Abstract
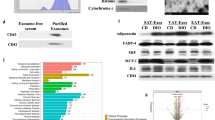
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) such as exosomes are secretory vesicles that act as autocrine, paracrine, or endocrine messengers; mediate intercellular cross-talk; and carry a cargo of various proteins. Because EVs can be transported to recipient cells via circulation, many researchers have been studying EVs from immune cells or cancer cells. Adipocytes are also considered endocrine cells and secrete adipokines such as adiponectin, regulating a variety of intracellular signaling pathways. Expansion of adipose tissue in obesity alters adipokine secretion, thereby increasing the risk of metabolic diseases. Characterization of adipocyte-derived exosomes is necessary to explain the communication between adipocytes and other cell types. In the present study, to identify proteins associated with adipocyte-derived exosomes, we isolated exosomes from adipose tissue of obese diabetic and obese nondiabetic rats. We identified proteins by analyzing exosomes from obese rats with type 2 diabetes and their matched control littermates using nano-liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry coupled with label-free relative quantification. We identified 509 proteins from adipocytes including 81 known adipokines; ~78 % of all the identified proteins were categorized as exosome-associated proteins. Among the protein profiles, we uncovered 128 upregulated and 72 downregulated proteins, which are differentially expressed in OLETF adipocyte-derived exosomes. This study seems to demonstrate for the first time hundreds of proteins in exosomes released by adipocytes in obese rats and rats with type 2 diabetes. Thus, protein profiles of exosomes from adipocytes possibly indicate the transmission of signals as part of cell–cell communication and should further our understanding of obesity- and diabetes-related diseases.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EVs:
-
Extracellular vesicles
- LETO:
-
Long-Evans Tokushima Otsuka
- OLETF:
-
Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima fatty
- UPLC:
-
Ultra-performance liquid chromatography
- GPI:
-
Glycophosphatidylinositol
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscope
- NTA:
-
Nanoparticle tracking analysis
- TEABC:
-
Triethylammonium bicarbonate
- DDA:
-
Data-dependent analysis
References
Skog J, Wurdinger T, van Rijn S, Meijer DH, Gainche L, Sena-Esteves M, Curry WT Jr, Carter BS, Krichevsky AM, Breakefield XO (2008) Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat Cell Biol 10(12):1470–1476. doi:10.1038/ncb1800
Valadi H, Ekstrom K, Bossios A, Sjostrand M, Lee JJ, Lotvall JO (2007) Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol 9(6):654–659. doi:10.1038/ncb1596
Deng ZB, Poliakov A, Hardy RW, Clements R, Liu C, Liu Y, Wang J, Xiang X, Zhang S, Zhuang X, Shah SV, Sun D, Michalek S, Grizzle WE, Garvey T, Mobley J, Zhang HG (2009) Adipose tissue exosome-like vesicles mediate activation of macrophage-induced insulin resistance. Diabetes 58(11):2498–2505. doi:10.2337/db09-0216
Gross JC, Chaudhary V, Bartscherer K, Boutros M (2012) Active Wnt proteins are secreted on exosomes. Nat Cell Biol 14(10):1036–1045. doi:10.1038/ncb2574
Luga V, Zhang L, Viloria-Petit AM, Ogunjimi AA, Inanlou MR, Chiu E, Buchanan M, Hosein AN, Basik M, Wrana JL (2012) Exosomes mediate stromal mobilization of autocrine Wnt-PCP signaling in breast cancer cell migration. Cell 151(7):1542–1556. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.11.024
Peinado H, Aleckovic M, Lavotshkin S, Matei I, Costa-Silva B, Moreno-Bueno G, Hergueta-Redondo M, Williams C, Garcia-Santos G, Ghajar C, Nitadori-Hoshino A, Hoffman C, Badal K, Garcia BA, Callahan MK, Yuan J, Martins VR, Skog J, Kaplan RN, Brady MS, Wolchok JD, Chapman PB, Kang Y, Bromberg J, Lyden D (2012) Melanoma exosomes educate bone marrow progenitor cells toward a pro-metastatic phenotype through MET. Nat Med 18(6):883–891. doi:10.1038/nm.2753
