Abstract
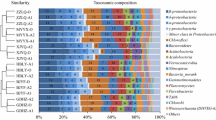
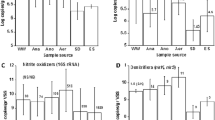
This study aimed to explore the microbial community variation and treatment ability of a full-scale anoxic–aerobic–anoxic–aerobic (AOAO) process used for optoelectronic wastewater treatment. The sludge samples in the biological treatment units were collected and subsequently subjected to polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis identification and the wastewater components such as BOD5 and NH3–N were evaluated during the processes. The group specific primers selected were targeting at the kingdom Bacteria, the Acidobacterium, the α-proteobacteria, the β-proteobacteria ammonia oxidizers, Actinobacteria and methyllotrophs, and the 16S rDNA clone libraries were established. Ten different clones were obtained using the Bacteria primers and eight different clones were obtained using the β-proteobacteria ammonia oxidizer primers. Over 95 % of BOD5 and 90 % of NH3–N were removed from the system. The microbial community analysis showed that the Janthinobacterium sp. An8 and Nitrosospira sp. were the dominant species throughout the AOAO process. Across the whole clone library, six clones showed closely related to Janthinobacterium sp. and these species seemed to be the dominant species with more than 50 % occupancy of the total population. Nitrosospira sp. was the predominant species within the β-proteobacteria and occupied more than 30 % of the total population in the system. These two strains were the novel species specific to the AOAO process for optoelectronic treatment, and they were found strongly related to the system capability of removing aquatic contaminants by inspecting the wastewater concentration variation across the system.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abulencia CB, Wyborski DL, Garcia JA, Podar M, Chen W, Chang SH, Chang HW, Watson D, Brodie EL, Hazen TC, Keller M (2006) Environmental whole-genome amplification to access microbial populations in contaminated sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:3291–3301
Amann RI, Ludwig W, Schleifer KH (1995) Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation. Microbiol Rev 59:143–169
Andrew EC, Meyers PR (2003) Rapid identification of filamentous actinomycetes to the genus level using genus-specific 16S rRNA gene restriction fragment patterns. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:1907–1915
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American Water Works Association, Greenberg
Barbara T, Wonerow K, Paschke K (1999) DGGE is more sensitive for the detection of somatic point mutations than direct sequencing. Biotechniques 27:266–268
Barns SM, Takala SL, Kuske CR (1999) Wide distribution and diversity of members of the bacterial kingdom Acidobacterium in the environment. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:1731–1737
Boon N, De Windt W, Verstraete W, Top EM (2001) Evaluation of nested PCR–DGGE (denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis) with group-specific 16S rRNA primers for the analysis of bacterial communities from different wastewater treatment plants. Fed Eur Microbiol Soc Microbiol Ecol 39:101–112
Breaker RR (2012) New insight on the response of bacteria to fluoride. Caries Res 46:78–81
Calheiros CSC, Duque AF, Moura A, Henriques IS, Correia A, Rangel AOSS, Castro PML (2009) Changes in the bacterial community structure in two-stage constructed wetlands with different plants for industrial wastewater treatment. Bioresour Technol 100:3228–3235
Calheiros CSC, Teixeira A, Pires C, Franco AR, Duque AF, Crispim LFC, Moura SC, Castro PML (2010) Bacterial community dynamics in horizontal flow constructed wetlands with different plants for high salinity industrial wastewater polishing. Water Res 44:5032–5038
Carr LM (1954) A toxic effect of fluoride. Nature 174:884–885
Chen RB (2001) Application of molecular techniques for biological processes of bacteria phase analysis. Master thesis, Institute of Environmental Engineering, National Central University, Chungli, Taiwan
