Abstract
Background
Interleukin-33 (IL-33) is a novel member of the IL-1 family of cytokines, and it is closely related to IL-18, one of the best characterized members of the IL-1 family. It’s been demonstrated that elevated levels of IL-18 are involved in a wide variety of tumors, especially in gastric cancer.
Aims
The purpose of this study was to determine the correlations between serum IL-33 levels and the clinicopathologic features in gastric cancer patients.
Methods
Serum samples were collected from 68 patients with gastric cancer and 57 controls. Serum IL-33 levels were measured by ELISA. Classical tumor markers of CEA and CA19-9 levels were routinely detected by chemiluminescence immunoassay. Western blot analysis was used to detect IL-33 expression in gastric cancer tissue samples and cell lines. The relationship between serum levels of IL-33 and clinical characteristics in patients was analyzed.
Results
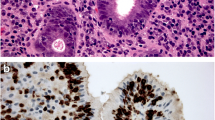
IL-33 levels in the serum of gastric cancer patients were significantly elevated in comparison with that of healthy volunteers. Furthermore, higher serum levels of IL-33 in gastric cancer patients were found to correlate with several poor prognostic factors like depth of invasion, distant metastasis and advanced stage (stage III/IV). On the other hand, serum IL-33 levels did not correlate with CEA and CA19-9. The expression of IL-33 protein was upregulated in carcinoma tissues in comparison with matched normal tissues, and no statistically significant difference was found between the four gastric cancer cell lines and human gastric epithelial cell line GES-1.
Conclusions
Serum IL-33 may be a useful biomarker for predicting the prognosis of gastric cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pisani P, Parkin DM, Ferlay J. Estimates of the worldwide mortality from eighteen major cancers in 1985. Implications for prevention and projections of future burden. Int J Cancer. 1993;55:891–903.
Terry MB, Gaudet MM, Gammon MD. The epidemiology of gastric cancer. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2002;12:111–127.
Ikeguchi M, Hatada T, Yamamoto M, et al. Serum interleukin-6 and -10 levels in patients with gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2009;12:95–100.
Seguchi T, Yokokawa K, Sugao H, Nakano E, Sonoda T, Okuyama A. Interleukin-6 activity in urine and serum in patients with bladder carcinoma. J Urol. 1992;148:791–794.
Fortis C, Foppoli M, Gianotti L, et al. Increased interleukin-10 serum levels in patients with solid tumors. Cancer Lett. 1996;104:1–5.
Kang JS, Bae SY, Kim HR, et al. Interleukin-18 increases metastasis and immune escape of stomach cancer via the downregulation of CD70 and maintenance of CD44. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30:1987–1996.
Thong-Ngam D, Tangkijvanich P, Lerknimitr R, Mahachai V, Theamboonlers A, Poovorawan Y. Diagnostic role of serum interleukin-18 in gastric cancer patients. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12:4473–4477.
Haghshenas MR, Hosseini SV, Mahmoudi M, Saberi-Firozi M, Farjadian S, Ghaderi A. IL-18 serum level and IL-18 promoter gene polymorphism in Iranian patients with gastrointestinal cancers. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;24:1119–1122.
Carriere V, Roussel L, Ortega N, et al. IL-33, the IL-1-like cytokine ligand for ST2 receptor, is a chromatin-associated nuclear factor in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:282–287.
Schmitz J, Owyang A, Oldham E, et al. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity. 2005;23:479–490.
Onda H, Kasuya H, Takakura K, et al. Identification of genes differentially expressed in canine vasospastic cerebral arteries after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1999;19:1279–1288.
Dinarello CA. Interleukin-1, interleukin-1 receptors and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Int Rev Immunol. 1998;16:457–499.
Park H, Byun D, Kim TS, et al. Enhanced IL-18 expression in common skin tumors. Immunol Lett. 2001;79:215–219.
Eissa SA, Zaki SA, El-Maghraby SM, Kadry DY. Importance of serum IL-18 and RANTES as markers for breast carcinoma progression. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2005;17:51–55.
Merendino RA, Gangemi S, Ruello A, et al. Serum levels of interleukin-18 and sICAM-1 in patients affected by breast cancer: preliminary considerations. Int J Biol Markers. 2001;16:126–129.
Lee S, Kang J, Cho M, et al. Profiling of transcripts and proteins modulated by K-ras oncogene in the lung tissues of K-ras transgenic mice by omics approaches. Int J Oncol. 2009;34:161–172.
Moussion C, Ortega N, Girard JP. The IL-1-like cytokine IL-33 is constitutively expressed in the nucleus of endothelial cells and epithelial cells in vivo: a novel ‘alarmin’? PLoS One. 2008;3:e3331.
Masamune A, Watanabe T, Kikuta K, Satoh K, Kanno A, Shimosegawa T. Nuclear expression of interleukin-33 in pancreatic stellate cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010;299:G821–G832.
Kakkar R, Lee RT. The IL-33/ST2 pathway: therapeutic target and novel biomarker. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008;7:827–840.
Trajkovic V, Sweet MJ, Xu D. T1/ST2–an IL-1 receptor-like modulator of immune responses. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2004;15:87–95.
Gayle MA, Slack JL, Bonnert TP, et al. Cloning of a putative ligand for the T1/ST2 receptor. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:5784–5789.
Kumar S, Minnich MD, Young PR. ST2/T1 protein functionally binds to two secreted proteins from Balb/c 3T3 and human umbilical vein endothelial cells but does not bind interleukin 1. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:27905–27913.
Ali S, Huber M, Kollewe C, Bischoff SC, Falk W, Martin MU. IL-1 receptor accessory protein is essential for IL-33-induced activation of T lymphocytes and mast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:18660–18665.
Chackerian AA, Oldham ER, Murphy EE, Schmitz J, Pflanz S, Kastelein RA. IL-1 receptor accessory protein and ST2 comprise the IL-33 receptor complex. J Immunol. 2007;179:2551–2555.
De Vita F, Orditura M, Galizia G, et al. Serum interleukin-10 levels in patients with advanced gastrointestinal malignancies. Cancer. 1999;86:1936–1943.
Sharma A, Rajappa M, Saxena A, Sharma M. Cytokine profile in Indian women with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cancer cervix. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2007;17:879–885.
Choi YS, Choi HJ, Min JK, et al. Interleukin-33 induces angiogenesis and vascular permeability through ST2/TRAF6-mediated endothelial nitric oxide production. Blood. 2009;114:3117–3126.
Becker CE, O’Neill LA. Inflammasomes in inflammatory disorders: the role of TLRs and their interactions with NLRs. Semin Immunopathol. 2007;29:239–248.
Kawabata T, Ichikura T, Majima T, et al. Preoperative serum interleukin-18 level as a postoperative prognostic marker in patients with gastric carcinoma. Cancer. 2001;92:2050–2055.
Iikura M, Suto H, Kajiwara N, et al. IL-33 can promote survival, adhesion and cytokine production in human mast cells. Lab Invest. 2007;87:971–978.
Salminen A, Kaarniranta K. Glycolysis links p53 function with NF-kappaB signaling: impact on cancer and aging process. J Cell Physiol. 2010;224:1–6.
Mancino A, Lawrence T. Nuclear factor-kappaB and tumor-associated macrophages. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:784–789.
Acknowledgments
We thank Zhongyin Yang, Department of General Surgery, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Pinghu Sun and Qiwen Ben contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, P., Ben, Q., Tu, S. et al. Serum Interleukin-33 Levels in Patients with Gastric Cancer. Dig Dis Sci 56, 3596–3601 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-011-1760-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-011-1760-5