Abstract
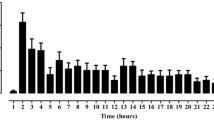
Nausea and vomiting are the most common symptoms in different diseases. Medicinal plants are considered as a reliable source of new drugs to control these symptoms. In this study, we evaluated the antiemetic and neuroprotective effects of the methanolic extract of Sambucus ebulus L. fruit and relationship between emesis (retching) and oxidative stress biomarkers in the mitochondria brain of young chickens. Emesis was induced by ipecac and copper sulphate (60 and 600 mg/kg, orally), respectively, and the methanolic extracts (50, 100, 200 mg/kg) were injected intraperitoneally (i.p.). The extract showed a significant antiemetic activity against ipecac and copper sulphate-induced emesis at all doses (p < 0.001; percentages of retching inhibition 46, 96.5 and 83 % against ipecac and 73, 79.5 and 69.2 % against copper sulphate, respectively). Lipid peroxidation (LPO) was significantly decreased (p < 0.001) at all doses of extract in retching induced by copper sulphate, and catalase (CAT) activity significantly increased (p < 0.05) in the extract (50 mg/kg) and metoclopromide groups in retching induced by ipecac in the chickens’ brain mitochondria. Protein carbonyl (PC) contents significantly (p < 0.05) decreased only in extract (100 mg/kg) group in retching induced by ipecac. Mitochondria function (MTT assay) significantly increased by extract (100 mg/kg) as compared to control group in retching induced by ipecac. The results of this study suggests that the extract has protective effects, possibly by central and peripheral mechanisms, and neuroprotective effect by increasing plasma antioxidants or scavenging of free radicals induced by retching. It seems that extract could prevent protein modification and improve oxidative stress in the early stages.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdala S, Dévora S, Martín-Herrera D, Pérez-Paz P. Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activity of Sambucus palmensis link, an endemic Canary Island species. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;155:626–32.
Abei H. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1984;105:121–6.
Ahmadiani A, Fereidoni M, Semnanian S, Kamalinejad M, Saremi S. Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects of Sambucus ebulus rhizome extract in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 1998;61:229–35.
Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–54.
Chashoo, I., Kumar, D., Bhat, Z., Khan, N., Kumar, V. & Nowshehri, J. A. 2012. Antimicrobial studies of Sambucus wightiana Wall. ex. Wight & Arn. J Pharm Res, 5.
Citores L, DE Benito FM, Iglesias R, Ferreras JM, Argüeso P, Jiménez P, et al. Presence of polymerized and free forms of the non-toxic type 2 ribosome-inactivating protein ebulin and a structurally related new homodimeric lectin in fruit of Sambucus ebulus L. Planta. 1998;204:310–7.
Darias V, Bravo L, Barquin E, Herrera DM, Fraile C. Contribution to the ethnopharmacological study of the Canary islands. J Ethnopharmacol. 1986;15:169–93.
de Benito FM, Citores L, Iglesias R, Ferreras JM, Soriano F, Arias J, et al. Ebulitins: a new family of type 1 ribosome-inactivating proteins (rRNA N-glycosidases) from leaves of Sambucus ebulus L. that coexist with the type 2 ribosome-inactivating protein ebulin 1. FEBS Lett. 1995;360:299–302.
Dubey P, Jayasooriya AP, Cheema SK. Fish oil induced hyperlipidemia and oxidative stress in BioF1B hamsters is attenuated by elderberry extract. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2012;37:472–9.
Ebrahimzadeh MA, Mahmoudi M, Karami M, Saeedi S, Ahmadi AH, Salimi E. Separation of active and toxic portions in Sambucus ebulus. Pak J Biol Sci. 2007;10:4171–3.
Ebrahimzadeh M, Nabavi S, Nabavi S. Antioxidant activities of methanol extract of Sambucus ebulus L. flower. Pak J Biol Sci. 2009a;12:447.
Ebrahimzadeh MA, Ehsanifar S, Eslami B. Sambucus ebulus elburensis fruit: a good source for antioxidants. Pharmacogn Mag. 2009b;4:213–8.
Ertuğ F. An ethnobotanical study in central Anatolia (Turkey). Econ Bot. 2000;54:155–82.
Gentile C, Tesoriere L, Butera D, Fazzari M, Monastero M, Allegra M, et al. Antioxidant activity of Sicilian pistachio (Pistacia vera L. var. Bronte) nut extract and its bioactive components. J Agric Food Chem. 2007;55:643–8.