Chen TK, Chen JN, Ni CH, Lin GT, Chang CY (2003) Application of a membrane bioreactor system for opto-electronic industrial wastewater treatment—a pilot study. Water Sci Technol 48:195–202
Chen HJ, Tseng DH, Huang SL (2005) Biodegradation of octylphenol polyethoxylate surfactant Triton X-100 by selected microorganisms. Bioresour Technol 96:1483–1491
Dunfield KE, King GM (2004) Molecular analysis of carbon monoxide-oxidizing bacteria associated with recent Hawaiian volcanic deposits. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:4242–4248
Ekaterina KG, Warmade W, Liu JC (2010) Removal of phosphate and fluoride from optoelectronic wastewater by calcite. Int J Environ Technol Manage 12:308–321
Eker S, Kargi F (2010) COD para-chlorophenol and toxicity removal from synthetic wastewater using rotating tubes biofilm reactor (RTBR). Bioresour Technol 101:9020–9024
Ferris MJ, Ward DM (1997) Seasonal distributions of dominant 16S rRNA-defined populations in a hot spring microbial mat examined by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:1375–1381
Fields MW, Carroll SL, Rhee SK, Bergman K, Yan T, Zhou J (2011) Impacts on microbial communities and cultivable isolates from groundwater contaminated with high levels of nitric acid-bearing uranium waste at the NABIR-FRC. NCBI GenBank. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=Nucleotide&list_uids=50830452&dopt=GenBank
Fuchs W, Binder H, Mavrias G, Braun R (2003) Anaerobic treatment of wastewater with high organic content using a stirred tank reactor coupled with a membrane filtration unit. Water Res 37:902–908
Gomes NCM, Heuer H, Schönfeld J, Costa R, Hagler-Mendonca L, Smalla K (2001) Bacterial diversity of the Rhizosphere of Maize (Zea Mays) grown in tropical soil studied by temperature gradient gel electrophoresis. Plant Soil 232:167–180
Heuer H, Krsek M, Baker P, Smalla K, Wellington EH (1997) Analysis of actinomycete communities by specific amplification of genes encoding 16S rRNA and gel-electrophoretic separation in denaturing gradients. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3233–3241
Hill TJ, Walsh KA, Harris JA, Moffett BF (2003) Using ecological diversity measures with bacterial communities. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 43:1–11
Holt JG, Kreig NR, Sneath PHA, Stanely JT, Williams ST (1994) Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology. Williams and Wilkins Publishers, Maryland
Juretschko S, Loy A, Lehner A, Wagner M (2002) The microbial community composition of a nitrifying-denitrifying activated sludge from an industrial sewage treatment plant analyzed by the full-cycle rDNA approach. Syst Appl Microbiol 25:84–99
Kalyuzhnaya MG, Hristova KR, Lidstrom ME, Chistoserdova L (2008) Characterization of a novel methanol dehydrogenase in representatives of Burkholderiales: implications for environmental detection of methylotrophy and evidence for convergent evolution. J Bacteriol 190:3817–3823
Kim YM, Lee DS, Park C, Park D, Park JM (2011) Effects of free cyanide on microbial communities and biological carbon and nitrogen removal performance in the industrial activated sludge process. Water Res 45:1267–1279
Kowalchuk GA, Stephen JR (2001) Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria: a model for molecular microbial ecology. Annu Rev Microbiol 55:485–529
Kowalchuk GA, Stephen JR, De Boer W, Prosser JI, Embley TM, Woldendorp JW (1997) Analysis of β-proteobacteria ammonia-oxidising bacteria in coastal sand dunes using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and sequencing of PCR amplified 16S rDNA fragments. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:1489–1497
Kubo M, Hiroe J, Murakami M, Fukami H, Tachiki T (2001) Treatment of hypersaline-containing wastewater with salt tolerant microorganisms. J Biosci Bioeng 91:222–228
Kusumoto S, Takikawa Y, Kijima T (2011) Occurrence of bacterial spot of strawberry by herbaspirillum sp. NCBI GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=Nucleotide&list_uids=67906138&dopt=GenBank. Accessed 20, Feb 2011
LaPara TM, Nakatsu CH, Pantea LM, Alleman JE (2001) Aerobic biological treatment of a pharmaceutical wastewater: effect of temperature on COD removal and bacterial community development. Water Res 35:4417–4425