Moon PG, You S, Lee JE, Hwang D, Baek MC (2011) Urinary exosomes and proteomics. Mass Spectrom Rev 30(6):1185–1202. doi:10.1002/mas.20319
Antonyak MA, Li B, Boroughs LK, Johnson JL, Druso JE, Bryant KL, Holowka DA, Cerione RA (2011) Cancer cell-derived microvesicles induce transformation by transferring tissue transglutaminase and fibronectin to recipient cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(12):4852–4857. doi:10.1073/pnas.1017667108
Sano S, Izumi Y, Yamaguchi T, Yamazaki T, Tanaka M, Shiota M, Osada-Oka M, Nakamura Y, Wei M, Wanibuchi H, Iwao H, Yoshiyama M (2014) Lipid synthesis is promoted by hypoxic adipocyte-derived exosomes in 3T3-L1 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 445(2):327–333. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.01.183
Muller G, Jung C, Straub J, Wied S, Kramer W (2009) Induced release of membrane vesicles from rat adipocytes containing glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored microdomain and lipid droplet signalling proteins. Cell Signal 21(2):324–338. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.10.021
Muller G, Schneider M, Biemer-Daub G, Wied S (2011) Microvesicles released from rat adipocytes and harboring glucosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins transfer RNA stimulating lipid synthesis. Cell Signal 23(7):1207–1223. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.03.013
Phoonsawat W, Aoki-Yoshida A, Tsuruta T, Sonoyama K (2014) Adiponectin is partially associated with exosomes in mouse serum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 448(3):261–266. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.04.114
Wellen KE, Hotamisligil GS (2005) Inflammation, stress, and diabetes. J Clin Investig 115(5):1111–1119. doi:10.1172/JCI25102
Kershaw EE, Flier JS (2004) Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism 89(6):2548–2556. doi:10.1210/jc.2004-0395
Scherer PE (2006) Adipose tissue: from lipid storage compartment to endocrine organ. Diabetes 55(6):1537–1545. doi:10.2337/db06-0263
Kannel WB, Cupples LA, Ramaswami R, Stokes J 3rd, Kreger BE, Higgins M (1991) Regional obesity and risk of cardiovascular disease; the Framingham Study. J Clin Epidemiol 44(2):183–190
Maeda K, Okubo K, Shimomura I, Mizuno K, Matsuzawa Y, Matsubara K (1997) Analysis of an expression profile of genes in the human adipose tissue. Gene 190(2):227–235
Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS, Spiegelman BM (1993) Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science 259(5091):87–91
Kobayashi K (2005) Adipokines: therapeutic targets for metabolic syndrome. Curr Drug Targets 6(4):525–529
Matsuzawa Y (2005) White adipose tissue and cardiovascular disease. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metabol 19(4):637–647. doi:10.1016/j.beem.2005.07.001
Lehr S, Hartwig S, Lamers D, Famulla S, Muller S, Hanisch FG, Cuvelier C, Ruige J, Eckardt K, Ouwens DM, Sell H, Eckel J (2012) Identification and validation of novel adipokines released from primary human adipocytes. Mol Cell Proteomics : MCP 11(1):M111 010504. doi:10.1074/mcp.M111.010504
Ishida K, Mizuno A, Min Z, Sano T, Shima K (1995) Which is the primary etiologic event in Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty rats, a model of spontaneous non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, insulin resistance, or impaired insulin secretion? Metab Clin Exp 44(7):940–945
Kawano K, Hirashima T, Mori S, Saitoh Y, Kurosumi M, Natori T (1992) Spontaneous long-term hyperglycemic rat with diabetic complications. Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) strain. Diabetes 41(11):1422–1428
Kawano K, Hirashima T, Mori S, Natori T (1994) OLETF (Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty) rat: a new NIDDM rat strain. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 24(Suppl):S317–S320
