Abstract
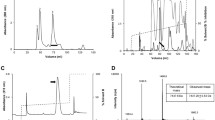
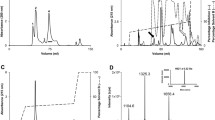
It has been recently demonstrated that the hemotoxic venom activity of several species of snakes can be inhibited by carbon monoxide (CO) or a metheme forming agent. These and other data suggest that the biometal, heme, may be attached to venom enzymes and may be modulated by CO. A novel fibrinogenolytic metalloproteinase, named CatroxMP-II, was isolated and purified from the venom of a Crotalus atrox viper, and subjected to proteolysis and mass spectroscopy. An ion similar to the predicted singly charged m/z of heme at 617.18 was identified. Lastly, CORM-2 (tricarbonyldichlororuthenium (II) dimer, a CO releasing molecule) inhibited the fibrinogenolytic effects of CatroxMP-II on coagulation kinetics in human plasma. In conclusion, we present the first example of a snake venom metalloproteinase that is heme-bound and CO-inhibited.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jaggar JH, Li A, Parfenova H, Liu J, Umstot ES, Dopico AM, Leffler CW (2005) Heme is a carbon monoxide receptor for large-conductance Ca2 + -activated K + channels. Circ Res 97:805–812
Ling K, Men F, Wang WC, Zhou YQ, Zhang HW, Ye DW (2017) Carbon monoxide and its controlled release: therapeutic application, detection, and development of carbon monoxide releasing molecules (CORMs). J Med Chem. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b01153
Motterlini R, Otterbein LE (2010) The therapeutic potential of carbon monoxide. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9:728–743
Nielsen VG (2018) Crotalus atrox venom exposed to carbon monoxide has decreased fibrinogenolytic activity in vivo in rabbits. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 122:82–86
Nielsen VG, Bazzell CM (2016) Carbon monoxide attenuates the effects of snake venoms containing metalloproteinases with fibrinogenase or thrombin-like activity on plasmatic coagulation. MedChemComm 7:1973–1979
Nielsen VG, Bazzell CM (2017) Carbon monoxide releasing molecule-2 inhibition of snake venom thrombin-like activity: novel biochemical “brake”? J Thromb Thrombolysis 43:203–208
Nielsen VG, Losada PA (2017) Direct inhibitory effects of carbon monoxide on six venoms containing fibrinogenolytic metalloproteinases. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 120:207–212
Nielsen VG, Matika RW (2017) Effects of iron and carbon monoxide on Lachesis muta muta venom-mediated degradation of plasmatic coagulation. Hum Exp Toxicol 36:727–733
Nielsen VG, Arkebauer MR, Vosseller K (2011a) Redox-based thrombelastographic method to detect carboxyhemefibrinogen-mediated hypercoagulability. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 22:657–661
Nielsen VG, Cohen JB, Malayaman SN, Nowak M, Vosseller K (2011b) Fibrinogen is a heme-associated, carbon monoxide sensing molecule: a preliminary report. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 22:443–447
Nielsen VG, Cerruti MA, Valencia OM, Amos Q (2016) Decreased snake venom metalloproteinase effects via inhibition of enzyme and modification of fibrinogen. Biometals 29:913–919
Nielsen VG, Frank N, Matika RW (2018a) Carbon monoxide inhibits hemotoxic activity of Elapidae venoms: potential role of heme. Biometals 31:51–59
Nielsen VG, Sánchez EE, Redford DT (2018b) Characterization of the rabbit as an in vitro and in vivo model to assess the effects of fibrinogenolytic activity of snake venom on coagulation. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 122:157–164
Raske M, Lewbart GA, Dombrowski DS, Hale P, Correa M, Christian LS (2012) Body temperatures of selected amphibian and reptile species. J Zoo Wildl Med 43:517–521
Refinetti R (1996) Comparison of the body temperature rhythms of diurnal and nocturnal rodents. J Exp Zool 275:67–70
Saffran WA, Gibson QH (1979) The effect of temperature on carbon monoxide binding to a root effect hemoglobin. J Biol Chem 254:1666–1670
Wills CA, Beaupre SJ (2000) An application of randomization for detecting evidence of thermoregulation in timber rattlesnakes (Crotalus horridus) from northwest Arkansas. Physiol Biochem Zool 73:325–334
Funding
Funding for this project was provided by the NIH/ORIP, Viper Resource Grant 5P40OD010960-14 (NNTRC, Texas A&M University-Kingsville, Dr. E.E. Sánchez) and NIH/NHLBI Grant# 1R15HL137134-01 (Dr. M. Suntravat). Additional support was provided by the Robert A. Welch Foundation Department Grant, Grant number AC-0006 (TAMUK-Department of Chemistry). We would also like to thank, Nora Diaz DeLeon and Mark Hockmüller (NNTRC Serpentarium curator) and all the NNTRC personnel. This investigation was also supported by the Departments of Medicine and Anesthesiology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suntravat, M., Langlais, P.R., Sánchez, E.E. et al. CatroxMP-II: a heme-modulated fibrinogenolytic metalloproteinase isolated from Crotalus atrox venom. Biometals 31, 585–593 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-018-0107-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-018-0107-5