Abstract
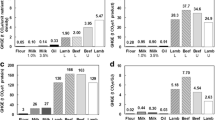
The potential greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from the production of food for three different diets are compared using consequential Life Cycle Assessment. Diet 1 is an Average Danish Diet (ADD); diet 2 is based on the Nordic Nutritional Recommendations (NNR), whilst diet 3 is a New Nordic Diet (NND) developed by the OPUS project. The NND contains locally produced Nordic foods where more than 75 % is organically produced. NNR and NND include less meat and more fruit and vegetables than the ADD. All diets were adjusted to contain a similar energy and protein content. The GHG emissions from the provision of NNR and NND were lower than for ADD, 8 % and 7 % respectively. If GHG emissions from transport (locally produced versus imported food) are also taken into account, the difference in GHG emissions between NND and ADD increases to 12 %. If the production method (organic versus conventional) is taken into account so that the ADD contains the actual ratio of organically produced food (6.6 %) and the NND contains 80 %, the GHG emissions for the NND are only 6 % less than for the ADD. When the NND was optimised to be more climate friendly, the global warming potential of the NND was 27 % lower than it was for the ADD. This was achieved by including less beef, and only including organic produce if the GHG emissions are lower than for the conventional version, or by substituting all meat with legumes, dairy products and eggs.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson K, Ohlsson T, Ohlsson P (1998) Screening LCA of tomato ketchup. J Clean Prod 6:277–288. doi:10.1016/S0959-6526(98)00027-4
Ardente F, Beccali G, Cellura M, Marvuglia A (2006) Poems: A case study of an Italian wine-producing firm. Envir Man 38:350–364. http://www.isa.utl.pt/der/ASAmb/DocumentosAulas/ParaAlunos/ACV_vinho.pdf. Accessed 12 April 2012.
Astrup A, Andersen NL, Stender S, Trolle E (2005) Kostrådene 2005. http://www.meraadet.dk/gfx/uploads/rapporter_pdf/Kostraadene%202005_www.pdf. Accessed 12 April 2012.
Audsley E, Brander M, Chatterton J, Murphy-Bokern D, Webster C, Williams A (2009) How low can we go? An assessment of greenhouse gas emissions from the UK food system and the scope to reduce them by 2050. Cranfield University, UK http://assets.wwf.org.uk/downloads/how_low_can_we_go.pdf. Accessed 12 April 2012.
Berlin J (2002) Environmental life cycle assessment (LCA) of Swedish semi-hard cheese. Int Dairy J 12:939–953. doi:10.1016/S0958-6946(02)00112-7
Carlsson-Kanyama A (1998) Climate change and dietary choices—how can emissions of greenhouse gases from food consumption be reduced? Food Policy 23:277–293. doi:10.1016/S0306-9192(98)00037-2
Cederberg C (2003) Life cycle assessment of animal products. In: Mattsson B, Sonesson U (eds.) Environmental Friendly Food Processing. CRC Press. ISBN 1 85573 677 2.
Cederberg C, Persson UM, Neovius K, Molander S, Clift R (2011) Including carbon emissions from deforestation in the Carbon Footprint of Brazilian Beef. Envir Sci & Tech 45:1773–1779. doi:10.1021/es103240z. http://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdfplus/10.1021/es103240z. Accessed 12 April 2012
Dalgaard R, Schmidt J, Halberg N, Christensen P, Thrane M, Pengue WA (2008) LCA of Soybean Meal. Int J LCA 13:240–254. doi:10.1065/lca2007.06.342
Dalgaard R, Halberg N, Hermansen JE (2007) Danish pork production. An environmental assessment. DJF Animal Science 82, 34pp. http://www.lcafood.dk/djfhus82ny.pdf. Accessed 12 April 2012
Ecoinvent (2010) Swiss Centre for Life Cycle Inventories. Ecoinvent database version 2.1. Process: Diesel, burned in diesel-electric generating se/GLO U'. http://www.ecoinvent.ch/. Accessed 12 April 2012
Edwards R, Mulligan D, Marelli L (2010) Indirect Land Use Change from increased biofuels demand. JRC Scientific and Technical Reports. http://ec.europa.eu/energy/renewables/studies/doc/land_use_change/study_4_iluc_modelling_comparison.pdf. Accessed 12 April 2012
FAO (2009) How to feed the World in 2050. Expert paper. http://www.fao.org/fileadmin/templates/wsfs/docs/expert_paper/How_to_Feed_the_World_in_2050.pdf . Accessed 12 April 2012
Foster C, Green K, Bleda M, Dewick P, Evans B, Flynn A, Mylan J (2006) Environmental impacts of food production and consumption. A report produced for the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs. http://www.ifr.ac.uk/waste/Reports/DEFRA-Environmental%20Impacts%20of%20Food%20Production%20%20Consumption.pdf. Accessed 12 April 2012
