Abstract
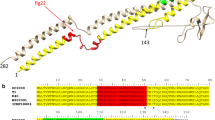
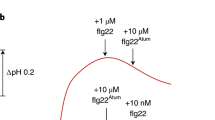
Bacterial flagellin is known to stimulate host immune responses in mammals and plants. In Arabidopsis thaliana, the receptor kinase FLS2 mediates flagellin perception through physical interaction with a highly conserved epitope in the N-terminus of flagellin, represented by the peptide flg22 derived from Pseudomonas syringae. The peptide flg22 is highly active as an elicitor in many plant species. In contrast, a shortened version of the same epitope derived from Escherichia coli, flg15E coli, is highly active as an elicitor in tomato but not in A. thaliana or Nicotiana benthamiana. Here, we make use of these species-specific differences in flagellin perception abilities to identify LeFLS2 as the flagellin receptor in tomato. LeFLS2 is most closely related to AtFLS2, indicating that it may represent the flagellin receptor of tomato. Expression of the LeFLS2 gene in Arabidopsis did not result in accumulation of its corresponding gene product, as indicated by experiments with LeFLS2-GFP fusions. In contrast, expression of LeFLS2-GFP fusions in N. benthamiana, a species that, like tomato, belongs to the Solanaceae, was obviously functional. N. benthamiana plants transiently expressing a LeFLS2-GFP fusion acquired responsiveness to flg15E coli to which they are normally unresponsive. Thus, LeFLS2 encodes a functional, specific flagellin receptor, the first to be identified in a plant family other than the Brassicaceae.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- At:
-
Arabidopsis thaliana
- BAK1:
-
BRI1-associated kinase 1
- BRI1:
-
Brassinosteroid Insensitive 1
- CDNA:
-
Complementary DNA
- CLV1:
-
CLAVATA 1
- Col-0:
-
Columbia-0
- E. coli :
-
Escherichia coli
- EFR:
-
EF-Tu receptor
- EF-Tu:
-
Elogation factor Tu
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- ERAD:
-
ER-associated protein degradation
- flg22:
-
Flagellin elicitor-active epitope
- FLS2:
-
Flagellin Sensing 2
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- GUS:
-
β-Glucoronidase
- Le:
-
Lycopersicum esculentum
- LRR:
-
Leucine-rich repeat
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- PAMP:
-
Pathogen-associated molecular pattern
- PRR:
-
Pattern recognition receptor
- P. syringae :
-
Pseudomonas syringae
- RACE:
-
Rapid amplification of cDNA ends
- RLK:
-
Receptor-like kinase
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction
- TLR:
-
Toll-like receptor
- Ws-0:
-
Wassilewskaja-0
References
Akira S, Takeda K (2004) Toll-like receptor signaling. Nat Rev Immunol 4:499–511
Asai T, Tena G, Plotnikova J et al (2002) MAP kinase signalling cascade in Arabidopsis innate immunity. Nature 415:977–983
Bauer Z, Gomez-Gomez L, Boller T, Felix G (2001) Sensitivity of different ecotypes and mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana toward the bacterial elicitor flagellin correlates with the presence of receptor-binding sites. J Biol Chem 276:45669–45676
Bukau B, Weissmann J, Horwich A (2006) Molecular chaperones and protein quality control. Cell 125:443–451
Che FS, Nakajima Y, Tanaka N, Iwano M, Yoshida T, Takayama S, Kadota I, Isogai A (2000) Flagellin from an incompatible strain of Pseudomonas avenae induces a resistance response in cultured rice cells. J Biol Chem 275:32347–32356
Chinchilla D, Bauer Z, Regenass M, Boller T, Felix G (2006) The Arabidopsis receptor kinase FLS2 binds flg22 and determines the specificity of flagellin perception. Plant Cell 18:1–12
Chisholm ST, Coaker G, Day B, Staskawicz BJ (2006) Host-microbe interactions: shaping the evolution of the plant immune response. Cell 124:803–814
Choe J, Kelker MS, Wilson IA (2005) Crystal structure of human toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) ectodomain. Science 309:581–585
Dievart A, Clark SE (2003) Using mutant alleles to determine the structure and function of leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinases. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:507–516
Dievart A, Clark SE (2004) LRR-containing receptors regulating plant development and defense. Development 131:251–261
Felix G, Duran JD, Volko S, Boller T (1999) Plants have a sensitive perception system for the most conserved domain of bacterial flagellin. Plant J 18:265–276
Felix G, Grosskopf DG, Regenass M, Boller T (1991) Rapid changes of protein phosphorylation are involved in transduction of the elicitor signal in plant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:8831–8834
Gomez-Gomez L, Bauer Z, Boller T (2001) Both the extracellular leucine-rich repeat domain and the kinase activity of FSL2 are required for flagellin binding and signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 13:1155–1163
Gomez-Gomez L, Boller T (2000) FLS2: an LRR receptor-like kinase involved in the perception of the bacterial elicitor flagellin in Arabidopsis. Mol Cell 5:1003–1011
Gomez-Gomez L, Felix G, Boller T (1999) A single locus determines sensitivity to bacterial flagellin in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 18:277–284
Hann DR, Rathjen JP (2007) Early events in the pathogenicity of Pseudomonas syringae on Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant J 49: 607–618
Heil F, Hemmi H, Hochrein H, Ampenberger F, Kirschning C, Akira S, Lipford G, Wagner H, Bauer S (2004) Species-specific recognition of single-stranded RNA via toll-like receptor 7 and 8. Science 303:1526–1529
