Abstract
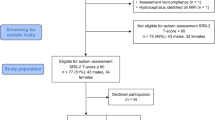
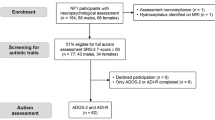
Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1) is a common autosomal dominant single-gene disorder, in which the co-occurrence of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) has attracted considerable research interest recently with prevalence estimates of 21–40 %. However, detailed characterization of the ASD behavioral phenotype in NF1 is still lacking. This study characterized the phenotypic profile of ASD symptomatology presenting in 4–16 year old children with NF1 (n = 36) using evidence from parent-rated Social Responsiveness Scale and researcher autism diagnostic observation Scale-2. Compared to IQ-matched reference groups of children with autism and ASD, the NF1 profile shows overall similarity but improved eye contact, less repetitive behaviors and better language skills.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahams, B. S., & Geschwind, D. H. (2008). Advances in autism genetics: On the threshold of a new neurobiology [Research support, N.I.H., extramural research support, Non-U.S. gov’t review]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 9(5), 341–355. doi:10.1038/nrg2346.
Acosta, M., Kardel, P., Walsh, K., Rosenbaum, K., Gioia, G., & Packer, R. (2011). Lovastatin as treatment for neurocognitive deficits in neurofibromatosis type 1: Phase 1 study. Pediatric Neurology, 45, 241–245.
Adviento, B., Corbin, I. L., Widjaja, F., Desachy, G., Enrique, N., Rosser, T., et al. (2014). Autism traits in the RASopathies. Journal of Medical Genetics, 51(1), 10–20. doi:10.1136/jmedgenet-2013-101951jmedgenet-2013-101951.
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Publishing.
Baird, G., Simonoff, E., Pickles, A., Chandler, S., Loucas, T., Meldrum, D., et al. (2006). Prevalence of disorders of the autism spectrum in a population cohort of children in south thames: The special needs and autism project (SNAP). The Lancet, 15(9531), 210–215.
Barton, B., & North, K. (2004). Social skills of children with neurofibromatosis type 1. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 46, 553–563.
Bruining, H., Eijkemans, M. J., Kas, M. J., Curran, S. R., Vorstman, J. A., & Bolton, P. F. (2014). Behavioral signatures related to genetic disorders in autism. Molecular Autism, 5(1), 11. doi:10.1186/2040-2392-5-112040-2392-5-11.
Constantino, J., Davis, S., Todd, R., Schindler, M.K., Gross, M., Brophy, S., et al. (2003). Validation of a brief quantitative measure of autistic traits: Comparison of the social responsiveness scale with the autism diagnostic interview-revised. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 33(4), 427–433.
Coude, F., Mignot, C., Lyonnet, S., & Munnich, A. (2007). Early grade repetition and inattention associated with neurofibromatosis type 1. Journal of Attention Disorders, 11, 101–105.
Costa, R., Federov, N., Kogan, J., Murphy, G., Stern, J., Ohno, M., et al. (2002). Mechanism for the learning deficits in a mouse model of neurofibromatosis type 1. Nature, 415, 526–530.
Deardorf MA, Clark DM, & Krantz ID (2005). Cornelia de Lange Syndrome. GeneReviewsTM[Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle.
Diggs-Andrews, K. A., & Gutmann, D. H. (2013). Modeling cognitive dysfunction in neurofibromatosis-1. Trends in Neurosciences, 36(4), 237–247. doi:10.1016/jtins.2012.12.002S0166-2236(12)00217-2.
Evans, D. G., Howard, E., Giblin, C., Clancy, T., Spencer, H., Huson, S. M., et al. (2010). Birth incidence and prevalence of tumor-prone syndromes: Estimates from a UK family genetic register service. [Research support, Non-U.S. Gov’t]. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A, 152A(2), 327–332. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.33139.
Fombonne, E., du Mazaubrun, C., Cans, C., & Grandjean, H. (1997). Autism and associated medical disorders in a large French epidemiological sample. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 36, 1561–1569.
Garg, S., Green, J., Leadbitter, K., Emsley, R., Lehtonen, A., Evans, D. G., et al. (2013). Neurofibromatosis type 1 and autism spectrum disorder. Pediatrics, 132(6), e1642–e1648. doi:10.1542/peds.2013-1868peds.2013-1868.
Geschwind, D. H. (2011). Genetics of autism spectrum disorders. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 15(9), 409–416. doi:10.1016/j.tics.2011.07.003S1364-6613(11)00145-8.
Gillberg, C., & Forsell, C. (1984). Childhood psychosis and neurofibromatosis—more than a coincidence? Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 14(1), 1–8.
Gotham, K., Pickles, A., & Lord, C. (2012). Trajectories of autism severity in children using standardized ADOS scores. Pediatrics, 130(5), e1278–e1284. doi:10.1542/peds.2011-3668peds.2011-3668.
Huijbregts, S., Jahja, R., De Sonneville, L., De Breij, S., & Swaab-Barneveld, H. (2010). Social information processing in children and adolescents with neurofibromatosis type 1. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 52(7), 620–625.
Kallarackal, A. J., Simard, J. M., & Bailey, A. M. (2013). The effect of apamin, a small conductance calcium activated potassium (SK) channel blocker, on a mouse model of neurofibromatosis 1. Behavioural Brain Research, 237, 71–75. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2012.09.009S0166-4328(12)00595-5.