Muller G, Ertl J, Gerl M, Preibisch G (1997) Leptin impairs metabolic actions of insulin in isolated rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem 272(16):10585–10593
Cho YE, Singh TS, Lee HC, Moon PG, Lee JE, Lee MH, Choi EC, Chen YJ, Kim SH, Baek MC (2012) In-depth identification of pathways related to cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity through an integrative method based on an informatics-assisted label-free protein quantitation and microarray gene expression approach. Mol Cell Proteomics MCP 11(1):M111 010884. doi:10.1074/mcp.M111.010884
Lee JE, Park JH, Moon PG, Baek MC (2013) Identification of differentially expressed proteins by treatment with PUGNAc in 3T3-L1 adipocytes through analysis of ATP-binding proteome. Proteomics 13(20):2998–3012. doi:10.1002/pmic.201200549
Tsou CC, Tsai CF, Tsui YH, Sudhir PR, Wang YT, Chen YJ, Chen JY, Sung TY, Hsu WL (2010) IDEAL-Q, an automated tool for label-free quantitation analysis using an efficient peptide alignment approach and spectral data validation. Mol Cell Proteomics MCP 9(1):131–144. doi:10.1074/mcp.M900177-MCP200
Moon PG, Kwack MH, Lee JE, Cho YE, Park JH, Hwang D, Kim MK, Kim JC, Sung YK, Baek MC (2013) Proteomic analysis of balding and non-balding mesenchyme-derived dermal papilla cells from androgenetic alopecia patients using on-line two-dimensional reversed phase-reversed phase LC-MS/MS. J Proteomics 85:174–191. doi:10.1016/j.jprot.2013.04.004
Muller G, Jung C, Wied S, Biemer-Daub G (2009) Induced translocation of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins from lipid droplets to adiposomes in rat adipocytes. Br J Pharmacol 158(3):749–770. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00360.x
Kim HS, Choi DY, Yun SJ, Choi SM, Kang JW, Jung JW, Hwang D, Kim KP, Kim DW (2012) Proteomic analysis of microvesicles derived from human mesenchymal stem cells. J Proteome Res 11(2):839–849. doi:10.1021/pr200682z
Hwang HH, Moon PG, Lee JE, Kim JG, Lee W, Ryu SH, Baek MC (2011) Identification of the target proteins of rosiglitazone in 3T3-L1 adipocytes through proteomic analysis of cytosolic and secreted proteins. Mol Cells 31(3):239–246. doi:10.1007/s10059-011-0026-6
Ertunc ME, Sikkeland J, Fenaroli F, Griffiths G, Daniels MP, Cao H, Saatcioglu F, Hotamisligil GS (2015) Secretion of fatty acid binding protein aP2 from adipocytes through a nonclassical pathway in response to adipocyte lipase activity. J Lipid Res 56(2):423–434. doi:10.1194/jlr.M055798
Aoki N, Yokoyama R, Asai N, Ohki M, Ohki Y, Kusubata K, Heissig B, Hattori K, Nakagawa Y, Matsuda T (2010) Adipocyte-derived microvesicles are associated with multiple angiogenic factors and induce angiogenesis in vivo and in vitro. Endocrinology 151(6):2567–2576. doi:10.1210/en.2009-1023
Muller G, Schneider M, Biemer-Daub G, Wied S (2011) Upregulation of lipid synthesis in small rat adipocytes by microvesicle-associated CD73 from large adipocytes. Obesity 19(8):1531–1544. doi:10.1038/oby.2011.29
Koeck ES, Iordanskaia T, Sevilla S, Ferrante SC, Hubal MJ, Freishtat RJ, Nadler EP (2014) Adipocyte exosomes induce transforming growth factor beta pathway dysregulation in hepatocytes: a novel paradigm for obesity-related liver disease. J Surg Res 192(2):268–275. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2014.06.050
Shono S, Kose H, Yamada T, Matsumoto K (2007) Proteomic analysis of a diabetic congenic rat identified age-dependent alteration of an acidic protein. J Med Investig JMI 54(3–4):289–294
Nakatani S, Kakehashi A, Ishimura E, Yamano S, Mori K, Wei M, Inaba M, Wanibuchi H (2011) Targeted proteomics of isolated glomeruli from the kidneys of diabetic rats: sorbin and SH3 domain containing 2 is a novel protein associated with diabetic nephropathy. Exp Diabetes Res 2011:979354. doi:10.1155/2011/979354
