Abstract
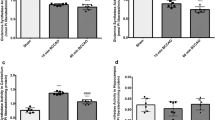
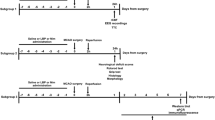
During an ischemic event, the well-regulated glutamate (Glu) homeostasis is disturbed, which gives rise to extremely high levels of this excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain tissues. It was earlier reported that the administration of oxaloacetate (OxAc) as a Glu scavenger reduces the Glu level in the brain by enhancing the brain-to-blood Glu efflux. Here, we studied the neuroprotective effect of OxAc administration in a new focal ischemic model in rats. Occlusion of the middle cerebral artery resulted in immediate reduction of the somatosensory-evoked responses (SERs), and the amplitudes remained at the reduced level throughout the whole ischemic period. On reperfusion, the SERs started to increase, but never reached the control level. OxAc proved to be protective, since the amplitudes started to recover even during the ischemia, and finally fully regained the control level. The findings of the histological measurements were in accordance with the electrophysiological data. After Fluoro Jade C staining, significantly fewer labeled cells were detected in the OxAc-treated group relative to the control. These results provide new evidence of the neuroprotective effect of OxAc against ischemic injury, which strengthens the likelihood of its future applicability as a novel neuroprotective agent for the treatment of ischemic stroke patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beart PM, O’Shea RD (2007) Transporters for L-glutamate: an update on their molecular pharmacology and pathological involvement. Br J Pharmacol 150:5–17
Bickel U, Yoshikawa T, Pardridge WM (2001) Delivery of peptides and proteins through the blood-brain barrier. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 46:247–279
Boyko M, Stepensky D, Gruenbaum BF, Gruenbaum SE, Melamed I, Ohayon S, Glazer M, Shapira Y, Zlotnik A (2012) Pharmacokinetics of glutamate-oxaloacetate transaminase and glutamate-pyruvate transaminase and their blood glutamate-lowering activity in naive rats. Neurochem Res 37:2198–2205
Campos F, Sobrino T, Ramos-Cabrer P, Argibay B, Agulla J, Perez-Mato M, Rodriguez-Gonzalez R, Brea D, Castillo J (2011a) Neuroprotection by glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase in ischemic stroke: an experimental study. J cereb blood flow metab 31:1378–1386
Campos F, Sobrino T, Ramos-Cabrer P, Castellanos M, Blanco M, Rodriguez-Yanez M, Serena J, Leira R, Castillo J (2011b) High blood glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase levels are associated with good functional outcome in acute ischemic stroke. J cereb blood flow metab 31:1387–1393
Campos F, Sobrino T, Ramos-Cabrer P, Castillo J (2012) Oxaloacetate: a novel neuroprotective for acute ischemic stroke. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 44:262–265
Campos F, Sobrino T, Perez-Mato M, Rodriguez-Osorio X, Leira R, Blanco M, Mirelman D, Castillo J (2013) Glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase: a new key in the dysregulation of glutamate in migraine patients. Cephalalgia 33:1148–1154
Choi DW (1988) Glutamate neurotoxicity and diseases of the nervous system. Neuron 1:623–634
Danbolt NC (2001) Glutamate uptake. Prog Neurobiol 65:1–105
Farkas T, Perge J, Kis Z, Wolff JR, Toldi J (2000) Facial nerve injury-induced disinhibition in the primary motor cortices of both hemispheres. Eur J Neurosci 12:2190–2194
Ginsberg MD (2008) Neuroprotection for ischemic stroke: past, present and future. Neuropharmacology 55:363–389
Gottlieb M, Wang Y, Teichberg VI (2003) Blood-mediated scavenging of cerebrospinal fluid glutamate. J Neurochem 87:119–126
Knapp L, Gellert L, Heredi J, Kocsis K, Olah G, Fuzik J, Kis Z, Vecsei L, Toldi J, Farkas T (2013) A simple novel technique to induce short-lasting local brain ischaemia in the rat. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. doi:10.1111/12069