LaPara TM, Nakatsu CH, Panteac LM, Alleman JE (2002) Stability of the bacterial communities supported by a seven-stage biological process treating pharmaceutical wastewater as revealed by PCR-DGGE. Water Res 36:638–646
Lei G, Ren H, Ding L, Wang F, Zhang X (2010) A full-scale biological treatment system application in the treated wastewater of pharmaceutical industrial park. Bioresour Technol 101:5852–5861
Lin CY (2004) 16S rDNA molecular techniques to investigate the membrane bioreactor for treating ABS wastewater nitrification-like state. Master thesis, Department of Environmental Engineering and Science, China Nan University of Pharmacy and Science, Tainan, Taiwan
Liu WT, Marsh TL, Cheng H, Forney LJ (1997) Characterization of microbial diversity by determining terminal restriction fragment length polymorphisms of genes encoding 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4516–4522
Ludwig W (1997) Detection and in situ identification of representatives of a widely distributed new bacterial phylum. FEMS Microbiol Lett 153:181–190
Muyzer G, De Waal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:695–700
Nubel U, Garcia-Pichel F, Muyzer G (1997) PCR primers to amplify 16S rRNA genes from cyanobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3327–3332
OITDA (2007) Future Vision of the Optoelectronics Industry: toward further growth by evolutionary technologies and progressive developments in an advancing borderless society. Optoelectronic Industry and Technology Development Association, Tokyo
Øvreås L (2000) Population and community level approaches for analysing microbial diversity in natural environments. Ecol Lett 3:236–251
Phillips CJ, Harris D, Dollhopf SL, Gross KL, Prosser JI, Paul EA (2000) Effects of agronomic treatments on structure and function of ammonia-oxidizing communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:5410–5418
Rittmann BE, McCarty PL (2001) Environmental biotechnology: principles and applications, 1st edn. McGraw-Hill Higher Education, New York
Schmidt HA, Strimmer K, Vingron M, Haeseler A (2002) TREE-PUZZLE: maximum likelihood phylogenetic analysis using quartets and parallel computing. Bioinformatics 18:502–504
Tchobanoglous G, Burton F, Stensel HD (2004) Wastewater engineering, treatment and reuse, 4th edn. Metcalf & Eddy Inc, New York
Tsien HC, Bratina BJ, Tsuji K, Hanson RS (1990) Use of oligodeoxynucleotide signature probes for identification of physiological groups of methylotrophic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:2858–2865
Vallaeys T, Topp E, Muyzer G, Macheret V, Laguerre G, Rigaud A, Soulas G (1997) Evaluation of denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis in the detection of 16S Rdna sequence variation in rhizobia and methanotrophs. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 24:279–285
Yan T, Te Q, Zhou J, Zhang C (2006) Diversity of functional genes for methanotrophs in sediments associated with gas hydrates and hydrocarbon seeps in the Gulf of Mexico. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 57:251–259
You SJ, Chen WY (2008) Ammonia oxidizing bacteria in a nitrite-accumulating membrane bioreactor. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 62:244–249
Zak LJ, Patterson J, Hancock J (2010) Benefits of synchronizing ovulation with porcine luteinizing hormone in a fixed-time insemination protocol in weaned multiparous sows. J Swine Health Prod 18:125–131
Zhou YZ (2002) Multi-stream to nitrogen and phosphorus into the system dynamic stability characteristics of treatment and control. Ph.D. dissertation, Institute of Environmental Engineering, National Central University, Chungli
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, HJ., Lin, YZ., Fanjiang, JM. et al. Microbial community and treatment ability investigation in AOAO process for the optoelectronic wastewater treatment using PCR-DGGE biotechnology. Biodegradation 24, 227–243 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-012-9579-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-012-9579-0