Abstract
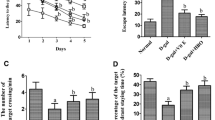
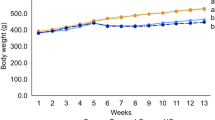
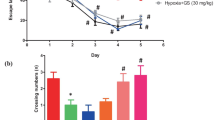
Our previous study demonstrated that hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) improved cognitive impairments mainly by regulating oxidative stress, inflammatory responses and aging-related gene expression. However, a method for preventing cognitive dysfunction has yet to be developed. In the present study, we explored the protective effects of HBO on the cholinergic system and apoptosis in d-galactose (d-gal)-treated mice. A model of aging was established via systemic intraperitoneal injection of d-gal daily for 8 weeks. HBO was administered during the last 2 weeks of d-gal injection. Our results showed that HBO in d-gal-treated mice significantly improved behavioral performance on the open field test and passive avoidance task. Studies on the potential mechanisms of this effect showed that HBO significantly reduced oxidative stress and blocked the nuclear factor-κB pathway. Moreover, HBO significantly increased the levels of choline acetyltransferase and acetylcholine and decreased the activity of acetylcholinesterase in the hippocampus. Furthermore, HBO markedly increased expression of the anti-apoptosis protein Bcl-2 and glial fibrillary acidic protein meanwhile decreased expression of the pro-apoptosis proteins Bax and caspase-3. Importantly, there was a significant reduction in expression of Aβ-related genes, such as amyloid precursor protein, β-site amyloid cleaving enzyme-1 and cathepsin B mRNA. These decreases were accompanied by significant increases in expression of neprilysin and insulin-degrading enzyme mRNA. Moreover, compared with the Vitamin E group, HBO combined with Vitamin E exhibited significant difference in part of the above mention parameters. These findings suggest that HBO may act as a neuroprotective agent in preventing cognitive impairments.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Helzner EP, Scarmeas N, Cosentino S, Tang MX, Schupf N, Stern Y (2008) Survival in Alzheimer disease: a multiethnic, population-based study of incident cases. Neurology 71:1489–1495
Soysal P, Stubbs B, Lucato P, Luchini C, Solmi M, Peluso R, Sergi G, Isik AT, Manzato E, Maggi S, Maggio M, Prina AM, Cosco TD, Wu YT, Veronese N (2016) Inflammation and frailty in the elderly: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res Rev 31:1–8
Reiman EM (2016) Alzheimer’s disease: attack on amyloid-beta protein. Nature 537:36–37
Lu J, Wu DM, Hu B, Cheng W, Zheng YL, Zhang ZF, Ye Q, Fan SH, Shan Q, Wang YJ (2010) Chronic administration of troxerutin protects mouse brain against d-galactose-induced impairment of cholinergic system. Neurobiol Learn Mem 93:157–164
Selkoe DJ, Hardy J (2016) The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease at 25 years. EMBO Mol Med 8:595–608
Teich AF, Arancio O (2012) Is the amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease therapeutically relevant? Biochem J 446:165–177
Qu F, Yang M, Rasooly A (2016) Dual signal amplification electrochemical biosensor for monitoring the activity and inhibition of the Alzheimer related protease beta-secretase (BACE1). Anal Chem 21:21
Mueller-Steiner S, Zhou Y, Arai H, Roberson ED, Sun B, Chen J, Wang X, Yu G, Esposito L, Mucke L, Gan L (2006) Antiamyloidogenic and neuroprotective functions of cathepsin B: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 51:703–714
Klein DM, Felsenstein KM, Brenneman DE (2009) Cathepsins B and L differentially regulate amyloid precursor protein processing. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 328:813–821
Ries M, Sastre M (2016) Mechanisms of abeta clearance and degradation by glial cells. Front Aging Neurosci 8:160
