Abstract
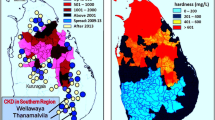
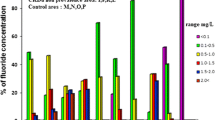
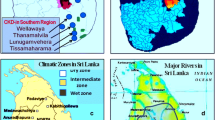
High incidence of chronic kidney disease of unknown aetiology (CKDU) in Sri Lanka is shown to correlate with the presence of irrigation works and rivers that bring-in ‘nonpoint source’ fertilizer runoff from intensely agricultural regions. We review previous attempts to link CKDU with As, Cd and other standard toxins. Those studies (e.g. the WHO-sponsored study), while providing a wealth of data, are inconclusive in regard to aetiology. Here, we present new proposals based on increased ionicity of drinking water due to fertilizer runoff into the river system, redox processes in the soil and features of ‘tank’-cascades and aquifers. The consequent chronic exposure to high ionicity in drinking water is proposed to debilitate the kidney via a Hofmeister-type (i.e. protein-denaturing) mechanism.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acquavella, J. F., Alexander, B. H., Mandel, J. S., Gustin, C., Baker, B., Chapman, P., et al. (2004). Glyphosate biomonitoring for farmers and their families: Results from the farm family exposure study. Environmental Health Perspectives, 112(3), 321–326.
Agriculture Dept Sl. (2013). Crop recommendations. http://www.agridept.gov.lk/index.php/si/crop-recommendations/903.
Alcźar, A. R (Nefrologia). (2008). 28 87–93 (suppl 3). http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19018,744.
Arora, P., Vasa, P., Brenner, D., Iglar, K., McFarlane, P., Morrison, H., et al. (2013). Prevalence estimates of chronic kidney disease in Canada: Results of a nationally representative survey. CMAJ, 185, E417–E423.
Baldwin, R. L. (1996). How hofmeister ion interactions affect protein stability. Biophysics Journal, 71, 2056–2063.
Bandara, J., Senevirathna, D. M. A. N., Dasanayake, D. M. R. S. B., Herath, V., Abeysekara, T., & Rajapaksha, K. (2008). Chronic renal failure among farm families in cascade irrigation systems in Sri Lanka associated with elevated dietary cadmium levels in rice and freshwater fish (tilapia). Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 30, 465–478.
BGS. (2001). Arsenic contamination of groundwater in Bangladesh: Final report. Tech. rep., British Geological Survey Keyworth, England.
CEA-SL. (2013). Tech. rep., CEA-SL, Central environmental authority, Sri Lanka. http://www.eco-web.com/reg/02553.html.
Chandrajith, R., Nanayakkara, S., Itai, K., Aturaliya, T. N. C., Dissanayake, C. B., Abeysekera, T., et al. (2011). Chronic kidney diseases of uncertain etiology in Sri Lanka: Geographic distribution and environmental implications. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 33, 267–278.
Clemens, R., Bjorvatn, K., Frengstad, B., Melaku, Z., Tekle-Haimanot, R., & Siewer, U. (2003). Drinking water quality in the Ethiopian section of the East African Rift valley I—data and health aspects. The Science of the Total Environment, 311, 65–80.
Coresh, J., Selvin, E., Stevens, L., Manzi, J., Kusek, J. W., Eggers, P., et al. (2007). Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA, 298, 2038–2047.
Gracia-Tabanino, R., Dominguez, J., Jansa, J. M., & Oliver, A. (2005). Proteinuria and chronic renal failure in the coast of El Salvador: Detection with low cost methods and associated factors. Nefrologia XXXV(1).
Gray, N. F. (2007). Drinking water quality. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Gunatilleke, N. (2013, October 7). Kidney disease now spreads to north. Daily news, Sri Lanka.
Gunawardane, R. P. (1987). Studies on complete and partial acidulation of Eppawel apatite. Journal National Science Council of Sri Lanka, 15, 183. http://thakshana.nsf.ac.lk/pdf/JNSF1-25/JNSF15_2/JNSF15_2_183.
Illeperuma, O. A. (2011). Geo-environmental factors associated in the Rajarata kidney disease. http://www.sundaytimes.lk/110731/Plus/plus_11.html.
Illeperuma, O. A., Dharmagunawardhane, H. A., & Herath, K. R. P. (2009). Dissolution of aluminium from substandard utensils under high fluoride stress: A possible risk factor for chronic renal failures in the North-Central province. Journal of the National Science Foundation of Sri Lanka, 37, 219–222.
