Abstract
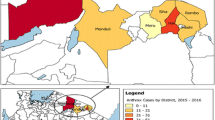
This retrospective study aimed to assess the spatial and temporal distribution of anthrax and to identify risk areas in Zimbabwe. The data were extracted from the monthly and annual reports of the Division of Livestock Production and Veterinary Services for the period 1967 to 2006. The data were analyzed in relation to temporal and spatial factors. The hot-dry season was found to be significantly (X 2 = 847.8, P < 0.001) associated with the occurrence of anthrax in cattle, and the disease was found to be approximately three times more likely to occur during this season compared to other seasons. Anthrax outbreaks demonstrated a gradual temporal increase from an annual mean of three outbreaks for the 5-year period (1967–1971) to 42 for the 5-year period (2002–2006). Similarly, the data demonstrated a spatial increase in the number of districts affected by anthrax between 1967 and 2006, with 12 districts affected for the 10-year period (1967–1976) that expanded to 42 districts for the 10-year period (1997–2006). The majority of outbreaks (83.7%) were recorded in rural areas, and 11 districts were found to be at a higher risk than others. There is need to develop differential vaccination strategy, other control strategies and preventive recommendations to reduce anthrax in high-risk districts. In the medium- to low-risk districts, maintenance of effective surveillance systems and improvement of awareness is very important to detect and contain outbreaks early.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beyer, W. And Turnbull, P.C.B., 2009. Anthrax in animals, Molecular Aspects of Medicine, 30, 481–489.
Blackburn, J.K., McNyset, K.M., Curtis, A. and Hugh-Jones, M.E., 2007. Modeling the geographic distribution of Bacillus anthracis, the causative agent of anthrax disease, for the contiguous United States using predictive ecologic niche modeling, American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 77, 1103–1110.
Clegg, S.B., Turnbull, P.C.B., Foggin, M. and Lindeque, P.M., 2007. Massive outbreak of anthrax in wildlife in the Malilangwe Wildlife Reserve, Zimbabwe, Veterinary Record, 160, 113--18
Cherkasskiy, B.L., 1999. A national register of historic and contemporary anthrax foci, Journal of Applied Microbiology, 87, 1921–95.
Davies, J.C. A., 1980. Transmission of anthrax, Central African Journal of Medicine, 26, 47.
Davies, J.C.A., 1982. A major epidemic of anthrax in Zimbabwe: 1, Central African Journal of Medicine, 28, 291–298.
Davies, J.C.A., 1983. A major epidemic of anthrax in Zimbabwe, Central African Journal of Medicine, 29, 8–12.
Davies, J.C.A., 1985. A major epidemic of anthrax in Zimbabwe, 2: the experience at the Beatrice Road Infectious Diseases Hospital, Harare, Central African Journal of Medicine, 31, 176–180.
De Vos, V., 1990. The ecology of anthrax in Kruger National Park, South Africa, Salisbury Medical Bulletin, 68 (special supplement), 19–23.
Dohoo, I., Martin, W., Stryhn, H. Veterinary Epidemiologic Research: AVC Inc., Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island, 2003.
Dragon, D.C. and Rennie, R.P., 1995. The ecology of anthrax spores: tough but not invincible, Canadian Veterinary Journal, 36, 295–301.
Dragon, D.C., Elkin, B.T., Nishi, J.S. and Ellsworth, T.R., 1999. A review of anthrax in Canada and implications for research on the disease in northern bison, Journal of Applied Microbiology, 87, 208–213.
Fasanella, A., Galante, D., Garofolo, G. and Hugh Jones, M., 2010. Anthrax undervalued zonoosis, Veterinary Microbiology, 140, 318–331.
Hambleton, P., Carman, J.A. and Melling J., 1984. Anthrax: the disease in relation to vaccines, Vaccine, 2, 125–131.
Hugh-Jones, M. and Blackburn, J., 2009. The ecology of Bacillus anthracis, Molecular Aspects of Medicine, 30, 356–367.
Johnson, R., 2005. Epizootiology and ecology of anthrax. In: United States Department of Agriculture, Center for Emerging Infections, Centers for Disease Control, Veterinary Services Report.
