Abstract
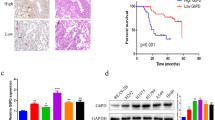
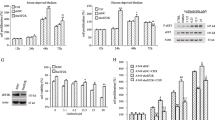
p90 ribosomal S6 kinase (p90RSK) constitutes a family of serine/threonine kinases that have been shown to be involved in cell proliferation of various malignancies via direct or indirect effects on the cell-cycle machinery. We investigated the role of p90RSK in lung adenocarcinomas and whether the inhibition of p90RSK diminishes cancer progression. Moreover, we investigated the involvement of glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β) and osteopontin (OPN) in the p90RSK-induced lung adenocarcinoma progression. p90RSK, OPN, and GSK-3β protein expressions were examined in the A549 human lung adenocarcinoma cell line in the presence and absence of BI-D1870 (BID), a p90RSK inhibitor. Gene expression of anti-apoptotic and pro-apoptotic markers namely Bcl2 and Bax, respectively, were studied by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. In addition, the A549 lung adenocarcinoma cell line was characterized for cell proliferation using the MTT assay and cell migration using the scratch migration assay. Our study revealed that total RSK1 protein expression is over expressed in the A549 human lung adenocarcinoma cell line, an effect which is significantly reduced upon pretreatment with BID (69.32 ± 12.41 % of control; P < 0.05). The inhibition of p90RSK also showed a significant suppression of cell proliferation (54.3 ± 6.73 % of control; P < 0.01) and cell migration (187.90 ± 16.10 % of control; P < 0.01). Treatment of the A549 cells with BID regressed the expression of Bcl2 mRNA (56.92 ± 6.07 % of control; P < 0.01). BID also regressed protein expression of OPN (79.57 ± 5.32 % of control; P < 0.05) and phospho-GSK-3β (73.04 ± 8.95 % of control; P < 0.05). The p90RSK has an essential role in promoting tumor growth and proliferation in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). BID may serve as an alternative cancer treatment in NSCLC.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- p90RSK:
-
p90 Ribosomal S6 kinase
- GSK:
-
Glycogen synthase kinase
- OPN:
-
Osteopontin
- BID:
-
BI-D1870
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinases
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2015) Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. doi:10.3322/caac.21254
Plaimee P, Weerapreeyakul N, Barusrux S, Johns NP (2015) Melatonin potentiates cisplatin-induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Cell Prolif 48:67–77. doi:10.1111/cpr.12158
Herbst RS, Heymach JV, Lippman SM (2008) Lung Cancer. N Engl J Med 359:1367–1380. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0802714
Larsen JE, Minna JD (2011) Molecular biology of lung cancer: clinical implications. Clin Chest Med 32:703–740. doi:10.1016/j.ccm.2011.08.003
Dela Cruz CS, Tanoue LT, Matthay RA (2011) Lung cancer: epidemiology, etiology, and prevention. Clin Chest Med 32:605–644. doi:10.1016/j.ccm.2011.09.001
Panov SZ (2005) Molecular biology of the lung cancer. Radiol Oncol 39:197–210
Gridelli C, Bareschino MA, Schettino C, Rossi A, Maione P, Ciardiello F (2007) Erlotinib in non-small cell lung cancer treatment: current status and future development. Oncologist 12:840–849. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.12-7-840
Anjum R, Blenis J (2008) The RSK family of kinases: emerging roles in cellular signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:747–758. doi:10.1038/nrm2509
Donati V, Boldrini L, Dell’Omodarme M, Prati MC, Faviana P, Camacci T, Lucchi M, Mussi A, Santoro M, Basolo F, Fontanini G (2005) Osteopontin expression and prognostic significance in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11:6459–6465. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0541
Mishra R (2010) Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta: can it be a target for oral cancer. Mol Cancer 9:144. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-9-144
Luo X, Ruhland MK, Pazolli E, Lind AC, Stewart SA (2011) Osteopontin stimulates preneoplastic cellular proliferation through activation of the MAPK pathway. Mol Cancer Res 9:1018–1029. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-10-0472
Lara R, Seckl MJ, Pardo OE (2013) The p90 RSK family members: common functions and isoform specificity. Cancer Res 73:5301–5308. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4448
Zeng J, Liu D, Qiu Z, Huang Y, Chen B, Wang L, Xu H, Huang N, Liu L, Li W (2014) GSK3beta overexpression indicates poor prognosis and its inhibition reduces cell proliferation and survival of non-small cell lung cancer cells. Plos One 9:e91231. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0091231
Aggarwal S, Kim SW, Ryu SH, Chung WC, Koo JS (2008) Growth suppression of lung cancer cells by targeting cyclic AMP response element-binding protein. Cancer Res 68:981–988. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-0249