Marosi M, Fuzik J, Nagy D, Rakos G, Kis Z, Vecsei L, Toldi J, Ruban-Matuzani A, Teichberg VI, Farkas T (2009) Oxaloacetate restores the long-term potentiation impaired in rat hippocampus CA1 region by 2-vessel occlusion. Eur J Pharmacol 604:51–57
Nagy D, Marosi M, Kis Z, Farkas T, Rakos G, Vecsei L, Teichberg VI, Toldi J (2009) Oxaloacetate decreases the infarct size and attenuates the reduction in evoked responses after photothrombotic focal ischemia in the rat cortex. Cell Mol Neurobiol 29:827–835
Nagy D, Knapp L, Marosi M, Farkas T, Kis Z, Vecsei L, Teichberg VI, Toldi J (2010) Effects of blood glutamate scavenging on cortical evoked potentials. Cell Mol Neurobiol 30:1101–1106
O’Kane RL, Martinez-Lopez I, DeJoseph MR, Vina JR, Hawkins RA (1999) Na(+)-dependent glutamate transporters (EAAT1, EAAT2, and EAAT3) of the blood-brain barrier. A mechanism for glutamate removal. J Biol Chem 274:31891–31895
Pawlik G, Rackl A, Bing RJ (1981) Quantitative capillary topography and blood flow in the cerebral cortex of cats: an in vivo microscopic study. Brain Res 208:35–58
Ruban A, Berkutzki T, Cooper I, Mohar B, Teichberg VI (2012) Blood glutamate scavengers prolong the survival of rats and mice with brain-implanted gliomas. Invest New Drugs 30:2226–2235
Teichberg VI (2011) GOT to rid the body of excess glutamate. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 31:1376–1377
Teichberg VI, Cohen-Kashi-Malina K, Cooper I, Zlotnik A (2009) Homeostasis of glutamate in brain fluids: an accelerated brain-to-blood efflux of excess glutamate is produced by blood glutamate scavenging and offers protection from neuropathologies. Neuroscience 158:301–308
Toldi J, Rojik I, Feher O (1994) Neonatal monocular enucleation-induced cross-modal effects observed in the cortex of adult rat. Neuroscience 62:105–114
Vesce S, Rossi D, Brambilla L, Volterra A (2007) Glutamate release from astrocytes in physiological conditions and in neurodegenerative disorders characterized by neuroinflammation. Int Rev Neurobiol 82:57–71
White BC, Sullivan JM, DeGracia DJ, O’Neil BJ, Neumar RW, Grossman LI, Rafols JA, Krause GS (2000) Brain ischemia and reperfusion: molecular mechanisms of neuronal injury. J Neurol Sci 179:1–33
Yamamoto HA, Mohanan PV (2003) Effect of alpha-ketoglutarate and oxaloacetate on brain mitochondrial DNA damage and seizures induced by kainic acid in mice. Toxicol Lett 143:115–122
Zlotnik A, Gurevich B, Tkachov S, Maoz I, Shapira Y, Teichberg VI (2007) Brain neuroprotection by scavenging blood glutamate. Exp Neurol 203:213–220
Zlotnik A, Gurevich B, Cherniavsky E, Tkachov S, Matuzani-Ruban A, Leon A, Shapira Y, Teichberg VI (2008) The contribution of the blood glutamate scavenging activity of pyruvate to its neuroprotective properties in a rat model of closed head injury. Neurochem Res 33:1044–1050
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to David Durham for linguistic correction of the manuscript. This study was financially supported by grants from TÁMOP 4.2.2-A-11/KONV-2012-0052, OTKA K105077 and Hungarian Brain Research Program—Grant No. KTIA_13_NAP-A-III/9. This research was realized in the frames of TÁMOP 4.2.4. A/2-11-1-2012-0001 “National Excellence Program—Elaborating and operating an inland student and researcher personal support system”. The project was subsidized by the European Union and co-financed by the European Social Fund.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Knapp, L., Gellért, L., Kocsis, K. et al. Neuroprotective Effect of Oxaloacetate in a Focal Brain Ischemic Model in the Rat. Cell Mol Neurobiol 35, 17–22 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-014-0064-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-014-0064-7