Abstract
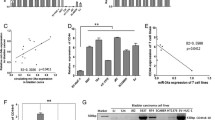
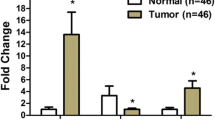
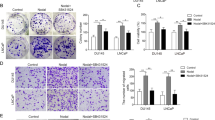
Angiogenin (ANG) is a multifunctional secreted protein that belongs to the pancreatic ribonuclease A super family, which has been conceived to play a more important role in cell survival, growth and proliferation than the mediation of angiogenesis. Accumulating evidences suggest that the expression and activity of ANG increased significantly in a variety of human cancers. Recent studies showed that ANG activates cell signaling pathway through the putative receptor on endothelial cells. However, the underlying mechanisms remain largely unknown. AKT/mTOR signaling pathway participates in cell growth, cell-cycle progression and cell apoptosis. The purpose of our study was to determine whether ANG implicated in growth and metastasis of bladder cancer cells through regulating AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. In this study, we constructed ANG siRNA plasmids that transfected into human bladder cancer T24 cells. We demonstrated that knockdown of ANG could inhibit cell proliferation, regulate cell cycle and induce apoptosis. We also found that down-regulation of ANG remarkably reduced the phosphorylation of signaling targets AKT, GSK-3β and mTOR. Furthermore, down-regulation of ANG increased expression of ribonuclease inhibitor, which is a cytoplasmic acidic protein with many functions. Finally, ANG siRNA led to the suppression for tumorigenesis and metastasis in vivo. Taken together, these findings highlight for the first time that ANG could play a pivotal role in the development of bladder cancer through regulating AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. The targeting of ANG and associated factors could provide a novel strategy to inhibit human bladder cancer.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang L, Graham PH, Hao J, Ni J, Bucci J, Cozzi PJ et al (2013) Acquisition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell phenotypes is associated with activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in prostate cancer radioresistance. Cell Death Dis 4:e875
Fett JW, Strydom DJ, Lobb RR, Alderman EM, Bethune JL, Riordan JF et al (1985) Isolation and characterization of angiogenin, an angiogenic protein from human carcinoma cells. Biochemistry 24:5480–5486
Ibaragi S, Yoshioka N, Li S, Hu MG, Hirukawa S, Sadow PM et al (2009a) Neamine inhibits prostate cancer growth by suppressing angiogenin-mediated rRNA transcription. Clin Cancer Res 15:1981–1988
Ibaragi S, Yoshioka N, Kishikawa H, Hu JK, Sadow PM, Li M et al (2009b) Angiogenin-stimulated rRNA transcription is essential for initiation and survival of AKT-induced prostate intraepithelial neoplasia. Mol Cancer Res 7:415–424
Ivanov P, Emara MM, Villen J, Gygi SP, Anderson P (2011) Angiogenin-induced tRNA fragments inhibit translation initiation. Mol Cell 43:613–623
Janku F, Wheler JJ, Westin SN, Moulder SL, Naing A, Tsimberidou AM et al (2012) PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors in patients with breast and gynecologic malignancies harboring PIK3CA mutations. J Clin Oncol 30:777–782
Janku F, Wheler JJ, Naing A, Falchook GS, Hong DS, Stepanek VM et al (2013) PIK3CA mutation H1047R is associated with response to PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway inhibitors in early-phase clinical trials. Cancer Res 73:276–284
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA: A Cancer J Clin 61:69–90
Kieran D, Sebastia J, Greenway MJ, King MA, Connaughton D, Concannon CG (2008) Control of motoneuron survival by angiogenin. J Neurosci 28:14056–14061
Kim HM, Kang DK, Kim HY, Kang SS, Chang SI (2007) Angiogenin-induced protein kinase B/Akt activation is necessary for angiogenesis but is independent of nuclear translocation of angiogenin in HUVE cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 352:509–513
Li S, Hu GF (2010) Angiogenin-mediated rRNA transcription in cancer and neurodegeneration. Int J Biochem Mol Biol 1:26–35
Li S, Hu GF (2012) Emerging role of angiogenin in stress response and cell survival under adverse conditions. J Cell Physiol 227:2822–2826
Li S, Ibaragi S, Hu GF (2011) Angiogenin as a molecular target for the treatment of prostate cancer. Curr Cancer Ther Rev 7:83–90
Li L, Pan XY, Shu J, Jiang R, Zhou YJ, Chen JX (2014) Ribonuclease inhibitor up-regulation inhibits the growth and induces apoptosis in murine melanoma cells through repression of angiogenin and ILK/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Biochimie 103:89–100