Garnett T (2008) Cooking up a Storm. Food, greenhouse emissions, and our changing climate. Food Climate Research Network. Centre for Environmental Strategy, University of Surrey. http://www.fcrn.org.uk/fcrn. Accessed 12 April 2012
Halberg N, Dalgaard R, Rasmussen MD (2006) Miljøvurdering af konventionel og økologisk avl af grøntsager. Danish Environmental Protection Agency. Working Report No. 5. http://www2.mst.dk/udgiv/publikationer/2006/87-7614-960-9/pdf/87-7614-961-7.pdf. Accessed 12 April 2012 (Danish)
Halberg N, Hermansen JE, Kristensen IS, Eriksen J, Tvedegaard N (2008) Comparative environmental assessment of three systems for organic pig production in Denmark. Proceedings of ISOFAR Conference: Organic Agriculture in Asia, Korea 13–14 March. Pp. 249–261. http://orgprints.org/15585/1/15585.pdf. Accessed 12 April 2012
Halberg N, Hermansen JE, Kristensen IS, Eriksen J, Tvedegaard N, Petersen BM (2010) Impact of organic pig production systems on CO2 emission, C sequestration and nitrate pollution. Agron Sustain Dev. 30:721–731. http://www.agronomy-journal.org/index.php?option=article&access=doi&doi=10.1051/agro/2010006. Accessed 12 April 2012
Hanssen OJ, Rukke E-L, Saugen B, Kolstad J, Hafrom P, Krogh L von, Raadal HL, Rønning A, Wigum KS (2007) The environmental effectiveness of the beverage sector in Norway in a factor 10 perspective. Int J Life Cycle Assess 12:257–265. http://www.springerlink.com/content/g6550442q5j957w3/. Accessed 11 May 2012.
IPCC (2007) IPCC Fourth Assessment Report: Climate Change 2007 (AR4). http://www.ipcc.ch/publications_and_data/publications_and_data_reports.shtml. Accessed 12 April 2012
Kilic A, Midilli A, Dincer I (2010) A strategic program to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from food industry. In: Dincer et al. (eds.), Global Warming, Green Energy and Technology, Springer Science+Business Media, LLC2010. doi:10.1007/978-1-4419-1017-2_10. Accessed 12 April 2012
Kristensen T, Mogensen, L. Knudsen MT, John E Hermansen (2011) Effect of production system and farming strategy on greenhouse gas emissions from commercial dairy farms in a life cycle approach. Livestock Sci. 140:136–148. doi:10.1016/j.livsci.2011.03.002. Accessed 12 April 2012
Larsen TM, Dalskov S-M, Baak M van, Jebb SA, Papadaki A, Pfeiffer AFH, Martinez JA, Handjieva-Darlenska T, Kunesová, Pihlsgård M, Stender S, Holst C, Saris WHM, Astrup A (2011) Diets with high or low protein content and glycemic index for weight-loss maintenance. New England J Med 363:2102–2113. http://www.nejm.org/doi/pdf/10.1056/NEJMoa1007137. Accessed 12 April 2012.
LCA Food Database (2004) http://www.lcafood.dk. Accessed 11 May 2012.
Macdiarmid J, Kyle J, Horgan G, Loe J, Fyfe C, Johnstone A (2011) Livewell: a balance of healthy and sustainable food choices. WWF. Rowett Institute of Nutrition and Health, University of Aberdeen. http://assets.wwf.org.uk/downloads/livewell_report_jan11.pdf. Accessed 12 April 2012
Mäder P, Fliessbach A, Dubois D, Gunst L, Fried P, Niggli U (2002) Soil Fertility and Biodiversity in Organic Farming. Science 296:1694–1697. doi:10.1126/science.1071148
Mithril C, Dragsted LO, Meyer C, Blauert E, Holt MK, Astrup A (2012) Guidelines for the New Nordic Diet. Public Health Nutrition. doi:10.1017/S136898001100351X
Niggli U, Schmid H, Fliessbach A (2008) Organic farming and climate Change. FiBL. International Trade Centre (ITC), Geneva. Technical Paper, 30pp. http://orgprints.org/13414/3/niggli-etal-2008-itc-climate-change.pdf. Accessed 12 April 2012
Nguyen TLT, Hermansen JE, Mogensen L (2010) Environmental consequences of different beef production systems in the EU. J Clean Prod 18:756–766. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2009.12.023
Nordic Council (2004) Nordic Nutrition Recommendations 2004—integrating nutrition and physical activity. http://www.norden.org/da/publikationer/publikationer/2004-013. Accessed 12 April 2012
Renouf MM, Wegener MK, Nielsen LK (2008) An environmental life cycle assessment comparing Australian sugarcane with US corn and UK sugar beet as producers of sugars for fermentation. Biomass Bioenergy 32:1144–1155. doi:10.1016/j.biombioe.2008.02.012
