Abstract
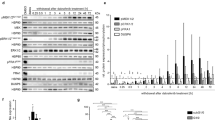
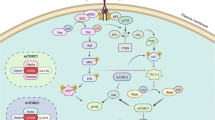
Phosphatase and tension homolog located on chromosome ten (PTEN) is a tumor suppressor as it negatively regulates activation of Akt. Mutation or deletion of PTEN has been found in as high as 80% of glioblastomas, which harbor aberrant cell signaling passing through the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) and Akt (PI3K/Akt) survival pathway. Glioblastoma cells without functional PTEN are not easily amenable to apoptosis. We investigated the possibility of modulation of signal transduction pathways for induction of apoptosis in human glioblastoma T98G (PTEN-harboring) and U87MG (PTEN-deficient) cell lines after treatment with the combination of all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ). Treatment with ATRA plus IFN-γ stimulated PTEN expression and suppressed Akt activation in T98G cells, whereas no PTEN expression but Akt activation in U87MG cells under the same conditions. Pretreatment of U87MG cells with the PI3K inhibitor LY294002 could prevent Akt activation. Interestingly, ATRA plus IFN-γ could significantly decrease cell viability and increase morphological features of apoptosis in both cell lines. Combination of ATRA and IFN-γ showed more efficacy than IFN-γ alone in causing apoptosis that occurred due to increases in Bax:Bcl-2 ratio, mitochondrial release of cytochrome c, and caspase-3 activity. Luciferase reporter gene assay showed that combination of ATRA and IFN-γ significantly down regulated transcriptional activity of the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), a survival signaling factor, in U87MG cells. Thus, combination of ATRA and IFN-γ caused significant amounts of apoptosis in T98G cells due to suppression of the PI3K/Akt survival pathway while the same treatment caused apoptosis in U87MG cells due to down regulation of the NF-κB activity. Therefore, the combination of ATRA and IFN-γ could modulate different survival signal transduction pathways for induction of apoptosis and should be considered as an effective therapeutic strategy for controlling the growth of both PTEN-harboring and PTEN-deficient glioblastomas.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi J, Ohbayashi K, Suzuki T, Sasaki T (1999) Cell cycle arrest and astrocytic differentiation resulting from PTEN expression in glioma cells. J Neurosurg 91:822–830
Asou N (2007) All-trans retinoic acid in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Intern Med 46:91–93
Cantley LC, Neel BG (1999) New insights into tumor suppression: PTEN suppresses tumor formation by restraining the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:4240–4245
Das A, Banik NL, Patel SJ, Ray SK (2004) Dexamethasone protected human glioblastoma U87MG cells from temozolomide induced apoptosis by maintaining Bax:Bcl-2 ratio and preventing proteolytic activities. Mol Cancer 3:1–10
Das A, Banik NL, Ray SK (2006) Mechanism of apoptosis with the involvement of calpain and caspase cascades in human malignant neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells exposed to flavonoids. Int J Cancer 119:2575–2585
Eng C (2003) PTEN: one gene, many syndromes. Hum Mutat 22:183–198
Ermoian RP, Furniss CS, Lamborn KR, Basila D, Berger MS, Gottschalk R, Nicholas MK, Stokoe D, Haas-Kogan DA (2002) Dysregulation of PTEN and protein kinase B is associated with glioma histology and patient survival. Clin Cancer Res 8:1100–1106
Fan X, Aalto Y, Sanko SG, Knuutila S, Klatzmann D, Castresana JS (2002) Genetic profile, PTEN mutation and therapeutic role of PTEN in glioblastomas. Int J Oncol 21:1141–1150
Garzon R, Pichiorri F, Palumbo T, Visentini M, Aqeilan R, Cimmino A, Wang H, Sun H, Volinia S, Alder H, Calin GA, Liu CG, Andreeff M, Croce CM (2007) MicroRNA gene expression during retinoic acid-induced differentiation of human acute promyelocytic leukemia. Oncogene 29:1–10
Haque A, Das A, Hajiaghamohseni LM, Younger A, Banik NL, Ray SK (2007) Induction of apoptosis and immune response by all-trans retinoic acid plus interferon-gamma in human malignant glioblastoma T98G and U87MG cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother 56:615–625
Hwang PH, Yi HK, Kim DS, Nam SY, Kim JS, Lee DY (2001) Suppression of tumorigenicity and metastasis in B16F10 cells by PTEN/MMAC1/TEP1 gene. Cancer Lett 172:83–91
Jendrossek V, Belka C, Bamberg M (2003) Novel chemotherapeutic agents for the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 12:1899–1924
Karin M, Lin A (2002) NF-κB at the crossroads of life and death. Nat Immunol 3:221–227
Kleihues P, Louis DN, Scheithauer BW, Rorke LB, Reifenberger G, Burger PC, Cavenee WK (2002) The WHO classification of tumors of the nervous system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61:215–225