Liu P, Cheng H, Roberts TM, Zhao JJ (2009) Targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 8:627–644
Luo F, Burke K, Kantor C, Miller RH, Yang Y (2014) Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 mediates adult OPC maturation and myelin repair through modulation of akt and gsk-3β signaling. J Neurosci 34:10415–10429
Malla R, Gopinath S, Alapati K, Gondi CS, Gujrati M, Dinh DH et al (2010) Downregulation of uPAR and cathepsin B induces apoptosis via regulation of Bcl-2 and Bax and inhibition of the PI3K/Akt pathway in gliomas. PLoS One 5:e13731
Muramatsu M, Yamamoto S, Osawa T, Shibuya M (2010) Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 signaling promotes mobilization of macrophage lineage cells from bone marrow and stimulates solid tumor growth. Cancer Res 70:8211–8221
Nilsson UW, Abrahamsson A, Dabrosin C (2010) Angiogenin regulation by estradiol in breast tissue: tamoxifen inhibits angiogenin nuclear translocation and antiangiogenin therapy reduces breast cancer growth in vivo. Clin Cancer Res 16:3659–3669
Paudel N, Sadagopan S, Chakraborty S, Sarek G, Ojala PM, Chandran B (2012) Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latency-associated nuclear antigen interacts with multifunctional angiogenin to utilize its antiapoptotic functions. J Virol 86:5974–5991
Pizzo E, Sarcinelli C, Sheng J, Fusco S, Formiggini F, Netti P et al (2013) Ribonuclease/angiogenin inhibitor 1 regulates stress-induced subcellular localization of angiogenin to control growth and survival. J Cell Sci 126:4308–4319
Reikvam H, Nepstad I, Bruserud Ø, Hatfield KJ (2013) Pharmacologic targeting of the PI3K/mTOR pathway controls release of angioregulators from primary human acute myeloid leukemia cells and their neighboring stromal cells. Oncotarget 4:830–843
Rosser CJ, Ross S, Chang M, Dai Y, Mengual L, Zhang G et al (2013) Multiplex protein signature for the detection of bladder cancer in voided urine samples. J Urol 190:2257–2262
Sheng J, Yu W, Gao X, Xu Z, Hu GF (2014) Angiogenin stimulates ribosomal RNA transcription by epigenetic activation of the ribosomal DNA promoter. J Cell Physiol 229:521–529
Suriano F, Altobelli E, Sergi F, Buscarini M (2013) Bladder cancer after radiotherapy for prostate cancer. Rev Urol 15:108–112
Trouillon R, Kang DK, Park H, Chang SI, O’Hare D (2010) Angiogenin induces nitric oxide synthesis in endothelial cells through PI-3 and Akt kinases. Biochemistry 49:3282–3288
Urquidi V, Goodison S, Kim J, Chang M, Dai Y, Rosser CJ (2012) Vascular endothelial growth factor, carbonic anhydrase 9, and angiogenin as urinary biomarkers for bladder cancer detection. Urology 79(1185):e1–6
Wei S, Gao X, Du J, Su J, Xu Z (2011) Angiogenin enhances cell migration by regulating stress fiber assembly and focal adhesion dynamics. PLoS One 6:e28797
Xiong D, Liou Y, Shu J, Li D, Zhang L, Chen J (2014) Down-regulating ribonuclease inhibitor enhances metastasis of bladder cancer cells through regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition and ILK signaling pathway. Exp Mol Pathol 96:411–421
Yao X, Li D, Xiong DM, Li L, Jiang R, Chen JX (2013) A novel role of ribonuclease inhibitor in regulation of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and ILK signaling pathway in bladder cancer cells. Cell Tissue Res 353:409–423
Yoshioka N, Wang L, Kishimoto K, Tsuji T, Hu GF (2006) A therapeutic target for prostate cancer based on angiogenin-stimulated angiogenesis and cancer cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:14519–14524
Yuan Y, Wang F, Liu XH, Gong DJ, Cheng HZ, Huang SD (2009) Angiogenin is involved in lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation and angiogenesis. Lung Cancer 66:28–36
Zhu J, Sheng J, Dong H, Kang L, Ang J, Xu Z (2013) Phospholipid scramblase 1 functionally interacts with angiogenin and regulates angiogenin-enhanced rRNA transcription. Cell Physiol Biochem 32:1695–1706
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81172424 and 81372203).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jing Shu, Mengge Huang have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shu, J., Huang, M., Tian, Q. et al. Downregulation of angiogenin inhibits the growth and induces apoptosis in human bladder cancer cells through regulating AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. J Mol Hist 46, 157–171 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-014-9608-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-014-9608-x