Abstract
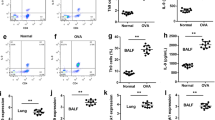
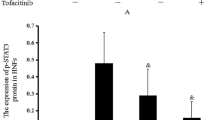
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) has recently been implicated as a key molecule for initiating allergic rhinitis (AR) at the cell-dendritic cell (DC) interface. Previous studies demonstrated that TSLP activated DCs to express more OX40 ligand (OX40L), which is associated with the initiation of T helper type 2 (Th2) cell responses. STAT phosphorylation has been reported to be promoted by TSLP. Thus, we investigated if the JAK/STAT pathway inhibitor CYT387 could affect TSLP-DC-mediated Th2 cell response in naive T cell and AR mice model. Western blot showed that the levels of phosphorylated JAK1, JAK2, STAT1, STAT3, and STAT5 were increased in TSLP-DCs, which can be offset by CYT387. Flow cytometry indicated that CYT387 had obviously down-regulated the surface maturation co-stimulatory molecules (CD11c, CD80, CD86, and MHCII) in DCs, which were increased by TSLP. Moreover, CYT387 markedly reduced the ability of TSLP-DCs to promote the differentiation of naive CD4+ T cells into IL-4-expressing Th2 cells. The histological examination showed that the CYT387-treated group showed less epithelial disruption, epithelial cell proliferation, and reduced eosinophil infiltration compared with AR group. Western blot and RT-PCR demonstrated that the expression of OX40L was increased in AR mice, but that it was decreased by CYT387. Furthermore, CYT387 treatment resulted in the reduction of IL-4 and IL-5 expression and increased IFN-γ level in AR mice, which was consistent with the levels of intracellular cytokine in Th2 cell. In conclusion, we suggest that blockading the JAK/STAT pathway restrains inflammatory Th2 cell response induced by TSLP-DCs in AR.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu Y, Lu X, Yu HJ et al (2010) The expression of osteopontin and its association with Clara cell 10 kDa protein in allergic rhinitis. Clin Exp Allergy 40:1632–1641
Meltzer EO, Blaiss MS, Derebery MJ et al (2009) Burden of allergic rhinitis: results from the Pediatric Allergies in America survey. J Allergy Clin Immunol 124:S43–S70
Brozek JL, Bousquet J, Baena-Cagnani CE et al (2010) Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) guidelines: 2010 revision. J Allergy Clin Immunol 126:466–476
Al-Shami A, Spolski R, Kelly J et al (2005) A role for TSLP in the development of inflammation in an asthma model. J Exp Med 202:829–839
Gauvreau GM, O’Byrne PM, Boulet LP et al (2014) Effects of an anti-TSLP antibody on allergen-induced asthmatic responses. N Engl J Med 370:2102–2110
Gao PS, Rafaels NM, Mu D et al (2010) Genetic variants in thymic stromal lymphopoietin are associated with atopic dermatitis and eczema herpeticum. J Allergy Clin Immunol 125(1403–1407):e1404
Mou Z, Xia J, Tan Y et al (2009) Overexpression of thymic stromal lymphopoietin in allergic rhinitis. Acta Otolaryngol 129:297–301
Akasaki S, Matsushita K, Kato Y et al (2016) Murine allergic rhinitis and nasal Th2 activation are mediated via TSLP- and IL-33-signaling pathways. Int Immunol 28:65–76
Salazar F, Ghaemmaghami AM (2013) Allergen recognition by innate immune cells: critical role of dendritic and epithelial cells. Front Immunol 4:356
Radulovic S, Calderon MA, Wilson D et al (2010) Sublingual immunotherapy for allergic rhinitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 12:CD002893
Ito T, Wang YH, Duramad O et al (2005) TSLP-activated dendritic cells induce an inflammatory T helper type 2 cell response through OX40 ligand. J Exp Med 202:1213–1223
Wang Q, Du J, Zhu J et al (2015) Thymic stromal lymphopoietin signaling in CD4(+) T cells is required for TH2 memory. J Allergy Clin Immunol 135(781–791):e783
Burrows KE, Dumont C, Thompson CL et al (2015) OX40 blockade inhibits house dust mite driven allergic lung inflammation in mice and in vitro allergic responses in humans. Eur J Immunol 45:1116–1128
Liu YJ (2007) Thymic stromal lymphopoietin and OX40 ligand pathway in the initiation of dendritic cell-mediated allergic inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol 120:238–244 (quiz 245–236)
Seshasayee D, Lee WP, Zhou M et al (2007) In vivo blockade of OX40 ligand inhibits thymic stromal lymphopoietin driven atopic inflammation. J Clin Invest 117:3868–3878
Zhang Y, Zhou B (2012) Functions of thymic stromal lymphopoietin in immunity and disease. Immunol Res 52:211–223
Ziegler SF (2010) The role of thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) in allergic disorders. Curr Opin Immunol 22:795–799
Ying S, O’Connor B, Ratoff J et al (2005) Thymic stromal lymphopoietin expression is increased in asthmatic airways and correlates with expression of Th2-attracting chemokines and disease severity. J Immunol 174:8183–8190