Koul D, Shen R, Bergh S, Sheng X, Shishodia S, Lafortune TA, Lu Y, de Groot F, Mills GB, Yung WK (2006) Inhibition of Akt survival pathway by a small-molecule inhibitor in human glioblastoma. Mol Cancer Ther 5:637–644
Kurose K, Zhou XP, Araki T, Cannistra SA, Maher ER, Eng C (2001) Frequent loss of PTEN expression is linked to elevated phosphorylated Akt levels, but not associated with p27 and cyclin D1 expression, in primary epithelial ovarian carcinomas. Am J Pathol 158:1895–1898
Lee R, Collins T (2001) NFκB and cell survival IAPs call for support. Circ Res 88:262–264
Li J, Yen C, Liaw D, Podsypanina K, Bose S, Wang SI, Puc J, Miliaresis C, Rodgers L, McCombie R, Bigner SH, Giovanella BC, Ittmann M, Tycko B, Hibshoosh H, Wigler MH, Parsons R (1997) PTEN, a putative protein tyrosine phosphatase gene mutated in human brain, breast, and prostate cancer. Science 275:1943–1947
Maier D, Jones G, Li X, Schonthal AH, Gratzl O, Van Meir EG, Merlo A (1999) The PTEN lipid phosphatase domain is not required to inhibit invasion of glioma cells. Cancer Res 59:5479–5482
Parney IF, Chang SM (2003) Current chemotherapy for glioblastoma. Cancer J 9:149–156
Pasquali D, Chieffi P, Deery WJ, Nicoletti G, Bellastella A, Sinisi AA (2005) Differential effects of all-trans retinoic acid (RA) on Erk1/2 phosphorylation and cAMP accumulation in normal and malignant human prostate epithelial cells: Erk1/2 inhibition restores RA-induced decrease of cell growth in malignant prostate cells. Eur J Endocrinol 152:663–669
Pasquali D, Rossi A, Prezioso D, Gentile V, Colantuoni V, Lotti T, Bellastella A, Sinisi AA (1999) Change in tissue transglutaminase activity and expression during retinoic acid-induced growth arrest and apoptosis in primary cultures of human epithelial prostate cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84:1463–1469
Ray SK, Wilford GG, Crosby CV, Hogan EL, Banik NL (1999) Diverse stimuli induce calpain overexpression and apoptosis in C6 glioma cells. Brain Res 829:18–27
Rong Y, Post DE, Pieper RO, Durden DL, Van Meir EG, Brat DJ (2005) PTEN and hypoxia regulate tissue factor expression and plasma coagulation by glioblastoma. Cancer Res 65:1406–1413
Shingu T, Yamada K, Hara N, Moritake K, Osago H, Terashima M, Uemura T, Yamasaki T, Tsuchiya M (2003) Growth inhibition of human malignant glioma cells induced by the PI3K-specific inhibitor. J Neurosurg 98:154–161
Simeone AM, Tari AM (2004) How retinoids regulate breast cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis. Cell Mol Life Sci 61:1475–1484
Soprano KJ, Purev E, Vuocolo S, Soprano DR (2006) Rb2/p130 and protein phosphatase 2A: key mediators of ovarian carcinoma cell growth suppression by all-trans retinoic acid. Oncogene 25:5315–5325
Stewart LA (2002) Chemotherapy in adult high-grade glioma: a systemic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data from 12 random trials. Lancet 359:1011–1018
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Gorlia T, Allgeier A, Lacombe D, Cairncross JG, Eisenhauer E, Mirimanoff RO, European Organisation for Research, Treatment of Cancer Brain Tumor and Radiotherapy Groups, National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group (2005) Radiodynamic therapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Eng J Med 352:987–996
Wang MY, Lu KV, Zhu S, Dia EQ, Vivanco I, Shackleford GM, Cavenee WK, Mellinghoff IK, Cloughesy TF, Sawyers CL, Mischel PS (2006) Mammalian target of rapamycin inhibition promotes response to epidermal growth factor receptor kinase inhibitors in PTEN-deficient and PTEN-intact glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res 66:7864–7869
Wong ML, Kaye AH, Hovens AM (2007) Targeting malignant glioma survival signalling to improve clinical outcomes. J Clin Neurosci 14:301–308
Zang C, Wachter M, Liu H, Posch MG, Fenner MH, Stadelmann C, von Deimling A, Possinger K, Black KL, Koeffler HP, Elstner E (2003) Ligands for PPARγ and RAR cause induction of growth inhibition and apoptosis in human glioblastomas. J Neurooncol 65:107–118
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the R01 (CA-91460 and NS-57811) grants from the National Institutes of Health (Bethesda, MD, USA) and also by a Spinal Cord Injury Research Fund (SCIRF-0803) grant from the State of South Carolina to S.K.R.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Special issue in honor of Naren Banik.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, R., Banik, N.L. & Ray, S.K. Combination of All-trans Retinoic Acid and Interferon-gamma Suppressed PI3K/Akt Survival Pathway in Glioblastoma T98G Cells whereas NF-κB Survival Signaling in Glioblastoma U87MG Cells for Induction of Apoptosis. Neurochem Res 32, 2194–2202 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9417-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9417-7