Abstract
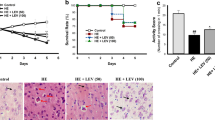
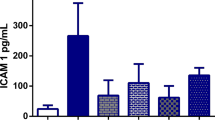
Cisplatin, one of the most active cytotoxic agents against cancer, has several toxicities. Hepatotoxicity is one of them occurred during high doses treatment. The aim of this study was to determine the effects of erdosteine against cisplatin-induced liver injury through tissue oxidant/antioxidant parameters and light microscopic evaluation. The rats were randomly divided into three groups: control (n=5), cisplatin (10 mg/kg, n=6) and cisplatin+erdosteine (50 mg/kg/day oral erdosteine, n=8) groups. The rats were sacrificed at the 5th day of cisplatin treatment. The liver tissues were examined with light microscopy and oxidant/antioxidant biochemical parameters. The malondialdehyde (MDA) and nitric oxide (NO) levels were increased in the cisplatin group in comparison with the control and cisplatin+erdosteine groups (p<0.05). There was no significant difference in MDA and NO levels between control and cisplatin+erdosteine groups. The activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) were higher in cisplatin+erdosteine group than cisplatin group (p<0.05). However, the CAT and GSH-Px activities were significantly lower in cisplatin group than in control group (p<0.05). The light microscopic examination revealed that cytoplasmic changes especially around cells of central vein were observed in cisplatin group. Hepatocellular vacuolization was seen in these cells. In the cisplatin plus erdosteine group, a decrease in cytoplasmic changes with the hepatocytes and sinusoidal dilatations around cells of central vein were noticed in as compared to cisplatin group. In the light of microscopic and biochemical results, it was concluded that cisplatin-induced liver damage in high dose and erdosteine prevented this toxic side effect by the way of its antioxidant and radical scavenging effects. (Mol Cell Biochem 278: 79–84, 2005)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van Basten JP, Schrafford-Koops H, Sleijfer DT, Pras E, Van Driel MF, Hoekstra HJ: Current concept about testicular cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol 23: 354–360, 1997
Thigpen T, Vance R, Puneky L, Khansurt T: Chemotherapy in advanced ovarian carcinoma: Current standards of care based on randomized trials. Gynecol Oncol 55: 97–607, 1994
Mollman JE, Glover DJ, Hogan WM, Furman RE: Cisplatin neurophaty risk factors, prognosis and protection by WR-2721. Cancer 61: 2192–2195, 1988
Screnci D, McKeage MJ: Platinum neurotoxicity: Clinical profiles, experimental models and neuroprotective approaches. J Inorg Biochem 77: 105–110, 1999
Weijl NI, Cleton FJ, Osanto S: Free radicals and antioxidants in chemotherapy-induced toxicity. Cancer Treat Rev 23: 209–240, 1997
Naziroglu M, Karaoglu A, Aksoy AO: Selenium and high dose vitamin E administration protects cisplatin-induced oxidative damage to renal, liver and lens tissues in rats. Toxicology 195: 221–230, 2004
Ozyurt H, Yıldırım Z, Kotuk M, Yılmaz HR, Yagmurca M, Iraz M, Sögüt S, Gergerlioglu S: Cisplatin-induced acute renal failure is ameliorated by erdosteine in a dose-dependent manner. J Appl Toxicol 24: 269–275, 2004
Fadillioglu E, Oztas E, Erdogan H, Yagmurca M, Sogut S, Ucar M, Irmak MK: Protective effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester on doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats. J App. Toxicol 24: 47–52, 2004
Fadillioglu E, Erdogan H: Effects of erdosteine treatment against doxorubicin-induced toxicity through erythrocyte and plasma oxidant/antioxidant status in rats. Pharmacol Res 47: 317–322, 2003
Yagmurca M, Erdogan H, Iraz M, Songur A, Ucar M, Fadillioglu E: Caffeic acid phenethyl ester as a protective agent against doxorubicin nephrotoxicity in rats. Clinica Chimica Acta 348: 27–34, 2004
Akyol O, Herken H, Uz E, Fadıllıoğlu E, Ünal S, Söğüt S, Özyurt H,. Savaş HA: The indices of endogenous oxidative and antioxidative processes in plasma from schizophrenic patients. The possible role of oxidant/antioxidant imbalance. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Bio Psychiatry 26: 995–1005, 2002