Ghannadi A, Ghassemi-Dehkordi N. Pharmacognostical investigations on Sambucus ebulus L. and Sambucus nigra L. DARU J Pharm Sci. 1997;7:55–65.
Ghazi-Khansari M, Mohammadi-Bardbori A, Hosseini MJ. Using Janus green B to study paraquat toxicity in rat liver mitochondria. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006;1090:98–107.
Hosseini M-J, Shaki F, Ghazi-Khansari M, Pourahmad J. Toxicity of vanadium on isolated rat liver mitochondria: a new mechanistic approach. Metallomics. 2013;5:152–66.
Hosseinzadeh H, Mirshojaeian M, Razavi BM. Antiemetic effect of Pistacia vera L. (pistachio) leaves and nuts aqueous extracts in young chicken. Pharmacol Online. 2008;2:568–71.
Jiménez P, Tejero J, Cordoba-Diaz D, Quinto EJ, Garrosa M, Gayoso MJ, et al. Ebulin from dwarf elder (Sambucus ebulus L.): a mini review. Toxins. 2015;7:648–58.
Kadiiska M, Gladen B, Baird D, Germolec D, Graham L, Parker C, et al. Biomarkers of oxidative stress study II: are oxidation products of lipids, proteins, and DNA markers of CCl4 poisoning? Free Radic Biol Med. 2005;38:698–710.
Kültür Ş. Medicinal plants used in Kırklareli Province (Turkey). J Ethnopharmacol. 2007;111:341–64.
Levine RL, Garland D, Oliver CN, Amici A, Climent I, Lenz A-G, et al. Determination of carbonyl content in oxidatively modified proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1990;186:464–78.
Pederzolli CD, Mescka CP, Zandoná BR, De Moura Coelho D, Sgaravatti ÂM, Sgarbi MB, et al. Acute administration of 5-oxoproline induces oxidative damage to lipids and proteins and impairs antioxidant defenses in cerebral cortex and cerebellum of young rats. Metab Brain Dis. 2010;25:145–54.
Rahimi-Esboei B, Ebrahimzadeh M, Gholami S, Falah-Omrani V. Anti-giardial activity of Sambucus ebulus. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013;17:2047–50.
Richelle M, Tavazzi I, Offord E. Comparison of the antioxidant activity of commonly consumed polyphenolic beverages (coffee, cocoa, and tea) prepared per cup serving. J Agric Food Chem. 2001;49:3438–42.
Saeedi Saravi SS, Shokrzadeh M. Histopathological and biochemical disorders following administration of Sambucus ebulus extract on mice and rats and preventive effects of vitamins C and E on renal and hepatic disorders. Pharmacogn Mag. 2009;5:131–5.
Shahraki J, Zareh M, Kamalinejad M, Pourahmad J. Cytoprotective effects of hydrophilic and lipophilic extracts of Pistacia vera against oxidative versus carbonyl stress in rat hepatocytes. Iran J Pharm Res. 2014;13:1263.
Tuzlaci E, Tolon E. Turkish folk medicinal plants, part III: Sile (Istanbul). Fitoterapia. 2000;71:673–85.
Wang Q, Kuang H, SU Y, Sun Y, Feng J, Guo R, et al. Naturally derived anti-inflammatory compounds from Chinese medicinal plants. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013;146:9–39.
Yang Y, Kinoshita K, Koyama K, Takahashi K, Tai T, Nunoura Y, et al. Novel experimental model using free radical-induced emesis for surveying anti-emetic compounds from natural sources. Planta Med. 1999;65:574–6.
Yeşilada E, Gürbüz IL, Shibata H. Screening of Turkish anti-ulcerogenic folk remedies for anti-Helicobacter pylori activity. J Ethnopharmacol. 1999;66:289–93.
Zhang F, Xu Z, Gao J, Xu B, Deng Y. In vitro effect of manganese chloride exposure on energy metabolism and oxidative damage of mitochondria isolated from rat brain. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2008;26:232–6.
Acknowledgments
Financial support for this work was provided by Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, Sari, Iran with reference number 1155.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fathi, H., Ebrahimzadeh, M.A., Ziar, A. et al. Oxidative damage induced by retching; antiemetic and neuroprotective role of Sambucus ebulus L.. Cell Biol Toxicol 31, 231–239 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-015-9307-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-015-9307-8