging mice after experimental stroke. Brain Behav Immun 25:1689–1700
Manzanero S, Gelderblom M, Magnus T, Arumugam T (2011) Calorie restriction and stroke. Exp Transl Stroke Med 3:8
Markus TM, Tsai SY, Bollnow MR, Farrer RG, O’Brien TE, Kindler-Baumann DR, Rausch M, Rudin M, Wiessner C, Mir AK, Schwab ME, Kartje GL (2005) Recovery and brain reorganization after stroke in adult and aged rats. Ann Neurol 58:950
Martín A, Rojas S, Chamorro A, Falcón C, Bargalló N, Planas AM (2006) Why does acute hyperglycemia worsen the outcome of transient focal cerebral ischemia? Role of corticosteroids, inflammation, and protein O-glycosylation. Stroke 37(5):1288–1295
Matsumoto H, Kumon Y et al (2007) Expression of CD200 by macrophage-like cells in ischemic core of rat brain after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. Neurosci Lett 418:44–48
McCabe C, Gallagher L, Gsell W, Graham D, Dominiczak AF, Macrae IM (2009) Differences in the evolution of the ischemic penumbra in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive and Wistar-Kyoto rats. Stroke 40(12):3864–388
McGuckin CP, Jurga M et al (2013) Ischemic brain injury: a consortium analysis of key factors involved in mesenchymal stem cell-mediated inflammatory reduction. Arch Biochem Biophys 534:88–97
Nenadovic V, Hutchison JS, Dominguez LG, Otsubo H, Gray MP, Sharma R, Belkas J, Velazquez JLP (2008) Fluctuations in cortical synchronization in pediatric traumatic brain injury. J Neurotraum 25:615–627
Neumann H (2001) Control of glial immune function by neurons. Glia 36(2):191–199
Pal G, Vincze C et al (2012) Time course, distribution and cell types of induction of transforming growth factor betas following middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat brain. PLoS ONE 7:e46731
Perry VH (2007) Stress primes microglia to the presence of systemic inflammation: implications for environmental influences on the brain. Brain Behav Immun 21:45–46
Piao CS, Gonzalez-Toledo ME, Gu X, Zhao LR (2012) The combination of stem cell factor and granulocyte-colony stimulating factor for chronic stroke treatment in aged animals. Exp Transl Stroke Med 24:25. doi:10.1186/2040-7378-4-25
Popa-Wagner A, Schröder E, Walker LC, Kessler C (1998) beta-Amyloid precursor protein and ss-amyloid peptide immunoreactivity in the rat brain after middle cerebral artery occlusion: effect of age. Stroke 29:2196–21202
Popa-Wagner A, Dinca I, Yalikun S, Walker L, Kroemer H, Kessler C (2006) Accelerated delimitation of the infarct zone by capillary-derived nestin-positive cells in aged rats. Curr Neurovasc Res 3:3–13
Popa-Wagner A, Badan I, Walker L, Groppa S, Patrana N, Kessler C (2007) Accelerated infarct development, cytogenesis and apoptosis following transient cerebral ischemia in aged rats. Acta Neuropathol 113:277–293
Popa-Wagner K, Stocker A, Balseanu A, Rogalewski A, Diederich K, Minnerup J, Margaritescu C, Schabitz W-R (2010) Effects of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor after stroke in aged rats. Stroke 41:1027–1031
Popa-Wagner A, Buga AM, Turner RC, Rosen CL, Toescu E (2012) Cerebrovascular disorders: role of aging. J Aging Res Editor 128–146
Porritt MJ, Chen M, Rewell SS, Dean RG, Burrell LM, Howells DW (2010) ACE inhibition reduces infarction in normotensive but not hypertensive rats: correlation with cortical ACE activity. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30:1520–1526
Ramos-Cabrer P, Justicia C, Wiedermann D, Hoehn M (2010) Stem cell mediation of functional recovery after stroke in the rat. PLoS ONE 5(9):e12779
Reid E, Graham D, Lopez-Gonzalez MR, Holmes WM, Macrae IM, McCabe C (2012) Penumbra detection using PWI/DWI mismatch MRI in a rat stroke model with and without comorbidity: comparison of methods. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 32:1765–1777
Rewell S, Fernandez J, Cox S, Spratt N, Hogan L, Aleksoska E, van Raay L, Liberatore G, Batchelor P, Howells D (2010) Inducing stroke in aged, hypertensive, diabetic rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30:729–733
Roger VL, Go AS et al (2011) Heart disease and stroke statistics–2011 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 123:e18–e209
Rosen CL, Dinapoli VA, Nagamine T, Crocco T (2005) Influence of age on stroke outcome following transient focal ischemia. J Neurosurg 103:687
Salminen A, Ojala J et al (2011) Astrocytes in the aging brain express characteristics of senescence-associated secretory phenotype. Eur J Neurosci 34:3–11
Savage CD, Lopez-Castejon G et al (2012) NLRP3-inflammasome activating DAMPs stimulate an inflammatory response in Glia in the absence of priming which contributes to brain inflammation after injury. Frontiers Immunol 3:288
Schmid-Elsaesser R, Hungerhuber E, Zausinger S, Baethmann A, Reulen H-J (1999) Combination drug therapy and mild hypothermia. A promising treatment strategy for reversible, focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke, 30:1891–1899
Seehafer JU, Kalthoff D, Farr TD, Wiedermann D, Hoehn M (2010) No increase of the blood oxygenation level-dependent functional magnetic resonance imaging signal with higher field strength: implications for brain activation studies. J Neurosci 30:5234–5241