Fleisher AS, Chen K, Quiroz YT, Jakimovich LJ, Gutierrez Gomez M, Langois CM, Langbaum JB, Roontiva A, Thiyyagura P, Lee W, Ayutyanont N, Lopez L, Moreno S, Munoz C, Tirado V, Acosta-Baena N, Fagan AM, Giraldo M, Garcia G, Huentelman MJ, Tariot PN, Lopera F, Reiman EM (2015) Associations between biomarkers and age in the presenilin 1 E280A autosomal dominant Alzheimer disease kindred: a cross-sectional study. JAMA Neurol 72:316–324
Paradies G, Petrosillo G, Paradies V, Ruggiero FM (2011) Mitochondrial dysfunction in brain aging: role of oxidative stress and cardiolipin. Neurochem Int 58:447–457
Pollack M, Phaneuf S, Dirks A, Leeuwenburgh C (2002) The role of apoptosis in the normal aging brain, skeletal muscle, and heart. Ann NY Acad Sci 959:93–107
Thees S, Hubbard GB, Winckler J, Schultz C, Rami A (2005) Specific alteration of the Bax/Bcl2 ratio and cytochrome c without execution of apoptosis in the hippocampus of aged baboons. Restor Neurol Neurosci 23:1–9
Niu YL, Zhang WJ, Wu P, Liu B, Sun GT, Yu DM, Deng JB (2010) Expression of the apoptosis-related proteins caspase-3 and NF-kappaB in the hippocampus of Tg2576 mice. Neurosci Bull 26:37–46
Yang WN, Han H, Hu XD, Feng GF, Qian YH (2013) The effects of perindopril on cognitive impairment induced by d-galactose and aluminum trichloride via inhibition of acetylcholinesterase activity and oxidative stress. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 115:31–36
Everitt BJ, Robbins TW (1997) Central cholinergic systems and cognition. Annu Rev Psychol 48:649–684
Conner JM, Culberson A, Packowski C, Chiba AA, Tuszynski MH (2003) Lesions of the Basal forebrain cholinergic system impair task acquisition and abolish cortical plasticity associated with motor skill learning. Neuron 38:819–829
Ikonomovic MD, Mufson EJ, Wuu J, Bennett DA, DeKosky ST (2005) Reduction of choline acetyltransferase activity in primary visual cortex in mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease. Arch Neurol 62:425–430
Lu J, Zheng YL, Luo L, Wu DM, Sun DX, Feng YJ (2006) Quercetin reverses d-galactose induced neurotoxicity in mouse brain. Behav Brain Res 171:251–260
Cui X, Zuo P, Zhang Q, Li X, Hu Y, Long J, Packer L, Liu J (2006) Chronic systemic d-galactose exposure induces memory loss, neurodegeneration, and oxidative damage in mice: protective effects of R-alpha-lipoic acid. J Neurosci Res 83:1584–1590
Wei H, Li L, Song Q, Ai H, Chu J, Li W (2005) Behavioural study of the d-galactose induced aging model in C57BL/6 J mice. Behav Brain Res 157:245–251
Tsai SJ, Yin MC (2012) Anti-oxidative, anti-glycative and anti-apoptotic effects of oleanolic acid in brain of mice treated by d-galactose. Eur J Pharmacol 689:81–88
Zhong SZ, Ge QH, Qu R, Li Q, Ma SP (2009) Paeonol attenuates neurotoxicity and ameliorates cognitive impairment induced by d-galactose in ICR mice. J Neurol Sci 277:58–64
Lei M, Hua X, Xiao M, Ding J, Han Q, Hu G (2008) Impairments of astrocytes are involved in the d-galactose-induced brain aging. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 369:1082–1087
Liu L, Su Y, Yang W, Xiao M, Gao J, Hu G (2010) Disruption of neuronal-glial-vascular units in the hippocampus of ovariectomized mice injected with d-galactose. Neuroscience 169:596–608
Lin X, Huang Z, Chen X, Rong Y, Zhang S, Jiao Y, Huang Q, Huang R (2014) Protective effect of Millettia pulchra polysaccharide on cognitive impairment induced by d-galactose in mice. Carbohydr Polym 101:533–543
Kumar A, Prakash A, Dogra S (2010) Naringin alleviates cognitive impairment, mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress induced by d-galactose in mice. Food Chem Toxicol 48:626–632
Bennett MH, Feldmeier J, Hampson NB, Smee R, Milross C (2016) Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for late radiation tissue injury. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 24:CD005005
Fife C.E. EKA, Workmanm WT (2016) Ethical issues, standards and quality control in practice of hyperbaric medicine. Springer, New York