Ren X, Wang L, Wu X (2016) A potential link between TSLP/TSLPR/STAT5 and TLR2/MyD88/NFkappaB-p65 in human corneal epithelial cells for Aspergillus fumigatus tolerance. Mol Immunol 71:98–106
Takai T, Chen X, Xie Y et al (2014) TSLP expression induced via Toll-like receptor pathways in human keratinocytes. Methods Enzymol 535:371–387
Wohlmann A, Sebastian K, Borowski A et al (2010) Signal transduction by the atopy-associated human thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) receptor depends on Janus kinase function. Biol Chem 391:181–186
Reche PA, Soumelis V, Gorman DM et al (2001) Human thymic stromal lymphopoietin preferentially stimulates myeloid cells. J Immunol 167:336–343
Rochman Y, Kashyap M, Robinson GW et al (2010) Thymic stromal lymphopoietin-mediated STAT5 phosphorylation via kinases JAK1 and JAK2 reveals a key difference from IL-7-induced signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:19455–19460
Roney K (2013) Bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. Methods Mol Biol 1031:71–76
Fu RH, Wang YC, Liu SP et al (2014) Dryocrassin suppresses immunostimulatory function of dendritic cells and prolongs skin allograft survival. Cell Transplant 23:641–656
Lowe B, Avila HA, Bloom FR et al (2003) Quantitation of gene expression in neural precursors by reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction using self-quenched, fluorogenic primers. Anal Biochem 315:95–105
Asher MI, Montefort S, Bjorksten B et al (2006) Worldwide time trends in the prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and eczema in childhood: ISAAC Phases One and Three repeat multicountry cross-sectional surveys. The Lancet 368:733–743
Ren JJ, Yu Z, Yang FL et al (2015) Effects of bifidobacterium breve feeding strategy and delivery modes on experimental Allergic Rhinitis mice. PLoS One 10:e0140018
Zhu DD, Zhu XW, Jiang XD et al (2009) Thymic stromal lymphopoietin expression is increased in nasal epithelial cells of patients with mugwort pollen sensitive-seasonal allergic rhinitis. Chin Med J 122:2303–2307
Akbari O, Freeman GJ, Meyer EH et al (2002) Antigen-specific regulatory T cells develop via the ICOS-ICOS-ligand pathway and inhibit allergen-induced airway hyperreactivity. Nat Med 8:1024–1032
de Lastic AL, Rodi M, Mouzaki A (2016) Effect of dendritic cell state and antigen-presentation conditions on resulting T-cell phenotypes and Th cytokine profiles. Immunobiology 221:862–870
Arima K, Watanabe N, Hanabuchi S et al (2010) Distinct signal codes generate dendritic cell functional plasticity. Sci Signal 3:ra4
Quentmeier H, Drexler HG, Fleckenstein D et al (2001) Cloning of human thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) and signaling mechanisms leading to proliferation. Leukemia 15:1286–1292
Liu YJ (2001) Dendritic cell subsets and lineages, and their functions in innate and adaptive immunity. Cell 106:259–262
Marten A, Greten T, Ziske C et al (2002) Generation of activated and antigen-specific T cells with cytotoxic activity after co-culture with dendritic cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother 51:25–32
Mansilla FC, Quintana ME, Langellotti C et al (2016) Immunization with Neospora caninum profilin induces limited protection and a regulatory T-cell response in mice. Exp Parasitol 160:1–10
Zheng Y, Manzotti CN, Liu M et al (2004) CD86 and CD80 differentially modulate the suppressive function of human regulatory T cells. J Immunol 172:2778–2784
Lim TS, Goh JK, Mortellaro A et al (2012) CD80 and CD86 differentially regulate mechanical interactions of T-cells with antigen-presenting dendritic cells and B-cells. PLoS One 7:e45185
Soumelis V, Reche PA, Kanzler H et al (2002) Human epithelial cells trigger dendritic cell mediated allergic inflammation by producing TSLP. Nat Immunol 3:673–680
Gonzalez-Rey E, Fernandez-Martin A, Chorny A et al (2006) Therapeutic effect of vasoactive intestinal peptide on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: down-regulation of inflammatory and autoimmune responses. Am J Pathol 168:1179–1188
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81300808, 81200731, 81470031).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Additional information
Zhaohui Shi and Weihong Jiang have contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Z., Jiang, W., Wang, M. et al. Inhibition of JAK/STAT pathway restrains TSLP-activated dendritic cells mediated inflammatory T helper type 2 cell response in allergic rhinitis. Mol Cell Biochem 430, 161–169 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-2963-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-2963-7