Ismael, D. S., Vollmannova, A., Timoracka, M., & Harnagozo, L. (2012). Risk of lentil seed contamination by risk metals from the soil. The Journal of Microbiology, Biotechnology and Food sciences, 2, 338.
ITFG. (2014). Glyphosate and chronic kidney disease—Sri Lanka. Tech. rep., industry task force on glyphosate. http://www.glyphosate.eu/glyphosate-and-chronic-kidney-disease-sri-lanka.
Jayasekara, J. M. K. B., Dissanayake, D. M., Adhikari, S. B., & Bandara, P. (2013). Geographical distribution of chronic kidney disease of unknown origin in north central region of Sri Lanka. Ceylon Medical Journal, 58, 6–9.
Jayasumana, C., Parangama, P., & Amarasinghe, M. (2011). Chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology (ckdu) and arsenic in ground water in Sri Lanka. Presence of arsenic in pesticides used in Sri Lanka. In Proceedings of workshop on challenges in groundwater management in Sri Lanka. http://www.wrb.gov.lk/web/images/stories/downloads/Scientific_Reportsproceeding_07_april_11.
Jayasumana, M. A. C. S., Paranagama, P. A., Amarasinghe, M. D., Wijewardane, K. M. R. C., Dahanayake, K. S., Fonseka, S. I., et al. (2013). Possible link of chronic arsenic toxicity with chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology in Sri Lanka. Journal of Natural Science Research, 3(1), 64–73.
Jayatilake, N., Mendis, S., Maheepala, P., Metha, R. F., & Project Team CNR. (2013). Chronic kidney disease of uncertain aetiology, prevalence and causative factors in a developing country. BMC Nephrology, 14, 180.
Jessani, S., Bux, R., & Jafar, T. (2014). Prevalence, determinants, and management of chronic kidney disease in Karachi, Pakistan—a community based cross-sectional study. BMC Nephrology, 15, 90.
Joshua, W. D., Thushyanthy, M., & Nanthagoban, N. (2013). Seasonal variation of water table and groundwater quality of the karst aquifer of the Jaffna peninsula-Sri Lanka. Journal of National Science Foundation of Sri Lanka, 41, 3–12.
Kulasooriya, S. A. (2011). Cyanobacteria: Pioneers of planet earth. Ceylon Journal of Science (Bio Sci), 40(2), 71–88.
Kulatunga, K. M. S. B., & Illeperuma, O. A. (2013). Fluoride assisted aluminium leaching during cooking and its relevance to chronic renal failure. In S. Yatigammana (ed.) International symposium, water quality and human health, vol 1, p 53.
Kuro-o, M. (2013). A phosphate-centric paradigm for pathophysiology and therapy of chronic kidney disease. Kidney International Supplements, 3, 420–426. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/kisup.2013.88.
Lasantha, P. A. P. G. R., Gonawala, J. M. L., & Wijekoon, D. (2008). Groundwater quality in Anuradhapura district with special reference to fluoride. Groundwater in Sri Lanka—a most precious but highly threatened resource. Occasional Publication by National Academy of Sciences of Sri Lanka, 1, 48–64.
Lin, B., Shao, L., Luo, Q., Ou-yang, L., Zhou, F., Du, B., He, Q., Wu, J., Xu, N., Chen, J. (2014). Prevalence of chronic kidney disease and its association with metabolic diseases: A cross-sectional survey in Zhejiang province, eastern China. BMC Nephrology, 15, 36.
Luyckx, V. A., & Brenner, B. M. (2005). Low birth weight, nephron number, and kidney disease. Kidney International Supplements, 68, S68–S77.
Mubarak, A. M. (2011). Current state of water-qualitymonitoring and lab facilities in Sri Lanka. http://tsunami.obeysekera.net/Presentations/Mubarak.
Nanayakkara, S., Senevirathna, S., Abeysekera, T., Chandrajith, R., Ratnatunga, N., Gunarathne, E., et al. (2014). An integrative study of the genetic, social and environmental determinants of chronic kidney disease characterized by tubulointerstitial damages in the north central region of Sri Lanka. Journal of Occupational Health, 56, 28–38.
Panabokke, C. R. (1959). Soil science, 87, 67–74.
Panabokke, C. R. (2007). Groundwater conditions in Sri Lanka. Colombo: National Science Foundation of Sri Lanka.
Paranagama, A., Jayasuriya, N., Bhuiyan, M. A. (2012). Water quality parameters in relation to chronic kidney disease in Sri Lanka. http://dl.lib.mrt.ac.lk/bitstream/handle/123/9042/SBE-12-191?sequence=1.
