Summary
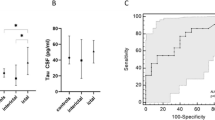
Although migraine has mainly been considered as a benign disease, there is cumulative evidence of silent changes in the brain, brainstem, or cerebellum and subtle subclinical cerebellar dysfunction. In this study, in order to investigate a possible neuronal and/or glial damage at the cellular level in migraine, we measured and compared serum levels of S100B which is a protein marker of glial damage or activation, and neuron specific enolase (NSE) which is a marker of neuronal damage, in migraine patients and control subjects. Serum levels of S100B and NSE were measured in blood samples from 41 patients with migraine-without aura taken during a migraine attack (ictal) and in the attack-free period between migraine attacks (interictal) and 35 age- and sex-matched controls. Patients with migraine-without aura had significantly higher ictal serum levels of S100B and NSE (P < 0.05, for both) than control subjects; whereas in the interictal phase, there was a significant increment only in S100B levels (P < 0.05) compared to controls. On the other hand, serum levels of S100B and NSE in ictal and interictal blood samples did not differ significantly. The findings of increased ictal serum S100B and NSE levels together with increased interictal levels of S100B suggested that migraine might be associated with glial and/or neuronal damage in the brain and a prolonged disruption of blood–brain barrier. Increased interictal serum levels of S100B might point out to an insidious and slow damaging process in migraine patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adami C, Sorci G, Blasi E, Agneletti AL, Bistoni F, Donato R (2001) S100B expression in and effects on microglia. Glia 33:131–142
Barger SW, van Eldik LJ, Mattson MP (1995) S100beta protects hippocampal neurons from damage induced by glucose deprivation. Brain Res 677:167–170
Biberthaler P, Mussack T, Wiedemann E et al (2001) Evaluation of S100b as a specific marker for neuronal damage due to minor head trauma. World J Surg 25:93–97
Bousser MG, Welch KMA (2005) Relation between migraine and stroke. Lancet Neurol 4:533–542
Capuano A, De Corato A, Lisi L, Tringali G, Navarra P, Della Russo C (2009) Proinflammatory-activated trigeminal satellite cells promote neuronal sensitization: relevance for migraine pathology. Mol Pain 5:43–55
Cooper EH (1994) Neuron-specific enolase. Int J Biol Markers 4:205–210
Craft JM, Watterson DM, Marks A, van Eldik L (2005) Enhanced susceptibility of S100B transgenic mice to neuroinflammation and neuronal dysfunction induced by intracerebroventricular infusion of human β-amyloid. Glia 51:209–216
Donato R (1999) Functional roles of S100 proteins, calcium binding proteins of the EF-hand type. Biochim Biophys Acta 1450:191–231
Ertan T, Eker E (2000) Reliability, validity, and factor structure of the geriatric depression scale in Turkish elderly: are there different factor structures for different cultures? Int Psychogeriatr 12:163–172
Etminan M, Takkouche B, Isorna FC, Sami A (2005) Risk of ischaemic stroke in people with migraine: systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Br Med J 330:63–65
Fogel W, Krieger D, Veith M et al (1997) Serum neuron-specific enolase as early predictor of outcome after cardiac arrest. Crit Care Med 25:1133–1138
Fulle S, Pietrangelo T, Mariggio MA et al (2000) Calcium and fos involvement in brain derived Ca2+ binding protein (S100) dependent apoptosis in rat phaeochromocytoma cells. Exp Physiol 85:243–253
Gerlach R, Demel G, Konig HG et al (2006) Active secretion of S100B from astrocytes during metabolic stress. Neuroscience 141:1697–1701
Ghanem G, Loir B, Morandini R et al (2001) On the release and half-life of S100B protein in the peripheral blood of melanoma patients. Int J Cancer 94:586–590
Green AJ, Harvey RJ, Thompson EJ, Rossor MN (1997) Increased S100β in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with frontotemporal dementia. Neurosci Lett 235:5–8
