Summary
-
1.
Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) is a rapidly progressive and fatal disease. Patients with CJD usually become akinetic mutism within approximately 6 months. In addition, clinical signs and symptoms at early stage of sporadic CJD may not be easy to distinguish from other neurodegenerative diseases by neurological findings. However, diagnostic biochemical parameters including 14-3-3 protein, S100, neuron-specific enorase in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) have been used as diagnostic markers, elevated titers of these markers can also be observed in CSF in other neurodegenerative diseases. Therefore, we examined other biochemical markers to discriminate CJD from other neurodegenerative diseases in CSF.
-
2.
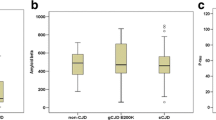
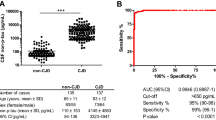
We analyzed CSF samples derived from 100 patients with various neurodegenerative disorders by Western blot of 14-3-3 protein, quantification of total tau (t-tau) protein, and phosphorylated tau (p-tau) protein. All patients with CJD in this study showed positive 14-3-3 protein and elevated t-tau protein (>1000 pg/mL) in CSF. We also detected positive 14-3-3 protein bands in two patients in non-CJD group (patients with dementia of Alzheimer's type; DAT) and also detected elevated t-tau protein in three patients in non-CJD group. Elevated t-tau protein levels were observed in two patients with DAT and in one patient with cerevrovascular disease in acute phase.
-
3.
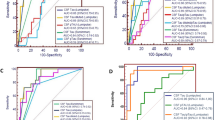
To distinguish patients with CJD from non-CJD patients with elevated t-tau protein in CSF, we compared the ratio of p-tau and t-tau proteins. The p-/t-tau ratio was dramatically and significantly higher in DAT patients rather than in CJD patients.
-
4.
Therefore, we concluded that the assay of t-tau protein may be useful as 1st screening and the ratio of p-tau protein/t-tau protein would be useful as 2nd screening to discriminate CJD from other neurodegenerative diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Demerosl, P., and Heiner, L., et al. (1999). Diffusion-weighted MRI in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurology 52(1):205–208.
Hsich, G., and Kenney, K., et al. (1996). The 14-3-3 brain protein in cerebrospinal fluid as a marker for transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. N. Engl. J. Med. 335(13):924–930.
Masters, C. L., Harris, J. O., Gajdusek, D. C., Gibbs, C. J., Jr., Bernoulli, C., and Asher, D. M.(1979). Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: Patterns of worldwide occurrence and the significance of familial and sporadic clustering. Ann. Neurol. 5(2):177–188.
Otto, M., and Wiltfang, J., et al. (2002). Tau protein and 14-3-3 protein in the differential diagnosis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurology 58(2):192–197.
Parchi, P., Giese, A., Capellari, S., Brown, P., Schulz-Schaeffer, W., Windl, O., Zerr, I., Budka, H., Kopp, N., Piccardo, P., Poser, S., Rojiani, A., Streichemberger, N., Julien, J., Vital, C., Ghetti, B., Gambetti, P., and Kretzschmar, H. (1999). Classification of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease based on molecular and phenotypic analysis of 300 subjects. Ann. Neurol. 46(2):224–233.
Van Everbroeck, B., Quoilin, S., Boons, J., Martin, J. J., and Cras, P. (2003). A prospective study of CSF markers in 250 patients with possible Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 74(9):1210–1214.
Zerr, I., Bodemer, M., and Gefeller, O., et al. (1998). Detection of 14-3-3 protein in the cerebrospinal fluid supports the diagnosis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Ann. Neurol. 43(1):32–40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Satoh, K., Shirabe, S., Eguchi, H. et al. 14-3-3 Protein, Total Tau and Phosphorylated Tau in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients with Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease and Neurodegenerative Disease in Japan. Cell Mol Neurobiol 26, 45–52 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-006-9370-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-006-9370-z