Abstract
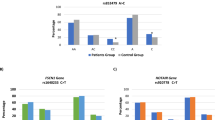
This study aimed to perform a meta-analysis to assess the association of survivin −31 G/C promoter polymorphism and cancer risk. Thirteen case–control studies identified through PubMed and published between 2007 and 2011 with a total of 3329 cancer cases and 3979 controls were included in this meta-analysis. Odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (95% CI) were used to investigate the strength of the association. Overall, the pooled analysis showed that survivin −31C allele was associated with 1.27 fold increased risk of cancer compared with the −31G allele (95% CI = 1.091–1.479; random model). Subgroup analyses based on type of cancer and ethnicity were also performed, and results indicated that survivin −31G/C polymorphism was not associated with risk of gastric cancer [OR = 2.879; 95% CI = 0.553–15.004) for CC vs.GG] and esophageal cancer [OR = 1.352; 95% CI = 0.494–3.699) for CC vs.GG]. Stratification on the basis of ethnicity showed that the risk due to −31C allele was significant only in Asian population [OR = 1.894; 95% CI = 1.206–2.974 for CC vs.GG]. The present meta-analysis suggests an important role of survivin −31 G/C polymorphism with cancer risk especially in Asian population. However, further studies with larger sample size are required to draw more comprehensive conclusions and provide more precise evidence in individual cancers.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altieri DC, Marchisio PC (1999) Survivin apoptosis: an interloper between cell death and cell proliferation in cancer. Lab Invest 79(11):1327–1333
Altieri DC (2003) Validating survivin as a cancer therapeutic target. Nat Rev Cancer 3(1):46–54. doi:10.1038/nrc968
Adida C, Crotty PL, McGrath J, Berrebi D, Diebold J, Altieri DC (1998) Developmentally regulated expression of the novel cancer anti-apoptosis gene survivin in human and mouse differentiation. Am J Pathol 152(1):43–49
Ambrosini G, Adida C, Altieri DC (1997) A novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and lymphoma. Nat Med 3(8):917–921
Fukuda S, Pelus LM (2006) Survivin, a cancer target with an emerging role in normal adult tissues. Mol Cancer Ther 5(5):1087–1098. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-05-0375
Ambrosini G, Adida C, Sirugo G, Altieri DC (1998) Induction of apoptosis and inhibition of cell proliferation by survivin gene targeting. J Biol Chem 273(18):11177–11182
Krieg A, Mahotka C, Krieg T, Grabsch H, Muller W, Takeno S, Suschek CV, Heydthausen M, Gabbert HE, Gerharz CD (2002) Expression of different survivin variants in gastric carcinomas: first clues to a role of survivin-2B in tumour progression. Br J Cancer 86(5):737–743. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6600153
Li F (2003) Survivin study: what is the next wave? J Cell Physiol 197(1):8–29. doi:10.1002/jcp.10327
Ikeguchi M, Ueta T, Yamane Y, Hirooka Y, Kaibara N (2002) Inducible nitric oxide synthase and survivin messenger RNA expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 8(10):3131–3136
Karam JA, Lotan Y, Ashfaq R, Sagalowsky AI, Shariat SF (2007) Survivin expression in patients with non-muscle-invasive urothelial cell carcinoma of the bladder. Urology 70(3):482–486. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2007.05.009
Lo Muzio L, Pannone G, Leonardi R, Staibano S, Mignogna MD, De Rosa G, Kudo Y, Takata T, Altieri DC (2003) Survivin, a potential early predictor of tumor progression in the oral mucosa. J Dent Res 82(11):923–928
Shariat SF, Lotan Y, Saboorian H, Khoddami SM, Roehrborn CG, Slawin KM, Ashfaq R (2004) Survivin expression is associated with features of biologically aggressive prostate carcinoma. Cancer 100(4):751–757. doi:10.1002/cncr.20039