Griffin WST, Sheng JG, McKenzie JE et al (1998a) Life-long overexpression of S100Bβ in Down’s syndrome: implications for Alzheimer pathogenesis. Neurobiol Aging 19:401–405
Griffin WST, Sheng JG, Royston MC et al (1998b) Glial-neuronal interactions in Alzheimer’s disease: the potential role of a “cytokine cycle” in disease progression. Brain Pathol 8:65–72
Gursoy-Ozdemir Y, Qiu J, Matsuoka N et al (2004) Cortical spreading depression activates and upregulates MMP-9. J Clin Investig 113:1447–1455
Harno H, Hirvonen T, Kaunisto MA et al (2003) Subclinical vestibulocerebellar dysfunction in migraine with and without aura. Neurology 61:1748–1752
Herrmann M, Ebert AD, Galazky I, Wunderlich MT, Kunz WS, Huth C (2000) Neurobehavioral outcome prediction after cardiac surgery: role of neurobiochemical markers of damage to neuronal and glial brain tissue. Stroke 31:645–650
Hu J, Castets F, Guevara JL, van Eldik LJ (1996) S100beta stimulates inducible nitric oxide synthetase activity and mRNA levels in rat cortical astrocytes. J Biol Chem 271:2543–2547
Hu J, Ferreira A, van Eldik LJ (1997) S100beta induces neuronal cell death through nitric oxide release from astrocytes. J Neurochem 69:2294–2301
Huttunen HJ, Kuja-Panula J, Sorci G, Agneleth AL, Donato R, Rauvala H (2000) Coregulation of neurite overgrowth and cell survival by amphoterin and S100 proteins through receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) activation. J Biol Chem 275:40091–40105
Ingebrigtsen T, Romner B (1996) Serial S-100B protein serum measurements related to early magnetic resonance imaging after minor head injury. J Neurosurg 85:945–948
Ingebrigtsen T, Romner B (2002) Biochemical serum markers of traumatic brain injury. J Trauma 52:798–808
Johnson P (1996) Markers of cerebral ischemia after cardiac surgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 10:120–126
Johnsson P, Lundqvist C, Lindgren A, Ferencz I, Alling C, Stahl E (1995) Cerebral complications after cardiac surgery assessed by S-100 and NSE levels in blood. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 9:694–699
Kapural M, Krizanac-Bengez L, Barnett G et al (2002) Serum S-100β as a possible marker of blood–brain barrier disruption. Brain Res 940:102–104
Kato K, Suzuki F, Morishita R, Asano T, Sato T (1990) Selective increase in S100B beta protein by aging in rat cerebral cortex. J Neurochem 54:1269–1274
Kruit M, van Buchem MA, Hofman PAM et al (2004) Migraine as a risk factor for subclinical brain lesions. JAMA 291:427–434
Lam AGM, Koppal T, Akama KT et al (2001) Mechanism of glial activation by S100B: involvement of the transcription factor NFκB. Neurobiol Aging 22:765–772
Li Y, Wang J, Sheng JG et al (1998) S100β increases levels of β-amyloid precursor protein and it’s encoding mRNA in rat neuronal cultures. J Neurochem 71:1421–1428
Li Y, Barger SW, Liu L, Mrak RE, Griffin WST (2000) S100B induction of the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 in neurons. J Neurochem 74:143–150
Marchi N, Cavaglia M, Fazio V, Bhudia S, Hallene K, Janigro D (2004) Peripheral markers of blood-brain damage. Clin Chim Acta 342:1–12
Marks A, O’Hanlon D, Lei M, Percy ME, Becker LE (1996) Accumulation of S100Bβ mRNA and protein in cerebellum during infancy in Down syndrome and control subjects. Mol Brain Res 36:343–348
Mrak RE, Sheng JG, Griffin WS (1996) Correlation of astrocytic S100B beta expression with dystrophic neuritis in amyloid plaques of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 55:273–279
Nygaard O, Langbakk B, Romner B (1998) Neuron-specific enolase concentrations in serum and cerebrospinal fluid in patients with no previous history of neurological disorder. Scand J Clin Lab Investig 58:183–186
Papandreou O, Soldatou A, Tsitsika A et al (2005) Serum S100β protein in children with acute recurrent headache: a potentially useful marker for migraine. Headache 45:1313–1316
Persson L, Hardemark HG, Gustafsson J et al (1987) S-100 protein and neuron-specific enolase in cerebrospinal fluid and serum: markers of cell damage in human central nervous system. Stroke 18:911–918
