Abstract
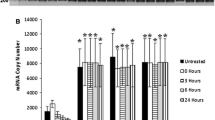
Production of heat shock protein 70 (HSP70/HSPA) is induced by a wide range of cellular stress conditions, such as cancer and hypoxia, with production also being linked to tumourigenesis. HSPA mRNA transcripts and proteins were examined in three human glioma cell lines, representing astrocytoma, oligodendroglioma and glioblastoma, plus 18 clinical brain tissue samples. GAPDH was used as a control gene throughout these studies and exhibited a consistent level of expression in a normal astrocyte cell line, tumourous cell lines and tissue samples. In contrast, the average HSPA mRNA copy numbers detected in glioblastoma tissue were between 1.8- and 8.8-fold higher than in lower grade glioma and control tissue, respectively, which is suggestive of a grade-related transcription profile. Similar patterns of grade-related expression were also observed in glioma cell lines. This study indicates for the first time that HSPA expression in glioma cells may possibly be grade related, and hence could have potential as a prognostic marker.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Graner MW, Raynes DA, Bigner DD, Guerriero V (2009) Heat shock protein 70-binding protein 1 is highly expressed in high-grade gliomas, interacts with multiple heat shock protein 70 family members, and specifically binds brain tumor cell surfaces. Cancer Sci 100:1870–1879
Ciocca DR, Calderwood SK (2005) Heat shock proteins in cancer: diagnostic, prognostic, predictive, and treatment implications. Cell Stress Chaperones 10:86–103
Oehler R, Schmierer B, Zellner M, Prohaska R, Roth E (2000) Endothelial cells downregulate expression of the 70 kDa heat shock protein during hypoxia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 274:542–547. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2000.3184
Kang EH, Kim DJ, Lee EY, Lee YJ, Lee EB, Song YW (2009) Downregulation of heat shock protein 70 protects rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes from nitric oxide-induced apoptosis. Arthritis Res Ther 11:R130. doi:10.1186/ar2797
Lanneau D, de Thonel A, Maurel S, Didelot C, Garrido C (2007) Apoptosis versus cell differentiation: role of heat shock proteins HSP90, HSP70 and HSP27. Prion 1:53–60
Beckmann RP, Mizzen LE, Welch WJ (1990) Interaction of Hsp 70 with newly synthesized proteins: implications for protein folding and assembly. Science 248:850–854
Seidberg NA, Clark RS, Zhang X, Lai Y, Chen M, Graham SH, Kochanek PM, Watkins SC, Marion DW (2003) Alterations in inducible 72-kDa heat shock protein and the chaperone cofactor BAG-1 in human brain after head injury. J Neurochem 84:514–521
Mayer MP, Bukau B (2005) Hsp70 chaperones: cellular functions and molecular mechanism. Cell Mol Life Sci 62:670–684. doi:10.1007/s00018-004-4464-6
Lindquist S, Craig EA (1988) The heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet 22:631–677. doi:10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.003215
Calderwood SK, Theriault JR, Gong J (2005) Message in a bottle: role of the 70-kDa heat shock protein family in anti-tumor immunity. Eur J Immunol 35:2518–2527. doi:10.1002/eji.200535002
Schmitt E, Gehrmann M, Brunet M, Multhoff G, Garrido C (2007) Intracellular and extracellular functions of heat shock proteins: repercussions in cancer therapy. J Leukoc Biol 81:15–27. doi:10.1189/jlb.0306167
Calderwood SK, Khaleque MA, Sawyer DB, Ciocca DR (2006) Heat shock proteins in cancer: chaperones of tumorigenesis. Trends Biochem Sci 31:164–172. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2006.01.006
Nylandsted J, Brand K, Jaattela M (2000) Heat shock protein 70 is required for the survival of cancer cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci 926:122–125
Ciocca DR, Rozados VR, Cuello Carrion FD, Gervasoni SI, Matar P, Scharovsky OG (2003) Hsp25 and Hsp70 in rodent tumors treated with doxorubicin and lovastatin. Cell Stress Chaperones 8:26–36
Rohde M, Daugaard M, Jensen MH, Helin K, Nylandsted J, Jaattela M (2005) Members of the heat-shock protein 70 family promote cancer cell growth by distinct mechanisms. Genes Dev 19:570–582. doi:10.1101/gad.305405