Tu CH, Liu WP, Dong M, Cai LP, Mo YQ, Yang DZ (2011) Protection of CHO cells by transfer of survivin driven by ovarian-specific promoter OSP-2. Mol Biol Rep 38(4):2323–2328. doi:10.1007/s11033-010-0365-y
Sui L, Dong Y, Ohno M, Watanabe Y, Sugimoto K, Tokuda M (2002) Survivin expression and its correlation with cell proliferation and prognosis in epithelial ovarian tumors. Int J Oncol 21(2):315–320
Kawasaki H, Altieri DC, Lu CD, Toyoda M, Tenjo T, Tanigawa N (1998) Inhibition of apoptosis by survivin predicts shorter survival rates in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 58(22):5071–5074
Raj D, Liu T, Samadashwily G, Li F, Grossman D (2008) Survivin repression by p53, Rb and E2F2 in normal human melanocytes. Carcinogenesis 29(1):194–201. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgm219
Velculescu VE, Madden SL, Zhang L, Lash AE, Yu J, Rago C, Lal A, Wang CJ, Beaudry GA, Ciriello KM, Cook BP, Dufault MR, Ferguson AT, Gao Y, He TC, Hermeking H, Hiraldo SK, Hwang PM, Lopez MA, Luderer HF, Mathews B, Petroziello JM, Polyak K, Zawel L, Kinzler KW et al (1999) Analysis of human transcriptomes. Nat Genet 23(4):387–388. doi:10.1038/70487
Altieri DC (2008) Survivin, cancer networks and pathway-directed drug discovery. Nat Rev Cancer 8(1):61–70. doi:10.1038/nrc2293
Kato J, Kuwabara Y, Mitani M, Shinoda N, Sato A, Toyama T, Mitsui A, Nishiwaki T, Moriyama S, Kudo J, Fujii Y (2001) Expression of survivin in esophageal cancer: correlation with the prognosis and response to chemotherapy. Int J Cancer 95(2):92–95. doi:10.1002/1097-0215(20010320)95:2<92:AID-IJC1016>3.0.CO;2-9
Sarela AI, Scott N, Ramsdale J, Markham AF, Guillou PJ (2001) Immunohistochemical detection of the anti-apoptosis protein, survivin, predicts survival after curative resection of stage II colorectal carcinomas. Ann Surg Oncol 8(4):305–310
Sarela AI, Macadam RC, Farmery SM, Markham AF, Guillou PJ (2000) Expression of the antiapoptosis gene, survivin, predicts death from recurrent colorectal carcinoma. Gut 46(5):645–650
Kajiwara Y, Yamasaki F, Hama S, Yahara K, Yoshioka H, Sugiyama K, Arita K, Kurisu K (2003) Expression of survivin in astrocytic tumors: correlation with malignant grade and prognosis. Cancer 97(4):1077–1083. doi:10.1002/cncr.11122
Vischioni B, van der Valk P, Span SW, Kruyt FA, Rodriguez JA, Giaccone G (2004) Nuclear localization of survivin is a positive prognostic factor for survival in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol 15(11):1654–1660. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdh436
Falleni M, Pellegrini C, Marchetti A, Oprandi B, Buttitta F, Barassi F, Santambrogio L, Coggi G, Bosari S (2003) Survivin gene expression in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. J Pathol 200(5):620–626. doi:10.1002/path.1388
Mellai M, Caldera V, Patrucco A, Annovazzi L, Schiffer D (2008) Survivin expression in glioblastomas correlates with proliferation, but not with apoptosis. Anticancer Res 28(1A):109–118
Dai J, Jin G, Dong J, Chen Y, Xu L, Hu Z, Shen H (2010) Prognostic significance of survivin polymorphisms on non-small cell lung cancer survival. J Thorac Oncol 5(11):1748–1754. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181f18cb9
Xu Y, Fang F, Ludewig G, Jones G, Jones D (2004) A mutation found in the promoter region of the human survivin gene is correlated to overexpression of survivin in cancer cells. DNA Cell Biol 23(9):527–537. doi:10.1089/1044549041939278
Woolf B (1955) On estimating the relation between blood group and disease. Ann Hum Genet 19(4):251–253
Thakkinstian A, McElduff P, D’Este C, Duffy D, Attia J (2005) A method for meta-analysis of molecular association studies. Stat Med 24(9):1291–1306. doi:10.1002/sim.2010