Shrivastava K, Gonzalez P et al (2012) The immune inhibitory complex CD200/CD200R is developmentally regulated in the mouse brain. J Comp Neurol 520:2657–2675
Sleight P (2001) The role of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in the treatment of hypertension. Curr Cardiol Rep 3:511–518
Soejima Y, Hu Q, Krafft PR, Fujii M, Tang J, Zhang JH (2013) Hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning attenuates hyperglycemia-enhanced hemorrhagic transformation by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinases in focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Exp Neurol. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2013.03.019
Sorrells SF, Caso JR et al (2009) The stressed CNS: when glucocorticoids aggravate inflammation. Neuron 64:33–39
Sutherland GR, Dix GA, Auer RN (1996) Effect of age in rodent models of focal and forebrain ischemia. Stroke 27:1663–1668
Tacutu R, Budovsky A, Fraifeld VE (2010) The NetAge database: a compendium of networks for longevity, age-related diseases and associated processes. Biogerontology 11:513–522
Tacutu R, Budovsky A, Yanai H, Fraifeld VE (2011) Molecular links between cellular senescence, longevity and age-related diseases—a systems biology perspective (2011). Aging (Albany NY) 3:1178–1191
Tchkonia T, Zhu Y et al (2013) Cellular senescence and the senescent secretory phenotype: therapeutic opportunities. J Clin Investig 123:966–972
Trueman RC, Harrison DJ, Dwyer DM, Dunnett SB, Hoehn M, Farr TD (2011) A critical re-examination of the intraluminal Filament MCAO model: impact of external carotid artery transection. Transl Stroke Res 2:651–661
van Meer MPA, Otte WM, van der Marel K, Nijboer CH, Kavelaars A, van der Sprenkel JWB, Viergever MA, Dijkhuizen RM (2012) Extent of bilateral neuronal network resorganization and functional recovery in relation to stroke severity. J Neurosci 32:4495–4507
Walters RJ, Fox NC, Schott JM, Crum WR, Stevens JM et al (2003) Transient ischaemic attacks are associated with increased rates of global cerebral atrophy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74:213–216
Wang LC, Futrell N, Wang DZ, Chen FJ, Zhai QH, Schultz LR (1995) A reproducible model of middle cerebral infarcts, compatible with long-term survival, in aged rats. Stroke 26:2087
Wang R-Y, Wang Sh-G, Yang Y-R (2003) Effect of age in rats following middle cerebral artery occlusion. Gerontology 49:27–32
Wang XJ, Zhang S et al (2011) Impaired CD200-CD200R-mediated microglia silencing enhances midbrain dopaminergic neurodegeneration: roles of aging, superoxide, NADPH oxidase, and p38 MAPK. Free Radical Biol Med 50:1094–1106
Weidenfeld J, Leker RR et al (2011) The function of the adrenocortical axis in permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion: effect of glucocorticoids on the neurological outcome. Brain Res 1407:90–96
Willette AA, Bendlin BB, McLaren DG, Canu E, Kastman EK, Kosmatka KJ, Xu G, Field AS, Alexander AL, Colman RJ, Weindruch RH, Coe CL, Johnson SC (2010) Agerelated changes in neural volume and microstructure associated with interleukin-6 are ameliorated by a calorie-restricted diet in old rhesus monkeys. Neuroimage 51(3):987–994
Wolfson M, Budovsky A, Tacutu R, Fraifeld V (2009) The signaling hubs at the crossroad of longevity and age-related disease networks. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41:516–520
Won SJ, Xie L, Kim SH, Tang H, Wang Y, Mao X (2006) Influence of age on the response to fibroblast growth factor-2 treatment in a rat model of stroke. Brain Res 1123:237–244
Wu W, Sun J, Jin Z, Guo X, Qiu Y, Zhu Y, Tong S (2011) Impaired neuronal synchrony after focal ischemic stroke in elderly patients. Clin Neurophysiol 122:21–26
Yusuf S (2000) After the HOPE Study. ACE inhibitor now for every diabetic patient? MMW Fortschr Med 142:10
Zhang L, Zhang RL, Wang Y, Zhang C, Zhang ZG, Meng H, Chopp M (2005) Functional recovery in aged and young rats after embolic stroke: treatment with a phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor. Stroke 36:847–852
Zhang X, Zhang G, Zhang H, Karin M, Bai H, Cai D (2008) Hypothalamic IKKbeta/NF-kappaB and ER stress link overnutrition to energy imbalance and obesity. Cell 135:61–73
Zhao CS, Puurunen K, Schallert T, Sivenius J, Jolkkonen J (2005) Effect of cholinergic medication, before and after focal photothrombotic ischemic cortical injury, on histological and functional outcome in aged and young adult rats. Behav Brain Res 156:85
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by UEFISCDI, PN-II-PT-PCCA-2011-3, Grant no 80/2012 to APW and UEFISCDI FLARE2 to AMB.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buga, AM., Di Napoli, M. & Popa-Wagner, A. Preclinical models of stroke in aged animals with or without comorbidities: role of neuroinflammation. Biogerontology 14, 651–662 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-013-9465-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-013-9465-0