Raabe A, Grolms C, Keller M, Dohnert J, Sorge O, Seifert V (1998) Correlation of computed tomography findings and serum brain damage markers following severe head injury. Acta Neurochir 140:787–792
Raabe A, Kopetsch O, Woszczyk A et al (2003) Serum S100B protein as a molecular marker in severe traumatic brain injury. Restor Neurol Neurosci 21:159–169
Reeves RH, Yao J, Crowley R et al (1994) Astrocytosis and axonal proliferation in the hippocampus of S100B transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:5359–5363
Reuter U, Bolay H, Jansen-Olesen I et al (2001) Delayed inflammation in rat meninges: implications for migraine pathophysiology. Brain 124:2490–2502
Rocca MA, Ceccarelli A, Falini A et al (2006) Brain gray matter changes in migraine patients with T2-visible lesions: a 3-T MRI study. Stroke 37:1765–1770
Rothermundt M, Arolt V, Wiesmann M, Missler U, Peters M, Kirchner H (2001) S-100B is increased in melancholic but not in non-melancholic major depression. J Affect Disord 66:89–93
Royds J, Timperley W, Taylor C (1981) Levels of enolase and other enzymes in the cerebrospinal fluid as indices of pathological change. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 44:1129–1135
Sandor PS, Mascia A, Seidel L, de Pasqua V, Schoenen J (2001) Subclinical cerebellar impairment in the common types of migraine: a three-dimensional analysis of reaching movements. Ann Neurol 49:668–672
Sarchielli P, Alberti A, Baldi A et al (2006) Proinflammatory cytokines, adhesion molecules, and lymphocyte integrin expression in the internal jugular blood of migraine patients without aura assessed ictally. Headache 46:200–207
Schmidt-Wilcke T, Gaenssbauer S, Neuner T, Bogdahn U, May A (2008) Subtle grey matter changes between migraine patients and healthy controls. Cephalalgia 28:1–4
Sheng JG, Ito K, Skinner RD et al (1996) In vivo and in vitro evidence supporting a role for the inflammatory cytokine interleukin-1 as a driving force in Alzheimer pathogenesis. Neurobiol Aging 17:761–766
Sheng JG, Mrak RE, Bales KR et al (2000) Overexpression of the neuritotrophic cytokine S100Bβ proceeds the appearance of neuritic β-amyloid plaques in APP717F mice. J Neurochem 74:295–301
Singh VK (1994) Studies of neuroimmune markers in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurobiol 9:73–81
Swartz RH, Kern RZ (2004) Migraine is associated with magnetic resonance imaging white matter abnormalities. Arch Neurol 61:1366–1368
Teepker M, Munk K, Mylius V et al (2009) Serum concentrations of S100b and NSE in migraine. Headache 49:245–252
Welch KMA, Nagesh V, Aurora SK, Gelman N (2001) Periaqueductal gray matter dysfunction in migraine: cause or the burden of illness? Headache 41:629–637
Wiesmann M, Missler U, Gottman D, Gehring S (1998) Plasma S-100b protein concentration in healthy adults is age and sex independent. Clin Chem 44:1056–1058
Wunderlich MT, Ebert AD, Kratz T, Gortler M, Jost S, Herrmann M (1999) The early neurobehavioural outcome after stroke is related to the release of neurobiochemical markers of brain damage. Stroke 30:1190–1195
Yao J, Kitt C, Reeves RH (1995) Chronic elevation of S100β protein does not alter APP mRNA expression or promote β-amyloid deposition in the brains of aging transgenic mice. Brain Res 702:32–36
Yilmaz IA, Ozge A, Erdal ME, Edgünlü TG, Erol-Çakmak S, Yalin OO (2010) Cytokine polymorphism in patients with migraine: some suggestive clues of migraine and inflammation. Pain Med 11:492–497
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the Akdeniz University Scientific Research Project Unit and was conducted at the Akdeniz University Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yılmaz, N., Karaali, K., Ozdem, S. et al. Elevated S100B and Neuron Specific Enolase Levels in Patients with Migraine-without Aura: Evidence for Neurodegeneration?. Cell Mol Neurobiol 31, 579–585 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-011-9651-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-011-9651-z