Wang YH, Chiou HY, Lin CT, Hsieh HY, Wu CC, Hsu CD, Shen CH (2009) Association between survivin gene promoter −31 C/G polymorphism and urothelial carcinoma risk in Taiwanese population. Urology 73(3):670–674. doi:S0090-4295(08)01675-0[pii]10.1016/j.urology.2008.09.048
Pennati M, Folini M, Zaffaroni N (2008) Targeting survivin in cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets 12(4):463–476. doi:10.1517/14728222.12.4.463
Ma F, Zhang H, Zhai Y, Huang W, Zhao C, Ou S, Zhou H, Yuan W, Wang Z, Wang H, Yue W, Yu L, Li P, Xia X, Cai M, Zhang Y, Cui Y, He F, Ma Y, Zhou G (2011) Functional polymorphism −31C/G in the promoter of BIRC5 gene and risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma among Chinese. PLoS One 6(2):e16748. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0016748
Bayram S, Akkiz H, Bekar A, Akgollu E (2011) The association between the survivin −31G/C promoter polymorphism and hepatocellular carcinoma risk in a Turkish population. Cancer Epidemiol. doi:10.1016/j.canep.2011.01.004
Borges BD, Burbano RR, Harada ML (2010) Survivin −31C/G polymorphism and gastric cancer risk in a Brazilian population. Clin Exp Med. doi:10.1007/s10238-010-0122-5
Kawata N, Tsuchiya N, Horikawa Y, Inoue T, Tsuruta H, Maita S, Sato S, Mitobe Y, Narita S, Habuchi T (2010) Two survivin polymorphisms are cooperatively associated with bladder cancer susceptibility. Int J Cancer. doi:10.1002/ijc.25850
Upadhyay R, Khurana R, Kumar S, Ghoshal UC, Mittal B (2010) Role of survivin gene promoter polymorphism (−31G>C) in susceptibility and survival of esophageal cancer in Northern India. Ann Surg Oncol. doi:10.1245/s10434-010-1371-y
Theodoropoulos GE, Michalopoulos NV, Panoussopoulos SG, Taka S, Gazouli M (2010) Effects of caspase-9 and survivin gene polymorphisms in pancreatic cancer risk and tumor characteristics. Pancreas 39(7):976–980. doi:10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181d705d4
Bae GU, Yang YJ, Jiang G, Hong M, Lee HJ, Tessier-Lavigne M, Kang JS, Krauss RS (2009) Neogenin regulates skeletal myofiber size and focal adhesion kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase activities in vivo and in vitro. Mol Biol Cell 20(23):4920–4931. doi:10.1091/mbc.E09-06-0491
Gazouli M, Tzanakis N, Rallis G, Theodoropoulos G, Papaconstantinou I, Kostakis A, Anagnou NP, Nikiteas N (2009) Survivin −31G/C promoter polymorphism and sporadic colorectal cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis 24(2):145–150. doi:10.1007/s00384-008-0601-2
Yang L, Zhu H, Zhou B, Gu H, Yan H, Tang N, Dong H, Sun Q, Cong R, Chen G, Wang B (2009) The association between the survivin C-31G polymorphism and gastric cancer risk in a Chinese population. Dig Dis Sci 54(5):1021–1028. doi:10.1007/s10620-008-0441-5
Jang JS, Kim KM, Kang KH, Choi JE, Lee WK, Kim CH, Kang YM, Kam S, Kim IS, Jun JE, Jung TH, Park JY (2008) Polymorphisms in the survivin gene and the risk of lung cancer. Lung Cancer 60(1):31–39. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2007.09.008
Borbely AA, Murvai M, Szarka K, Konya J, Gergely L, Hernadi Z, Veress G (2007) Survivin promoter polymorphism and cervical carcinogenesis. J Clin Pathol 60(3):303–306. doi:10.1136/jcp.2006.037804
Cheng ZJ, Hu LH, Huang SJ (2008) Correlation of −31G/C polymorphisms of survivin promoter to tumorigenesis of gastric carcinoma. Ai Zheng 27(3):258–263
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by fellowship grants from Counsel of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) and Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India.
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srivastava, K., Srivastava, A. & Mittal, B. Survivin promoter −31G/C (rs9904341) polymorphism and cancer susceptibility: a meta-analysis. Mol Biol Rep 39, 1509–1516 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-0889-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-0889-9