Davis CA, Nick HS, Agarwal A: Manganese superoxide dismutase attenuates cisplatin-induced renal injury: Importance of superoxide. J Am Soc Nephrol 12: 2683–2690, 2001
Yildirim Z, Sogut S, Odaci E, Iraz M, Ozyurt H, Kotuk M, Akyol O: Oral erdosteine administration attenuates cisplatininduced renal tubular damage in rats. Pharmacol Res 47: 149–156, 2003
Gazzani G, Fregnan GB, Vandoni G: In vitro protection by erdosteine against oxidative inactivation of alpha-1-antitrypsin by cigarette smoke. Respiration 55:113–118, 1989
Dechant KL, Noble S: Erdosteine. Drugs 52: 875–881, 1996
Fadillioglu E, Erdogan H, Sogut S, Kuku I: Protective effects of erdosteine against doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy in rats. J Appl Toxicol 23: 71–74, 2003
Sogut S, Ozyurt H, Armutcu F, Kart L, Iraz M, Akyol O, Ozen S, Kaplan S, Temel I, Yildirim Z: Erdosteine prevents bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 494: 213–220, 2004
Terzi A, Iraz M, Sahin S, Ilhan A, Idiz N, Fadillioglu E: Protective effects of erdosteine on rotenone induced oxidant injury in liver tissue. Toxicol Indust Health 20: 141–147, 2004
Irmak MK, Koltuksuz U, Kutlu NO, Yagmurca M, Ozyurt H, Karaman A, Akyol O: The effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester on ischemia-reperfusion injury in comparison with alpha-tocopherol in rat kidneys. Urol Res 29: 190–193, 2001
Lowry O, Rosenbraugh N, Farr L. Rondall R: Protein measurement with the folin-phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193: 265–275, 1951
Aebi H: Catalase. In: HU Bergmeyer (ed). Methods of Enzymatic Analysis, Academic Press, New York and London, 1974, pp. 673–677
Paglia DE, Valentine WN: Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med 70: 158–169, 1967
Esterbauer H, Cheeseman KH: Determination of aldehydic lipid peroxidation products: Malonaldehyde and 4-hydroxynonenal. In: Packer, AN Glazer (eds). Methods in Enzymology, V 186, Oxygen radicals in biological systems. Academic Press, California, 1990, pp. 407–421
Sun Y, Oberley LW, Li Y: A simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin Chem 34: 497–500, 1988
Cortas NK, Wakid NW: Determination of inorganic nitrate in serum and urine by a kinetic cadmium-reduction method. Clin Chem 36: 1440–1443, 1990
Zicca A, Cafaggi S, Mariggio MA, Vannozzi MO, Ottone M, Bocchini V, Caviglioli G, Viale M: Reduction of cisplatin hepatotoxicity by procainamide hydrochloride in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 442: 265–72, 2002
Vermorken JB, Pinedo HM: Gastrointestinal toxicity of cis-diammi- nedichloroplatinum(II). Neth J Med 25: 270–274, 1982
Jie l, Liu Y, Habeebu SSM, and Kalssen CD: Metallothionein (MT)-null mice are senstive to cispaltin-induced hepatotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 149: 24–31, 1998
Kobayashi K, Tsukamoto I: Prolonged Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) activation and the upregulation of p53 and p21 WAFI/CIPI preceded apopotosis in hepatocytes after partial hepatectomy and cisplatin. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1537: 79–88, 2001
Yilmaz HR, Sogut S, Ozyurt B, Ozugurlu F, Sahin S, Isik B, Uz E, Ozyurt H: The activities of liver adenosine deaminase, xanthine oxidase, catalase, superoxide dismutase enzymes and the levels of malondialdehyde and nitric oxide after cisplatin toxicity in rats: Protective effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester. Toxicol Indust Health 21: 67–73, 2005
Fadillioglu E, Yılmaz HR, Erdogan H, Sogut S: The activities of tissue xanthine oxidase and adenosine deaminase and the levels of hydroxyproline and nitric oxide in rat hearts subjected to doxorubicine: protective effect of erdosteine. Toxicology 191: 153–158, 2003
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koc, A., Duru, M., Ciralik, H. et al. Protective agent, erdosteine, against cisplatin-induced hepatic oxidant injury in rats. Mol Cell Biochem 278, 79–84 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-005-6630-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-005-6630-z