Oh-Ishi M, Satoh M, Maeda T (2000) Preparative two-dimensional gel electrophoresis with agarose gels in the first dimension for high molecular mass proteins. Electrophoresis 21(9):1653–1669. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1522-2683(20000501)21:9<1653:AID-ELPS1653>3.0.CO;2-9
Catalan V, Gomez-Ambrosi J, Rodriguez A, Silva C, Rotellar F, Gil MJ, Cienfuegos JA, Salvador J, Fruhbeck G (2008) Expression of caveolin-1 in human adipose tissue is upregulated in obesity and obesity-associated type 2 diabetes mellitus and related to inflammation. Clin Endocrinol 68(2):213–219. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.2007.03021.x
Otsu K, Toya Y, Oshikawa J, Kurotani R, Yazawa T, Sato M, Yokoyama U, Umemura S, Minamisawa S, Okumura S, Ishikawa Y (2010) Caveolin gene transfer improves glucose metabolism in diabetic mice. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 298(3):C450–C456. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00077.2009
Wang H, Eckel RH (2009) Lipoprotein lipase: from gene to obesity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 297(2):E271–E288. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.90920.2008
Hida K, Wada J, Zhang H, Hiragushi K, Tsuchiyama Y, Shikata K, Makino H (2000) Identification of genes specifically expressed in the accumulated visceral adipose tissue of OLETF rats. J Lipid Res 41(10):1615–1622
Lee DH, Park DB, Lee YK, An CS, Oh YS, Kang JS, Kang SH, Chung MY (2005) The effects of thiazolidinedione treatment on the regulations of aquaglyceroporins and glycerol kinase in OLETF rats. Metab Clin Exp 54(10):1282–1289. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2005.04.015
Rodriguez A, Catalan V, Gomez-Ambrosi J, Fruhbeck G (2006) Role of aquaporin-7 in the pathophysiological control of fat accumulation in mice. FEBS Lett 580(20):4771–4776. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2006.07.080
Burkart A, Shi X, Chouinard M, Corvera S (2011) Adenylate kinase 2 links mitochondrial energy metabolism to the induction of the unfolded protein response. J Biol Chem 286(6):4081–4089. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.134106
Sugimoto K, Tsuruoka S, Fujimura A (2001) Effect of enalapril on diabetic nephropathy in OLETF rats: the role of an anti-oxidative action in its protective properties. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 28(10):826–830
Okuno Y, Matsuda M, Kobayashi H, Morita K, Suzuki E, Fukuhara A, Komuro R, Shimabukuro M, Shimomura I (2008) Adipose expression of catalase is regulated via a novel remote PPARgamma-responsive region. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 366(3):698–704. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.12.001
Quiroga AD, Lian J, Lehner R (2012) Carboxylesterase1/Esterase-x regulates chylomicron production in mice. PLoS One 7(11):e49515. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0049515
Quiroga AD, Li L, Trotzmuller M, Nelson R, Proctor SD, Kofeler H, Lehner R (2012) Deficiency of carboxylesterase 1/esterase-x results in obesity, hepatic steatosis, and hyperlipidemia. Hepatology 56(6):2188–2198. doi:10.1002/hep.25961
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the grant of Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2010-0022811 to M.C.B.) and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (2014R1A5A2009242 to M.C.B.) and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant (NRF-2013R1A6A3A01024597 to P.G.M.).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with protocols approved by Kyungpook National University (KNU) Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees (IACUCs).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, JE., Moon, PG., Lee, IK. et al. Proteomic Analysis of Extracellular Vesicles Released by Adipocytes of Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) Rats. Protein J 34, 220–235 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10930-015-9616-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10930-015-9616-z