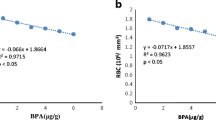
Abstract
Bisphenol-A (BPA) is an environmental contaminant used in the manufacturing of polycarbonate plastics and epoxy resins, which has been discovered in freshwater systems worldwide as a result of effluent from manufacturing. This bioactive molecule is an estrogen mimic and has become a concern for exposure, especially during development, resulting in its removal from baby bottles and other consumer products. BPA is an endocrine disruptor in a variety of species and has been classified as a toxic substance in multiple countries. In this study, we examined the effect of BPA exposure on leukocyte counts in wild yellow perch, Perca flavescens. Yellow perch were exposed to either 2, 4, and 8 ppb BPA; Saprolegnia; or a blank control for a period of 7 days. Leukocyte blood counts were significantly higher in Saprolegnia, 4 ppb BPA, and 8 ppb BPA treatments compared to control. To test compound effects of BPA and Saprolegnia on leukocyte counts over a 7-day period, perch were exposed to either 4 ppb BPA, 4 ppb BPA + Saprolegnia, or control. Leukocyte counts were significantly higher in the 4 ppb BPA treatment relative to control. The 4 ppb BPA + Saprolegnia treatment was numerically elevated from the control, exhibiting a 153 % increase relative to control. BPA represents a contaminant with immunomodulatory properties that remain to be determined.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belfroid, A., van Velzen, M., van der Horst, B., & Vethaak, D. (2002). Occurrence of bisphenol A in surface water and uptake in fish: evaluation of field measurements. Chemosphere, 49(1), 97–103.
Burridge, E. (2008). Chemical profile: bisphenol A. European Chemistry News.
Cavalieri, E. L., & Rogan, E. G. (2010). Is bisphenol A a weak carcinogen like the natural estrogens and diethylstilbestrol? IUBMB Life, 62(10), 746–751.
Daoust, P., Larson, B., & Johnson, G. (1989). Mycobacteriosis in yellow perch (Perca flavescens) from two lakes in Alberta. Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 25(1), 31–37.
Davis, A. K., Maney, D. L., & Maerz, J. C. (2008). The use of leukocyte profiles to measure stress in vertebrates: a review for ecologists. Functional Ecology, 22(5), 760–772.
Forson, D. D., & Storfer, A. (2006). Atrazine increases ranavirus susceptibility in the tiger salamander, Ambystoma tigrinum. Ecological Applications, 16(6), 2325.
Gerwick, L., Corley-Smith, G., & Bayne, C. J. (2007). Gene transcript changes in individual rainbow trout livers following an inflammatory stimulus. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 22(3), 157–171.
Hoeger, B., van den Heuvel, M. R., Hitzfeld, B. C., & Dietrich, D. R. (2004). Effects of treated sewage effluent on immune function in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquatic Toxicology, 70(4), 345–355.
Howen, B. (2000). Blood film preparation and staining procedures. Laboratory Haematology, 6, 1.
Kalair, J. S., Mishra, V. S., & Singh, R. K. (1993). Pesticide sumithion induced haematological changes in mud eel Amphipnous cuchia. Biological Membranes, 19, 41–48.
Kazner, C., Lehnberg, K., Kovolova, L., et al. (2008). Removal on endocrine disruptors and cytostatics from effluent by nanofiltration in combination with adsorption on powdered activated carbon. Water Science and Technology, 58(8), 1699–1706.
Keppel, G. (1982). Design and analysis: a researchers handbook. New Jersey: Prentice-Hall.
Klečka, G. M., Staples, C. A., Clark, K. E., van der Hoeven, N., Thomas, D. E., & Hentges, S. G. (2009). Exposure analysis of bisphenol A in surface water systems in North America and Europe. Environmental Science & Technology, 43(16), 6145–6150.
Mekkawy, A. I., Mahmoud, U. M., & Sayed, A. E. (2011). Effects of 4-nonylphenol on blood cells of the African catfish Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822). Tissue & Cell, 43(4), 223–229.