Li G, Xu Y, Guan D, Liu Z, Liu DX (2011) HSP70 protein promotes survival of C6 and U87 glioma cells by inhibition of ATF5 degradation. J Biol Chem 286:20251–20259. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.211771
Wei YQ, Zhao X, Kariya Y, Teshigawara K, Uchida A (1995) Inhibition of proliferation and induction of apoptosis by abrogation of heat-shock protein (HSP) 70 expression in tumor cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother 40:73–78
Nylandsted J, Rohde M, Brand K, Bastholm L, Elling F, Jaattela M (2000) Selective depletion of heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) activates a tumor-specific death program that is independent of caspases and bypasses Bcl-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:7871–7876
Chandana SR, Movva S, Arora M, Singh T (2008) Primary brain tumors in adults. Am Fam Physician 77:1423–1430
Khalil AA (2007) Biomarker discovery: a proteomic approach for brain cancer profiling. Cancer Sci 98:201–213. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2007.00374.x
Robins HI, Chang S, Butowski N, Mehta M (2007) Therapeutic advances for glioblastoma multiforme: current status and future prospects. Curr Oncol Rep 9:66–70
Stupp R, Hegi ME, van den Bent MJ, Mason WP, Weller M, Mirimanoff RO, Cairncross JG (2006) Changing paradigms—an update on the multidisciplinary management of malignant glioma. Oncologist 11:165–180
Patel R, Shervington L, Lea R, Shervington A (2008) Epigenetic silencing of telomerase and a non-alkylating agent as a novel therapeutic approach for glioma. Brain Res 1188:173–181. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2007.10.043
Santoro MG (2000) Heat shock factors and the control of the stress response. Biochem Pharmacol 59:55–63
Ciocca DR, Clark GM, Tandon AK, Fuqua SA, Welch WJ, McGuire WL (1993) Heat shock protein hsp70 in patients with axillary lymph node-negative breast cancer: prognostic implications. J Natl Cancer Inst 85:570–574
Soussi T, Lozano G (2005) p53 mutation heterogeneity in cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 331:834–842. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.03.190
Lebret T, Watson RW, Molinie V, O’Neill A, Gabriel C, Fitzpatrick JM, Botto H (2003) Heat shock proteins HSP27, HSP60, HSP70, and HSP90: expression in bladder carcinoma. Cancer 98:970–977. doi:10.1002/cncr.11594
Syrigos KN, Harrington KJ, Karayiannakis AJ, Sekara E, Chatziyianni E, Syrigou EI, Waxman J (2003) Clinical significance of heat shock protein-70 expression in bladder cancer. Urology 61:677–680
Piura B, Rabinovich A, Yavelsky V and Wolfson M (2002) Heat shock proteins and malignancies of the female genital tract. Harefuah 141:969–972, 1010, 1009
Thanner F, Sutterlin MW, Kapp M, Rieger L, Kristen P, Dietl J, Gassel AM, Muller T (2003) Heat-shock protein 70 as a prognostic marker in node-negative breast cancer. Anticancer Res 23:1057–1062
Ricaniadis N, Kataki A, Agnantis N, Androulakis G, Karakousis CP (2001) Long-term prognostic significance of HSP-70, c-myc and HLA-DR expression in patients with malignant melanoma. Eur J Surg Oncol 27:88–93. doi:10.1053/ejso.1999.1018
Santarosa M, Favaro D, Quaia M, Galligioni E (1997) Expression of heat shock protein 72 in renal cell carcinoma: possible role and prognostic implications in cancer patients. Eur J Cancer 33:873–877
Sagol O, Tuna B, Coker A, Karademir S, Obuz F, Astarcioglu H, Kupelioglu A, Astarcioglu I, Topalak O (2002) Immunohistochemical detection of pS2 protein and heat shock protein-70 in pancreatic adenocarcinomas. Relationship with disease extent and patient survival. Pathol Res Pract 198:77–84. doi:10.1078/0344-0338-00190
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Brain Tumour North West (BTNW) for providing the tissue for this study. This work was supported by a grant from the University of Central Lancashire and Sydney Driscoll Neuroscience Foundation (SDNF).
Conflict of interest
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beaman, G.M., Dennison, S.R., Chatfield, L.K. et al. Reliability of HSP70 (HSPA) expression as a prognostic marker in glioma. Mol Cell Biochem 393, 301–307 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2074-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2074-7