Ballif BA, Blenis J (2001) Molecular mechanisms mediating mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase (MEK)-MAPK cell survival signals. Cell Growth Differ 12:397–408
Rangaswami H, Bulbule A, Kundu GC (2006) Osteopontin: role in cell signaling and cancer progression. Trends Cell Biol 16:79–87. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2005.12.005
Hoshino R, Chatani Y, Yamori T, Tsuruo T, Oka H, Yoshida O, Shimada Y, Ari-i S, Wada H, Fujimoto J, Kohno M (1999) Constitutive activation of the 41-/43-kDa mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway in human tumors. Oncogene 18:813–822. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202367
Roux PP, Richards SA, Blenis J (2003) Phosphorylation of p90 ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) regulates extracellular signal-regulated kinase docking and RSK activity. Mol Cell Biol 23:4796–4804. doi:10.1128/mcb.23.14.4796-4804.2003
Lara R, Mauri FA, Taylor H, Derua R, Shia A, Gray C, Nicols A, Shiner RJ, Schofield E, Bates PA, Waelkens E, Dallman M, Lamb J, Zicha D, Downward J, Seckl MJ, Pardo OE (2011) An siRNA screen identifies RSK1 as a key modulator of lung cancer metastasis. Oncogene 30:3513–3521. doi:10.1038/onc.2011.61
Sapkota GP, Cummings L, Newell FS, Armstrong C, Bain J, Frodin M, Grauert M, Hoffmann M, Schnapp G, Steegmaier M, Cohen P, Alessi DR (2007) BI-D1870 is a specific inhibitor of the p90 RSK (ribosomal S6 kinase) isoforms in vitro and in vivo. Biochem J 401:29–38. doi:10.1042/BJ20061088
Sulzmaier FJ, Ramos JW (2013) RSK isoforms in cancer cell invasion and metastasis. Cancer Res 73:6099–6105. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-1087
Deng X (2014) Bcl2 family functions as signaling target in nicotine-/NNK-induced survival of human lung cancer cells. Scientifica 2014:215426. doi:10.1155/2014/215426
Frame S, Cohen P (2001) GSK3 takes centre stage more than 20 years after its discovery. Biochem J 359:1–16
Shijubo N, Uede T, Kon S, Maeda M, Segawa T, Imada A, Hirasawa M, Abe S (1999) Vascular endothelial growth factor and osteopontin in stage I lung adenocarcinoma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 160:1269–1273. doi:10.1164/ajrccm.160.4.9807094
Peng B, Wang YH, Huang Z, Feng SJ, Wang YS (2014) Prognostic significance of osteopontin in patients with lung cancer: a meta-analysis. Int J Clin Exp Med 7:4616–4626
Lucien F, Brochu-Gaudreau K, Arsenault D, Harper K, Dubois CM (2011) Hypoxia-induced invadopodia formation involves activation of NHE-1 by the p90 ribosomal S6 kinase (p90RSK). Plos One 6:e28851. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0028851
Harguindey S, Arranz JL, Polo Orozco JD, Rauch C, Fais S, Cardone RA, Reshkin SJ (2013) Cariporide and other new and powerful NHE1 inhibitors as potentially selective anticancer drugs—an integral molecular/biochemical/metabolic/clinical approach after one hundred years of cancer research. J Transl Med 11:282. doi:10.1186/1479-5876-11-282
Cardone RA, Casavola V, Reshkin SJ (2005) The role of disturbed pH dynamics and the Na+/H+ exchanger in metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer 5:786–795. doi:10.1038/nrc1713
Li S, Bao P, Li Z, Ouyang H, Wu C, Qian G (2009) Inhibition of proliferation and apoptosis induced by a Na+/H+ exchanger-1 (NHE-1) antisense gene on drug-resistant human small cell lung cancer cells. Oncol Rep 21:1243–1249
Amith SR, Fong S, Baksh S, Fliegel L (2015) Na(+)/H(+) exchange in the tumour microenvironment: does NHE1 drive breast cancer carcinogenesis? Int J Dev Biol 59:367–377. doi:10.1387/ijdb.140336lf
Amith SR, Wilkinson JM, Fliegel L (2016) Na+/H+ exchanger NHE1 regulation modulates metastatic potential and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of triple-negative breast cancer cells. Oncotarget. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.8520
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Qatar University Internal Grant (QU-UG2013/2014).
Author contribution
Nabeel Abdulrahman, Noufira Poomakkoth, Maiy Jaballa, Sadaf Riaz, Somaya Abdelaziz, and Aya Issa performed the research. Nabeel Abdulrahman, Noufira Poomakkoth, and Fatima Mraiche provided intellectual contributions and research assistance. Nabeel Abdulrahman and Fatima Mraiche contributed in the analysis of the data. Nabeel Abdulrahman, Noufira Poomakkoth, Maiy Jaballa and Fatima Mraiche wrote the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdulrahman, N., Jaballah, M., Poomakkoth, N. et al. Inhibition of p90 ribosomal S6 kinase attenuates cell migration and proliferation of the human lung adenocarcinoma through phospho-GSK-3β and osteopontin. Mol Cell Biochem 418, 21–29 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-016-2727-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-016-2727-9