Milla, S., Depiereux, S., & Kestemont, P. (2011). The effects of estrogenic and androgenic endocrine disruptors on the immune system of fish: a review. Ecotoxicology, 20(2), 305–319.
Minghong, W., Hai, X., Ming, Y., & Gang, X. (2011). Effects of chronic bisphenol A on hepatic antioxidant parameters in medaka (Oryzias latipes). Toxicological & Environmental Chemistry, 93, 270–278.
Muzzarelli, R. A. A., Muzzarelli, C., Tarsi, R., Miliani, M., Gabbanelli, F., & Cartolari, M. (2001). Fungistatic activity of modified chitosans against Saprolegnia parasitica. Biomacromolecules, 2(1), 165–169.
Neish, G. A. (1975). Carbenicillin as an aid in obtaining bacteria-free cultures of Saprolegnia species. Mycologia, 67(6), 1192–1197.
O'Halloran, K., Ahokas, J. T., & Wright, P. F. A. (1998). Response of fish immune cells to in vitro organotin exposures. Aquatic Toxicology, 40(2–3), 141–156.
Ohta, Y., & Flajnik, M. (2006). IgD, like IgM, is a primordial immunoglobulin class perpetuated in most jawed vertebrates. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103(28), 10723–10728.
Plouffe, D. A., Hanington, P. C., Walsh, J. G., Wilson, E. C., & Belosevic, M. (2005). Comparison of select innate immune mechanisms of fish and mammals. Xenotransplantation, 12(4), 266–277.
Rice, C. D., Kergosien, D. H., & Adams, S. M. (1996). Innate immune function as a bioindicator of pollution stress in fish. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 33(2), 186–192.
Rivas, A., Lacroix, M., Olea-Serrano, F., Laios, I., Leclercq, G., & Olea, N. (2002). Estrogenic effect of a series of bisphenol analogues on gene and protein expression in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 82(1), 45–53.
Scott, W. B., & Crossman, E. J. (1973). Freshwater fishes of Canada. Bulletin of the Fisheries Research Board of Canada, 184, 1–966.
Singh, N. N., & Srivastava, A. K. (2010). Haematological parameters as bioindicators of insecticide exposure in teleosts. Ecotoxicology, 19(5), 838–854.
Staples, C. A., Dorn, P. B., Klecka, G. M., O'Block, S. T., & Harris, L. R. (1998). A review of the environmental fate, effects, and exposures of bisphenol A. Chemosphere, 36(10), 2149–2173.
Van West, P. (2006). Saprolegnia parasitica, an oomycete pathogen with a fishy appetite: new challenges for an old problem. Mycologist, 20, 99–104.
Weng, Y., Hsu, P., Liyanarachchi, S., et al. (2010). Epigenetic influences of low-dose bisphenol A in primary human breast epithelial cells. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 248, 111–121.
Yin, D., Hu, S., Gu, Y., Wei, L., Liu, S., & Zhang, A. (2007). Immunotoxicity of bisphenol A to Carassius auratus lymphocytes and macrophages following in vitro exposure. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 19(2), 232–237.
Yurino, H., Ishikawa, S., Sato, T., et al. (2004). Endocrine disruptors (environmental estrogens) enhance autoantibody production by B1 cells. Toxicological Sciences, 81(1), 139–147.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Todd Bowerman and Doug McIntyre for help in collecting yellow perch. Ashley Ryan assisted with all analytical work and photography. Thank you to Rebecca Mulligan for helping culture Saprolegnia. This study was funded by Nipissing University and all work was conducted under Nipissing University Animal Care Committee protocol #PR2010-04-04-20.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rogers, J.A., Mirza, R.S. The Effects of Bisphenol-A on the Immune System of Wild Yellow Perch, Perca flavescens . Water Air Soil Pollut 224, 1728 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1728-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1728-5