Rusyniak DE, Kirk MA, May JD, Kao LW, Brizendine EJ, Welch JL, Cordell WH, Alonso RJ (2003) Hyperbaric oxygen therapy in acute ischemic stroke: results of the hyperbaric oxygen in acute ischemic stroke trial pilot study. Stroke 34:571–574
Yildiz S, Uzun G, Kiralp MZ (2006) Hyperbaric oxygen therapy in chronic pain management. Curr Pain Headache Rep 10:95–100
Stepien K, Ostrowski RP, Matyja E (2016) Hyperbaric oxygen as an adjunctive therapy in treatment of malignancies, including brain tumours. Med Oncol 33:16–814
Teguh DN, Raap RB, Struikmans H, van Hulst RA (2016) Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for chronic bowel dysfunction after pelvic radiotherapy. Lancet Oncol 17:e130–e131
Zhang D, Ma Y (2015) Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation improves both hearing function and tinnitus perception in sudden sensorineural hearing loss patients. Sci Rep 5:14796
Yu QH, Zhang PX, Liu Y, Liu W, Yin N (2016) Hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning protects the lung against acute pancreatitis induced injury via attenuating inflammation and oxidative stress in a nitric oxide dependent manner. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 478:93–100
Nicoara D, Zhang Y, Nelson JT, Brewer AL, Maharaj P, DeWald SN, Shirachi DY, Quock RM (2016) Hyperbaric oxygen treatment suppresses withdrawal signs in morphine-dependent mice. Brain Res 1:434–437
Chaillou T, Lanner JT (2016) Regulation of myogenesis and skeletal muscle regeneration: effects of oxygen levels on satellite cell activity. FASEB J 30:3929–3941
Duan S, Shao G, Yu L, Ren C (2015) Angiogenesis contributes to the neuroprotection induced by hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning against focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Int J Neurosci 125:625–634
Chen C, Chen W, Nong Z, Ma Y, Qiu S, Wu G (2016) Cardioprotective Effects of Combined Therapy with Hyperbaric Oxygen and Diltiazem Pretreatment on Myocardial Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury in Rats. Cell Physiol Biochem 38:2015–2029
Liu JR, Zhao Y, Patzer A, Staak N, Boehm R, Deuschl G, Culman J, Bonny C, Herdegen T, Eschenfelder C (2010) The c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) inhibitor XG-102 enhances the neuroprotection of hyperbaric oxygen after cerebral ischaemia in adult rats. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 36:211–224
Gamdzyk M, Malek M, Bratek E, Koks A, Kaminski K, Ziembowicz A, Salinska E (2016) Hyperbaric oxygen and hyperbaric air preconditioning induces ischemic tolerance to transient forebrain ischemia in the gerbil. Brain Res 1:257–265
Pan X, Chen C, Huang J, Wei H, Fan Q (2015) Neuroprotective effect of combined therapy with hyperbaric oxygen and madopar on 6-hydroxydopamine-induced Parkinson’s disease in rats. Neurosci Lett 600:220–225
Chen X, Li Y, Chen W, Nong Z, Huang J, Chen C (2016) Protective effect of hyperbaric oxygen on cognitive impairment induced by d-galactose in Mice. Neurochem Res 41:3032–3041
Lin X, Zhang S, Huang R, Wei L, Tan S, Liang C, Lv S, Chen Y, Liang S, Tian Y, Lu Z, Huang Q (2014) Protective effect of madecassoside against cognitive impairment induced by d-galactose in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 124:434–442
Chen C, Nong Z, Huang J, Chen Z, Zhang S, Jiao Y, Chen X, Huang R (2014) Yulangsan polysaccharide attenuates withdrawal symptoms and regulates the NO pathway in morphine-dependent rats. Neurosci Lett 570:63–68
Doan VM, Chen C, Lin X, Nguyen VP, Nong Z, Li W, Chen Q, Ming J, Xie Q, Huang R (2015) Yulangsan polysaccharide improves redox homeostasis and immune impairment in d-galactose-induced mimetic aging. Food Funct 6:1712–1718
Cui X, Wang L, Zuo P, Han Z, Fang Z, Li W, Liu J (2004) d-Galactose-caused life shortening in Drosophila melanogaster and Musca domestica is associated with oxidative stress. Biogerontology 5:317–325
