Abstract
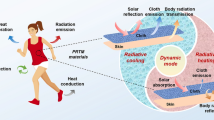
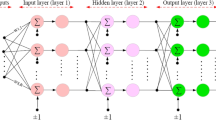
This paper presented a modeling method based on L-W Surface. We obtained our body CT data by CT scan, and get simulation manikin through the 3D reconstruction. We gridded manikin by thermal environment of the digital home, then build multi-scale coupling calculated model based on three-dimensional grid manikins and 25-node physiological model. At last, this paper described the body’s adjustment process from the physical point of view, and experimental results showed that the performance of clothing’s heat and moisture transfer could be dynamically simulated by computer. It also could get simulation effect of human heat and moisture feeling.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheng Y, Niu J, Gao N (2012) Thermal comfort models: a review and numerical investigation. Build Environ 47:13–22
Havenith G, Heus R, Lotens WA (1990a) Resultant clothing insulation––a function of body movement, posture, wind, clothing fit and ensemble thickness[J]. Ergonomics 33(1):67–84
Havenith G, Heus R, Lotens WA (1990b) Clothing ventilation, vapor resistance and permeability index_changes due to posture, movement and wind[J]. Ergonomics 33(8):989–1005
R. Holopainen (2012) A human thermal model for improved thermal comfort, Ph. D. Thesis, Aalto University
Jia N, Yu L, Yang KX et al (2016) A novel exercise Thermophysiology comfort prediction model with fuzzy logic[J]. Mob Inf Syst. doi:10.1155/2016/8586493
Li Y, Wang Z, Hu J Y (1999) Mathematical simulation and experimental verification of fabric thermal and moisture perceptions∥the SEM Annual Conference on The Interdependence Between Theoretical, Experimental and Computational Mechanics[C].Cincinnati, USA
Li Y, QY Zhu, and ZX Luo (2001) Numerical simulation of heat transfer coupled with moisture sorption and liquid transport in porous textiles. In the 6th Asian Textile Conference. Hong Kong
Luo X, Nie H et al (2002) Recurrence surfaces on arbitrary quadrilateral mesh. J Comput Appl Math 144:221–232
Luo XN, Liu N, Gao CY (2004) Fairing geometric modeling based on 4-point interpolatory subdivision scheme. J Comput Appl Math 163(1):189–197
Murakami S, Kato S, Zeng J (1998) Combined simulation of airflow, radiation and moisture transport for heat release from human body[J]. Roomvent 98(b):141–150
Shin-ichi Tanabe, Kozo Kobayashi, Junta Nakano, Yoshiichi Ozeki (2002) Evaluation of Thermal comfort using combined multi-node termoregulation (65MN) and radiation models and computational fluid dynamics (CFD), Energy and Buildings 34(6):637–646
Wang R, Li Y et al (2004) Rational recurrence curves and recurrence surfaces in multivariate B-form on some regions. J Comput Appl Math 163:277–285
Wang R, Du H, Zhou F, Deng D, Liu Y (2014) An adaptive neural fuzzy network clothing comfort evaluation model and application in digital home. Multimedia Tools and Applications 71:395–410
Yan C, Zhang Y, Dai F et al (2013) Highly parallel framework for HEVC motion estimation on many-Core platform[C]// data compression conference. IEEE Computer Society 63-72
Yan C, Zhang Y, Xu J et al (2014a) A highly parallel framework for HEVC coding unit partitioning tree decision on many-core processors[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Lett 21(5):573–576
Yan C, Zhang Y, Xu J et al (2014b) Efficient parallel framework for HEVC motion estimation on many-Core processors[J]. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 24(12):2077–2089
Yan C, Zhang Y, Dai F et al (2014c) Parallel deblocking filter for HEVC on many-core processor[J]. Electron Lett 50(5):367–368
Yan C, Zhang Y, Dai F et al (2014d) Efficient parallel HEVC intra-prediction on many-core processor[J]. Electron Lett 50(11):805–806
Zhu F, Yu Z, Qianqian F, Dehong X (2013) Moisture diffusivity in structure of random fractal fiber bed. Physics Letter A 377:2324–2328
Acknowledgements
The Project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.61402185), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (No. 2015A030313382), and Guangdong Provincial Public Research and Capacity Building Foundation funded project (Nos. 2016A020223012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Q., Wang, Z., Wang, F. et al. Thermal comfort research on human CT data modeling. Multimed Tools Appl 77, 6311–6326 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-4537-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-4537-9