Helenius A, Aebi M (2004) Roles of N-linked glycans in the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Biochem 73:1019–1049
Hubert DA, Tornero P, Belkhadir Y, Krishna P, Takahashi A, Shirasu K, Dangl JL (2003) Cytosolic HSP90 associates with and modulates the Arabidopsis RPM1 disease resistance protein. EMBO J 22:5679–5689
Kobe B, Kajava AV (2001) The leucine-rich repeat as a protein recognition motif. Curr Opin Struct Biol 11:725–732
Kunze G, Zipfel C, Robatzek S, Niehaus K, Boller T, Felix G (2004) The N terminus of bacterial elongation factor Tu elicits innate immunity in Arabidopsis plants. Plant Cell 16:3496–3507
Lord JM, Davey J, Frigero L, Roberts LM (2000) Endoplasmic reticulum-associated protein degradation. Semin Cell Dev Biol 11:159–164
Medzhitov R, Janeway CA Jr (2002) Decoding the patterns of self and nonself by the innate immune system. Science 296:298–300
Meindl T, Boller T, Felix G (2000) The bacterial elicitor flagellin activates its receptor in tomato cells according to the address-message concept. Plant Cell 12:1783–1794
Meusser B, Hirsch C, Jarosch E, Sommer T (2005) ERAD: the long road to destruction. Nat Cell Biol 7:766–772
Montoya T, Nomura T, Farrar K, Kanata T, Yokota T Bishop GJ (2002) Cloning the tomato curl3 gene highlights the putative dual role of the leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase tBRI1/SR160 in plant steroid hormone and peptide hormone signaling. Plant Cell 14:3163–3176
Muller J, Piffanelli P, Devoto A, Miklis M, Elliot C, Ortmann B, Schulze-Lefert P, Panstruga R (2005) Conserved ERAD-like quality control of a plant polytopic membrane protein. Plant Cell 17:149–163
Nuhse TS, Peck SC, Hirt H, Boller T (2000) Microbial elicitors induce activation and dual phosphorylation of the Arabidopsis thaliana MAPK 6. J Biol Chem 275: 7521–7526
Pfund C, Tans-Kersten J, Dunning FM, Alonso JM, Ecker JR, Allen C, Bent AF (2004) Flagellin is not a major defense elicitor in Ralstonia solanacearum cells or extracts applied to Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 17:696–706
Pimpl P, Taylor JP, Snowden C, Hillmer S, Robinson DG, Denecke J (2006) Golgi-mediated vacuolar sorting of the endoplasmic reticulum chaperone BiP may play an active role in quality control within the secretory pathway. Plant Cell 18:198–211
Rechsteiner M, Rogers SW (1996) PEST sequences and regulation by proteolysis. Trends Biochem Sci 21:267–271
Robatzek S, Chinchilla D, Boller T (2006) Ligand-induced endocytosis of the pattern recognition receptor FLS2 in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev 20:537–542
Ron M, Avni A (2004) The receptor for the fungal elicitor ethylene-inducing xylanase is a member of a resistance-like gene family in tomato. Plant Cell 16:1604–1615
Shiu SH, Bleecker AB (2001) Receptor-like kinases from Arabidopsis form a monophyletic gene family related to animal receptor kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:10763–10768
Smith KD, Andersen-Nissen E, Hayashi F, Strobe K, Bergman MA, Barrett SL, Cookson BT, Aderem A (2003) Toll-like receptor 5 recognizes a conserved site on flagellin required for protofilament formation and bacterial motility. Nat Immunol 4:1247–1253
Sun W, Dunning FM, Pfund C, Weingarten R, Bent AF (2006) Within-species flagellin polymorphism in Xanthomonas campestris pv campestris and its impact on elicitation of Arabidopsis FLAGELLIN SENSING2-dependent defenses. Plant Cell 18:764–779
van der Hoorn RA, Wulff BB, Rivas S, Durrant MC, van der Ploeg A, de Wit PJ, Jones JD (2005) Structure-function analysis of cf-9, a receptor-like protein with extracytoplasmic leucine-rich repeats. Plant Cell 17:1000–1015
Vert G, Nemhauser JL, Geldner N, Hong F, Chory J (2005) Molecular mechanisms of steroid hormone signaling in plants. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 21:177–201
Walker JC (1994) Structure and function of the receptor-like protein kinases of higher plants. Plant Mol Biol 26:1599–1609
Xu WH, Wang YS, Liu GZ, Chen X, Tinjuangjun P, Pi LY, Song WY (2006) The autophosphorylated Ser686, Thr688, and Ser689 residues in the intracellular juxtamembrane domain of XA21 are implicated in stability control of rice receptor-like kinase. Plant J 45:740–751
Zipfel C, Kunze G, Chinchilla D, Caniard A, Jones JDG, Boller T, Felix G (2006) Perception of the bacterial PAMP EF-Tu by the receptor EFR restricts Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Cell 125:749–760
Zipfel C, Robatzek S, Navarro L, Oakeley E, Jones JDG, Felix G, Boller T (2004) Bacterial disease resistance in Arabidopsis through flagellin perception. Nature 428:764–767
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Helge Sierotzki (Syngenta, Switzerland) for kindly providing tomato plants variety “Roter Gnom” and Heidrun Häweker for technical support. This work was supported by DFG to S.R. (SFB670), and by a grant of the Swiss National Science Foundation to T.B.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robatzek, S., Bittel, P., Chinchilla, D. et al. Molecular identification and characterization of the tomato flagellin receptor LeFLS2, an orthologue of Arabidopsis FLS2 exhibiting characteristically different perception specificities. Plant Mol Biol 64, 539–547 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-007-9173-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-007-9173-8