Perera, M. B. U., Yatigammana, S. K., Kulasooriya, S. A., & Athukorala, N. P. (2013). Distribution of cylinfrospermopsis raciborskii (a toxin producing cyanobacterium) in freshwater reservoirs of Sri Lanka. In Proceedings of international symposium: Water quality and human health, Peradeniya, Sri Lanka, p 29.
Ramachandran, S. (1994). Renal diseases: Sri Lankan and global spectrum. Journal of Ceylon College of Physicians, 27, 27–35.
Rathmalgodage, N. (2012). Variation of water quality in selected water bodies in Anuradhapura. Master’s thesis, Sabaragamuwa University, Sri Lanka.
Smith, P. H., & Raymond, K. N. (1988). Inorganic Chemistry, 27, 1056–1061.
Subasinghe, M. M., Jinadasa, B., & Wicramasinghe, I. (2012). The potential health and environmental impact of exposure to hazardous natural and man-made chemicals. In Proceedings of first national symposium-environmental health, Colombo, p 15. http://www.ejustice.lk/PDF/1st%20National%20Sympoium%20proceedings%20copy.
Tanchev, Y., & Dorossiev, D. (1991). The first clinical description of Balkan endemic nephropathy (1956), its validity 35 years later. IARC Scientific Publications, 115, 21–28.
Thatte, L., Oster, J., Singer, I., Bourgoignie, J., Fishman, L., & Roos, B. (1995). American Journal of Medical Sciences, 310(4), 167–174.
Thelen, K. D., Jackson, E. P., & Penner, D. (1995). Weed Science, 42, 541–548.
Thompson, T., Fawell, J., Kunikane, S., Jackson, D., Appleyard, S., Callan, P., et al. (2007). Chemical safety of drinking water: Assessing priorities for risk management. Tech. rep., WHO, Geneva.
TOXINET. (1992). National library of medicine. Hazardous substances databank. Tech. rep., TOXNET, Medlars management section, Bethesda, MD. USA.
US-EPA. (2003). National management measures to control nonpoint source pollution from agriculture. Tech. rep., US-EPA. http://water.epa.gov/polwaste/nps/agriculture/agmm_index.cfm.
US-epa. (2013). Tech. rep., US-EPA, US environmental protection agency. http://water.epa.gov/drink/contaminants/.
Vereecken, H. (2005). Mobility and leaching of glyphosate: A review. Pest Management Science, 61, 1139–1151.
Waidyanatha, P. (2013, October 22). The Island Newspaper. http://www.island.lk/index.php?page_cat=article-details&page=article-details&code_title=90645.
Waidyanatha, U. P. S., Yogaratnam, N., & Ariyaratne, W. A. (1979). Mycorrhizal infection on growth and nitrogen fixation of pueraria and stylosanthes uptake of phosphorus from two rock phosphates. New Phytologist, 82, 147.
Wanigasuriya, K. P., Peiris-John, R. J., & Wickremasinghe, R. (2011). Chronic kidney disease of unknown aetiology in Sri Lanka: Is cadmium a likely cause? BMC Nephrology, 12, 32. http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2369/12/32,downloaded 21-Nov-2013.
Wasana, H. M. S., Aluthpatabendi, D., & Bandara, J. (2012). Drinking water quality assessment towards CKDU in the NCP, Sri Lanka. In International symposium, water quality and human health, vol 1, p 66.
WHO-guidelines. (2011). Background document for development of WHO guidelines for drinking-water quality. Tech. rep., WHO. http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/dwq/chemicals/hardness.
WHO-SL-reports. (2013). Chronic kidney disease of unknown aetiology (CKDu): A new threat to health. http://dh-web.org/place.names/posts/index.html#ckdu. Accessed November 12, 2013.
Yatigammana, S. (Ed.). (2012). Water quality and human health. Peradeniya, Sri Lanka.
Yusuke, T., Jha, V., becker, G., Chen, H. C., Perkovic, V., Prodjosudjadi, W., et al. (2010). A challenge to chronic kidney disease in Asia: The report of the second asian forum of chronic kidney disease initiative. Nephrology, 15, 248–252.
Zhang, Z., Xu X., Fan, H., Li, D., & Den, H. (2013). Higher serum chloride concentrations are associated with acute kidney injury in unselected critically ill patients. BMC Nephrology, 14, 235. http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2369/14/235.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dharma-wardana, M.W.C., Amarasiri, S.L., Dharmawardene, N. et al. Chronic kidney disease of unknown aetiology and ground-water ionicity: study based on Sri Lanka. Environ Geochem Health 37, 221–231 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-014-9641-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-014-9641-4