Krab, L., de Goede-Bolder, A., Aarsen, F., Pluijm, S., Bouman, M., van der Geest, J., et al. (2008). Effect of simvastatin on cognitive functioning in children with neurofibromatosis type 1: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA, 300(3), 287–294.
Lehtonen, A., Howie, E., Trump, D., & Huson, S. M. (2013). Behaviour in children with neurofibromatosis type 1: Cognition, executive function, attention, emotion, and social competence. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 55(2), 111–125. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8749.2012.04399.x.
Lord, C., Rutter, M., DiLavore, P. C., Risi, S., Gotham, K., & Bishop, S. L. (2012). Autism diagnostic observation schedule, second edition (ADOS-2) manual (part I): Modules 1-4. Torrance, CA: Western Psychological Services.
Mautner, V. F., Kluwe, L., Friedrich, R. E., Roehl, A. C., Bammert, S., Högel, J., et al. (2010). Clinical characterisation of 29 neurofibromatosis type-1 patients with molecularly ascertained 1.4 Mb type-1 NF1 deletions. Journal of Medical Genetics, 47(9), 623–630.
Moss, J., Howlin, P., Magiati, I., & Oliver, C. (2012). Characteristics of autism spectrum disorder in Cornelia de Lange syndrome. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 53(8), 883–891. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2012.02540.x.
Mouridsen, S., Andersen, L., Sörensen, S., Rich, B., & Isager, T. (1992). Neurofibromatosis in infantile autism and other types of childhood psychoses. Acta Paedopsychiatrica: International Journal of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 55, 15–18.
National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Conference. (1988). Neurofibromatosis conference statement. Archives of Neurology, 45, 575–578.
Noll, R., Reiter-Purtill, J., Moore, B., Schorry, E., Lovell, A., Vannatta, K., et al. (2007). Social, emotional, and behavioral functioning of children with NF1. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A, 143A, 2261–2273.
Oliver, C., Berg, K., Moss, J., Arron, K., & Burbidge, C. (2011). Delineation of behavioral phenotypes in genetic syndromes: Characteristics of autism spectrum disorder, affect and hyperactivity. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 41(8), 1019–1032. doi:10.1007/s10803-010-1125-5.
Oliver, C., Horsler, K., Berg, K., Bellamy, G., Dick, K., & Griffiths, E. (2007). Genomic imprinting and the expression of affect in Angelman syndrome: What’s in the smile? Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 48(6), 571–579. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2007.01736.x.
Pinto, D., Delaby, E., Merico, D., Barbosa, M., Merikangas, A., Klei, L., et al. (2014). Convergence of genes and cellular pathways dysregulated in autism spectrum disorders. The American Journal of Human Genetics, 94(5), 677–694. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2014.03.018S0002-9297(14)00150-5.
Plasschaert, E., Descheemaeker, M. J., Van Eylen, L., Noens, I., Steyaert, J., & Legius, E. (2014). Prevalence of autism spectrum disorder symptoms in children with neurofibromatosis type 1. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part B: Neuropsychiatric Genetics. doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.32280.
Rogers, S. J., Wehner, D. E., & Hagerman, R. (2001). The behavioral phenotype in fragile X: Symptoms of autism in very young children with fragile X syndrome, idiopathic autism, and other developmental disorders. Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics, 22(6), 409–417.
Rudacille, D. (2011). How many tests does it take to diagnose autism? http://sfari.org/news-and-opinion/news/2011/how-many-tests-does-it-take-to-diagnose-autism. Accessed 9 July 2014.
Simonoff, E., Pickles, A., Charman, T., Chandler, S., Loucas, T., & Baird, G. (2008). Psychiatric disorders in children with autism spectrum disorders: Prevalence, comorbidity, and associated factors in a population-derived sample. Journal of American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 47(8), 921–929.
Skuse, D. H. (2007). Rethinking the nature of genetic vulnerability to autistic spectrum disorders. [Research support, N.I.H., extramural research support, Non-U.S. Gov’t]. Trends in Genetics, 23(8), 387–395. doi:10.1016/j.tig.2007.06.003.
Tordjman, S., Anderson, G. M., Botbol, M., Toutain, A., Sarda, P., Carlier, M., et al. (2012). Autistic disorder in patients with Williams-Beuren syndrome: A reconsideration of the Williams-Beuren syndrome phenotype. PLoS ONE, 7(3), e30778. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0030778PONE-D-11-09003.
van der Vaart, T., Plasschaert, E., Rietman, A. B., Renard, M., Oostenbrink, R., Vogels, A., et al. (2013). Simvastatin for cognitive deficits and behavioural problems in patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1-SIMCODA): A randomised, placebo-controlled trial. The Lancet Neurology, 12(11), 1076–1083. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70227-8S1474-4422(13)70227-8.
Walsh, K. S., Velez, J. I., Kardel, P. G., Imas, D. M., Muenke, M., Packer, R. J., et al. (2013). Symptomatology of autism spectrum disorder in a population with neurofibromatosis type 1. [Research Support, N.I.H., Extramural]. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 55(2), 131–138. doi:10.1111/dmcn.12038.
Wechsler, D. (2004). The Wechsler intelligence scale for children—fourth edition. London: Pearson Assessment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Shruti Garg and Ellen Plasschaert have contributed equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garg, S., Plasschaert, E., Descheemaeker, MJ. et al. Autism Spectrum Disorder Profile in Neurofibromatosis Type I. J Autism Dev Disord 45, 1649–1657 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-014-2321-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-014-2321-5