Keim, P., Van Ert, M.N., Pearson, T., Vogler, A.J., Huynh, L.Y. and Wagner, D.M., 2003. Anthrax molecular epidemiology and forensics: using the appropriate marker for different evolutionary scales, Infection, Genetics and Evolution, 4, 205–213.
Kobuch, W. E., Davies, J., Fleischer, K., Isaacson, M. and Turnbull, P. C. B., 1990. A clinical and epidemiological study of 621 patients with anthrax in western Zimbabwe, Proceedings of the international workshop on anthrax, Salisbury Medical Bulletin, 68(supplement), 34–38.
Lawrence, J. A., Foggin, C. M. and Norval, R. A., 1980. The effects of war on the control of diseases of livestock in Rhodesia (Zimbabwe), Veterinary Record, 107, 82–85.
Levy, L.M., Baker, N. and Meyer, M.P., 1981. Anthrax meningitis in Zimbabwe, Central African Journal of Medicine, 27, 101–104.
Lindeque, P.M. and Turnbull, P.C., 1994. Ecology and epidemiology of anthrax in Etosha National Park, Namibia, Onderstepoort Journal of Veterinary Research, 61, 71–83.
Matope, G., Bhebhe, E., Muma, J.B, Lund, A., Skjerve, E., (2010) Herd-level factors for Brucella seropositivity in cattle reared in smallholder dairy farms of Zimbabwe. Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 94, 213–221.
Mckendrick, D.R.A., 1980. Anthrax and its transmission to humans, Central African Journal of Medicine, 26, 126–128.
Nass, M., 1992. Anthrax epizootic in Zimbabwe 1978–1980: due to deliberate spread?, PSR Quarterly 2, 198–209.
OIE., 1997. OIE Animal Health and Disease Control Report 1997. Office International Des Epizooties, Paris, France.
Pugh, A.O. and Davies, J.C.A., 1990. Human anthrax in Zimbabwe, Salisbury Medical Bulletin, 68 (special supplement), 32–33.
Smith, K.L., De Vos, V., Bryden, H.B., Hugh-Jones, M.E., Klevytska, A., Price, L.B., Keim, P. and Scholl, D.T., 1999. Meso-scale ecology of anthrax in southern Africa: a pilot study of diversity and clustering, Journal of Applied Microbiology, 87, 204–207.
Smith, K.L., De Vos, V., Price, L.B., Hugh-Jones, M.E. and Keim, P., 2000. Bacillus anthracis diversity in Kruger National Park, Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 38, 3780–3784.
Starr, J.R., 1988. Weather, climate and animal performance, Technical Note No. 190, World Meteorological Organization, Geneva, Switzerland.
Stein, C.D., 1945. The history and distribution of anthrax in livestock in the United States, Veterinary Medicine (Praha), 40, 340–349.
Stein, C.D. and van Ness, G.B., 1955. A ten year survey of anthrax in livestock with special reference to outbreaks in 1954, Veterinary Medicine (Praha), 50, 579–590.
Webster, A.J.F., 1981. Weather and infectious disease in cattle, Veterinary Record, 108, 183–187.
WHO, 2005. Guidelines for the Surveillance and Control of anthrax in humans and animals, Emerging and Communicable Disease Surveillance, Control. http://www.who.int/emc.
Turnbull, P.C.B., Hudson, R.A., Ward, M.J., Jones, M.N., Quinn, C.P., Finnie, N.J., Duggleby, C.J., Kramer, J.M. and Melling, J., 1990. Bacillus anthracis but not always anthrax, Journal of Applied Bacteriology, 72, 21–28.
Turner, M., 1980. Anthrax in humans in Zimbabwe, Central African Journal of Medicine, 26, 291–298.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Department of Veterinary Technical Services, Dr Donora of the Department of Veterinary Field Services for allowing access to anthrax records.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chikerema, S.M., Pfukenyi, D.M., Matope, G. et al. Temporal and spatial distribution of cattle anthrax outbreaks in Zimbabwe between 1967 and 2006. Trop Anim Health Prod 44, 63–70 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-011-9888-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-011-9888-z