Salomone R (2003) Life cycle assessment applied to coffee production: Investigating environmental impacts to aid decision making for improvements at company level. Food, Agric Envir 1:295–300. http://isites.harvard.edu/fs/docs/icb.topic267876.files/Coffee%20Life%20Cycle.pdf. Accessed 12 April 2012
Saunders C, Barber A, Taylor G (2006) Food miles—comparative energy/emissions performance of New Zealand’s agriculture Industry. Research Report No. 205. http://www.lincoln.ac.nz/documents/2328_rr285_s13389.pdf. Accessed 12 April 2012
Saxe H (2011) Diet as a healthy and cost-effective instrument in environmental protection. In: Nriagu JO (ed.) Encyclopedia of Environmental Health, volume 2, pp. 70–82 Burlington: Elsevier. http://www.waterstones.com/waterstonesweb/products/jerome+o-+nriagu/encyclopedia+of+environmental+health/7968186/. Accessed 12 April 2012
Saxe H, Jensen RB, Petersen ML (2006) Fødevarers Miljøeffekter. Det politiske ansvar og det personlige valg. Institute of Environmental Assessment. English abstract. http://www.dors.dk/graphics/Synkron-Library/Publikationer/IMV/2006/fdevare.pdf. Accessed 12 April 2012 (in Danish)
Schmidt J (2010) Comparative life cycle assessment of rapeseed oil and palm oil. Int J Life Cycle Assess 15:183–197. doi:10.1007/s11367-009-0142-0
Statistics Denmark (2011) Value of import and export after SITC main categories, country and import and export. http://www.statistikbanken.dk/statbank5a/default.asp?w=1280
Stehfest E, Bouwman L, van Vuuren DP (2009) Climate benefits of changing diet. Clim Chang 95:83–102. doi:10.1007/s10584-008-9534-6
Thomassen MA, van Calker KJ, Smits MCJ, Iepema GL, de Boer IJM (2008) Life cycle assessment of conventional and organic milk production in the Netherlands. Agric Syst 96:95–107. doi:10.1016/j.agsy.2007.06.001
Tukker A, Bausch-Goldbohm S, Verheijden M, de Koning A, Kleijn R, Wolf O, Domínguez IP (2009) Environmental impacts of diet changes in the EU. JRC European Comission. European Joint Research Centre. Institute of Prospective Technological Studies. Report no. EUR 23783 EN. ftp://ftp.jrc.es/pub/EURdoc/JRC50544.pdf. Accessed 12 April 2012
Vieux F, Darmon N, Touazi D, Soler LG (2012) Greenhouse gas emissions of self-selected individual diets in France: Changing the diet structure or consuming less? Ecological Economics 75:91–101. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2012.01.003. Accessed 12 April 2012
Wallén A, Brandt N, Wennersten R (2004) Does the Swedish consumer’s choice of food influence greenhouse emissions? Environ Sci & Pol 7:525–535. doi:10.1016/j.envsci.2004.08.004
Weidema BP, Wesnæs M, Hermansen J, Kristensen T, Halberg N (2008) Environmental Improvement Potentials of Meat and Dairy Products. JRC Scientific and Technical Report. EUR 23491 EN. ftp://ftp.jrc.es/pub/library/Impro_Meet.pdf. Accessed 12 April 2012
Weidema BP (2009) Using the budget constraint to monetarise impact assessment results. Ecol Econ 68:1591–1598. doi:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2008.01.019
Weiske A, Vabitsch A, Olesen JE, Schelde K, Michel J, Friedrich R, Kaltschmitt M (2006) Mitigation of greenhouse gas emissions in European conventional and organic dairy farming. Agric Acosys & Envir 112:221–232. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2005.08.023
Williams AG, Audsley E, Sandars DL (2006) Determining the environmental burdens and resource use in the production of agricultural and horticultural commodities. Defra project report ISO205. Natural Resource Management Institute, Cranfield University. Silsoe Research Institute.
Økologisk Landsforening (2009) Økologisk markedsnotat. http://www.okologi.dk/media/229957/markedsnotat2009.pdf. Accessed 12 April 2012 (in Danish)
Acknowledgements
The study is part of the OPUS project 'Optimal well-being, development and health for Danish children through a healthy New Nordic Diet. Supported by a grant from the Nordea Foundation. We thank the Danish National Food Institute and 2.-0 LCA Consultants for providing the data on the volumes of food and beverages produced to make up the three diets
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saxe, H., Larsen, T.M. & Mogensen, L. The global warming potential of two healthy Nordic diets compared with the average Danish diet. Climatic Change 116, 249–262 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-012-0495-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-012-0495-4