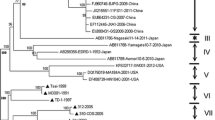
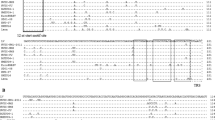
Thirteen isolates of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) from different provinces of China were studied and compared with several PRRSV isolates from other countries. Phylogenetic analysis shows that all Chinese isolates of PRRSV in this study belong to the American genotype, except for one strain, B13, which clustered as a European genotype. Sequence analysis revealed that PRRSV Chinese isolates of the American genotype were highly similar in the ORF5 sequence and could be classified into two subclades. One contains PRRSV isolates that are more closely related to the American vaccine strain MLV Resp and its parent strain VR-2332, and the other contains ones only distantly related to them. Within the Chinese isolates slight genetic variation occurred, and some strains may originate directly from the vaccine virus.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Albina, E., (1997). Epidemiology of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS): An overview. Vet. Microbiol. 55:309–316.
Allende, R., Lewis, T. L., Lu, Z., Rock, D. L., Kutish, G. F., Ali, A., Doster, A. R., and Osorio, F. A. (1999). North American and European porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome viruses differ in non-structural protein coding regions. J. Gen. Virol. 80:307–315.
Allende, R., Kutish, G. F., Laegreid, W., Lu, Z., Lewis, T. L., Rock, D. L., Friesen, J., Galeota, J. A., Doster, A. R., and Osorio, F. A. (2000). Mutations in the genome of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus responsible for the attenuation phenotype. Arch. Virol. 145:1149–1161.
Andreyev, V. G., Wesley, R. D., Mengeling, W. L., Vorwald, A. C., and Lager, K. M. (1997). Genetic variation and phylogenetic relationships of 22 porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) field strains based on sequence analysis of open reading frame 5. Arch. Virol. 142:993–1001.
Cavanagh, D. (1997). Nidovirales: A new order comprising Coronaviridae and Arteriviridae. Arch. Virol. 142:629–633.
Cheon, D. S., and Chae, C. (2000). Restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of open reading frame 5 gene of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus isolates in Korea. Arch. Virol. 145:1481–1488.
Forsberg, R., Storgaard, T., Nielsen, H. S., Oleksiewicz, M. B., Cordioli, P., Sala, G., Hein, J., and Botner, A. (2002). The genetic diversity of European type PRRSV is similar to that of the North American type but is geographically skewed within Europe. Virology 299:38–47.
Gao, Z. Q., Guo, X., and Yang, H. C., (2004). Genomic characterization of two Chinese isolates of porcine respiratory and reproductive syndrome virus. Arch. Virol. 149:1341–1351.
Goldberg, T. L., Hahn, E. C., Weigel, R. M., and Scherba, G. (2000). Genetic, geographical, and temporal variation of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in Illinois. J. Gen. Virol. 81:171–179.
Kang, S. Y., Yun, S. I., Park, H. S., Park, C. K., Choi, H. S., and Lee, Y. M. (2004). Molecular characterization of PL97-1, the first Korean isolate of the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Virus. Res. 104:165–179.
Kapur, V., Elam, M. R., Pawlovich, T. M., and Murtaugh, M. P. (1996). Genetic variation in porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus isolates in the midwestern United States. J. Gen. Virol. 77:1271–1276.
Keffaber, K. K. (1989). Reproductive failure of unknown etiology. Am. Assoc. Swine Pract. Newslett. 1:1–9.
Key, K. F., Haqshenas, G., Guenette, D. K., Swenson, S. L., Toth, T. E., and Meng, X. J. (2001). Genetic variation and phylogenetic analyses of the ORF5 gene of acute porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus isolates. Vet. Microbiol. 83:249–263.
Kumar, S., Tamura, K., Jakobsen, I. B., and Nei, M. (2001). MEGA2: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis software. Bioinformatics 17:1244–1245.
Larochelle, R., D'Allaire, S., Magar, R. (2003). Molecular epidemiology of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) in Québec. Virus Res. 96:3–14.
Meng, X. J. (2000). Heterogeneity of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus: Implications for current vaccine efficacy and future vaccine development. Vet. Microbiol. 74:309–329.
Meng, X. J., Paul, P. S., Halbur, P. G., and Lum, M. A. (1995). Phylogenetic analyses of the putative M (ORF 6) and N (ORF 7) genes of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV): Implication for the existence of two genotypes of PRRSV in the U.S.A. and Europe. Arch. Virol. 140:745–755.
Meulenberg, J. J., Hulst, M. M., de Meijer, E. J., Moonen, P.L., den Besten, A., de Kluyver, E. P., Wensvoort, G., and Moormann, R. J. (1993). Lelystad virus, the causative agent of porcine epidemic abortion and respiratory syndrome (PEARS), is related to LDV and EAV. Virology 192:62–72.
Murtaugh, M. P., Elam, M. R., and Kakach, L. T. (1995). Comparison of the structural protein coding sequences of the VR-2332 and Lelystad virus strains of the PRRS virus. Arch. Virol. 140:1451–1460.
Oleksiewicz, M. B., Botner, A., Nielsen, J., and Storgaard, T. (1999). Determination of 5′-leader sequences from radically disparate strains of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus reveals the presence of highly conserved sequence motifs. Arch. Virol. 144:981–987.
Paton, D. J., Brown, I. H., Edwards, S., and Wensvoort, G., (1991). Blue ear disease of pigs. Vet. Rec. 128:617.
Suarez, P., Zardoya, R., Martin, M. J., Prieto, C., Dopazo, J., Solana, A., and Castro, J. M. (1996). Phylogenetic relationships of European strains of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) inferred from DNA sequences of putative ORF-5 and ORF-7 genes. Virus Res. 42:159–165.
Thanawongnuwech, R., Amonsin, A., Tatsanakit, A., and Damrongwatanapokin, S. (2004). Genetics and geographical variation of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) in Thailand. Vet. Microbiol. 101:9–21.
Thompson, J. D., Gibson, T. J., Plewniak, F., Jeanmougin, F., and Higgins, D. G. (1997). The ClustalX windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 24:4876–4882.
Wootton, S., Yoo, D., and Rogan, D. (2000). Full-length sequence of a Canadian porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) isolate. Arch. Virol. 145:2297–2323.
Yang, H. C., Huang, F. F., Guo, X., Gao, Y., Li, H., and Chen, S., (2001). Sequencing of genome of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus isolate BJ-4. J. Agric. Biotechnol. 9:212–218.
Yoshii, M., Kaku, Y., Murakami, Y., Shimizu, M., Kato, K., and Ikeda, H. (2004). Polymerase chain reaction-based genetic typing of Japanese porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. J. Vet. Diagnos. Invest. 16:342–347.
Yoshii, M., Kaku, Y., Murakami, Y., Shimizu, M., Kato, K., and Ikeda, H. (2005). Genetic variation and geographic distribution of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in Japan. Arch. Virol. 150:2313–2324.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by a grant from Zhejiang Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 398492).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Liu, T., Zhu, CG. et al. Genetic Variation of Chinese PRRSV Strains Based on ORF5 Sequence. Biochem Genet 44, 421–431 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-006-9039-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-006-9039-9