Zhang Q, Li X, Cui X, Zuo P (2005) D-galactose injured neurogenesis in the hippocampus of adult mice. Neurol Res 27:552–556
Fan SH, Zhang ZF, Zheng YL, Lu J, Wu DM, Shan Q, Hu B, Wang YY (2009) Troxerutin protects the mouse kidney from d-galactose-caused injury through anti-inflammation and anti-oxidation. Int Immunopharmacol 9:91–96
Parameshwaran K, Irwin MH, Steliou K, Pinkert CA (2010) d-galactose effectiveness in modeling aging and therapeutic antioxidant treatment in mice. Rejuvenation Res 13:729–735
Lu J, Wu DM, Zheng YL, Hu B, Zhang ZF, Ye Q, Liu CM, Shan Q, Wang YJ (2010) Ursolic acid attenuates d-galactose-induced inflammatory response in mouse prefrontal cortex through inhibiting AGEs/RAGE/NF-kappaB pathway activation. Cereb Cortex 20:2540–2548
Srikanth V, Maczurek A, Phan T, Steele M, Westcott B, Juskiw D, Münch G (2011) Advanced glycation endproducts and their receptor RAGE in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 32:763–777
Takai S, Nagaki M, Imao M, Kimura K, Kozawa O, Moriwaki H (2007) Intrinsic resistance to TNF-alpha-induced hepatocyte apoptosis in ICR mice correlates with expression of a short form of c-FLIP. Lab Invest 87:572–581
Kang J, Park EJ, Jou I, Kim JH, Joe EH (2001) Reactive oxygen species mediate A beta(25–35)-induced activation of BV-2 microglia. Neuroreport 12:1449–1452
Lee SY, Lee JH, Yoo HS, Yun YP, Oh KW, Ha TY, Hong JT (2005) Inhibitory effect of green tea extract on beta-amyloid-induced PC12 cell death by inhibition of the activation of NF-kappaB and ERK/p38 MAP kinase pathway through antioxidant mechanisms. Mol Brain Res 140:45–54
Bohnen NI, Albin RL (2011) The cholinergic system and Parkinson disease. Behav Brain Res 221:564–573
Tyagi E, Agrawal R, Nath C, Shukla R (2010) Cholinergic protection via alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and PI3K-Akt pathway in LPS-induced neuroinflammation. Neurochem Int 56:135–142
Zhang X, Jin C, Li Y, Guan S, Han F, Zhang S (2013) Catalpol improves cholinergic function and reduces inflammatory cytokines in the senescent mice induced by d-galactose. Food Chem Toxicol 58:50–55
Terry AV Jr, Mahadik SP (2007) Time-dependent cognitive deficits associated with first and second generation antipsychotics: cholinergic dysregulation as a potential mechanism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 320:961–968
Hasselmo ME (2006) The role of acetylcholine in learning and memory. Curr Opin Neurobiol 16:710–715
Danial NN, Korsmeyer SJ (2004) Cell death: critical control points. Cell 116:205–219
Akifusa S, Kamio N, Shimazaki Y, Yamaguchi N, Nishihara T, Yamashita Y (2009) Globular adiponectin-induced RAW 264 apoptosis is regulated by a reactive oxygen species-dependent pathway involving Bcl-2. Free Radic Biol Med 46:1308–1316
Kim HW, Rapoport SI, Rao JS (2010) Altered expression of apoptotic factors and synaptic markers in postmortem brain from bipolar disorder patients. Neurobiol Dis 37:596–603
Cai X, Zhang H, Tong D, Tan Z, Han D, Ji F, Hu W (2011) Corosolic acid triggers mitochondria and caspase-dependent apoptotic cell death in osteosarcoma MG-63 cells. Phytother Res 25:1354–1361
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Guangxi Scientific Research and Technology Development Research Projects (14124003-9 and AB16380179), the Guangxi Sanitation Research Project (Z2016582 and Z2013394), the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (0728081). The authors wish to thank Dr. Jun Chen for his technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Chunxia Chen and Luying Huang have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, C., Huang, L., Nong, Z. et al. Hyperbaric Oxygen Prevents Cognitive Impairments in Mice Induced by d-Galactose by Improving Cholinergic and Anti-apoptotic Functions. Neurochem Res 42, 1240–1253 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-2166-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-2166-8