Abstract
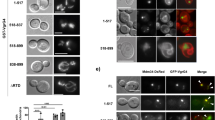
Shigella type III effector OspF, a nuclear translocation protein, has been showed to have an essential role in Shigella flexneri infection and virulence; OspF increases inflammation and induces bacterial invasion by down-regulating MAPK kinases pathway. Nevertheless, the exact mechanisms underlying its nuclear translocation and signaling remain unclear. In the following study, we constructed series of OspF truncated mutants to identify the OspF nuclear localization signals which mapped to the amino acids 209–239. Moreover, we found that this sequence was essential to bind the canonical nuclear import adaptor importin α1. Additionally, the 209–239 residues deletion mutant could not bind the importin α1. Consistent with this observation, our results revealed that OspF can inhibit the MAPK signals in the nucleus. Moreover, OspF translocate to the nucleus through Ran-GTPase and importin α1-dependent manner. These results can provide new avenues for depicting the biological functions of OspF during Shigella infection.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- T3SS:
-
Type III secretion system
- NPCs:
-
Nuclear pore complexes
- NLS:
-
Nuclear localization signals
References
Arbibe L, Sansonetti P (2007) Shigella flexneri modulates host cell epigenetic information as a strategy to shape the transcriptional response. Med Sci 23:238–240
Arbibe L, Kim DW, Batsche E, Pedron T, Mateescu B, Muchardt C, Parsot C, Sansonetti PJ (2007) An injected bacterial effector targets chromatin access for transcription factor NF-kappaB to alter transcription of host genes involved in immune responses. Nat Immunol 8:47–56
Ashida H, Ogawa M, Mimuro H, Kobayashi T, Sanada T, Sasakawa C (2011) Shigella are versatile mucosal pathogens that circumvent the host innate immune system. Curr Opin Immunol 23:448–455
Chook YM, Suel KE (2011) Nuclear import by karyopherin-betas: recognition and inhibition. Biochim Biophys Acta 1813:1593–1606
Dingwall C, Robbins J, Dilworth SM, Roberts B, Richardson WD (1988) The nucleoplasmin nuclear location sequence is larger and more complex than that of SV-40 large T antigen. J Cell Biol 107:841–849
Duong-Ly KC, Gabelli SB (2015) Affinity purification of a recombinant protein expressed as a fusion with the maltose-binding protein (MBP) tag. Methods Enzymol 559:17–26
Guo ZJ, Wang DX, Yao Q, Chen KP, Zhang CX (2010) Identification of a novel functional nuclear localization signal in the protein encoded by open reading frame 47 of Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus. Arch Virol 155:1943–1950
Hale TL (1991) Genetic basis of virulence in Shigella species. Microbiol Rev 55:206–224
Jankowski R, Czubryt MP, Pierce GN (2000) The nuclear protein import assay in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 44:421–427
Jo K, Kim EJ, Yu HJ, Yun CH, Kim DW (2017) Host cell nuclear localization of Shigella flexneri effector OspF Is facilitated by SUMOylation. J Microbiol Biotechnol 27:610–615
Kalderon D, Richardson WD, Markham AF, Smith AE (1984) Sequence requirements for nuclear location of simian virus 40 large-T antigen. Nature 311:33–38
Lee BJ, Cansizoglu AE, Suel KE, Louis TH, Zhang Z, Chook YM (2006) Rules for nuclear localization sequence recognition by karyopherin beta 2. Cell 126:543–558
Li H, Xu H, Zhou Y, Zhang J, Long C, Li S, Chen S, Zhou JM, Shao F (2007) The phosphothreonine lyase activity of a bacterial type III effector family. Science 315:1000–1003
Lippmann J, Gwinner F, Rey C, Tamir U, Law HK, Schwikowski B, Enninga J (2015) Bacterial internalization, localization, and effectors shape the epithelial immune response during Shigella flexneri infection. Infect Immun 83:3624–3637
Lott K, Bhardwaj A, Sims PJ, Cingolani G (2011) A minimal nuclear localization signal (NLS) in human phospholipid scramblase 4 that binds only the minor NLS-binding site of importin alpha1. J Biol Chem 286:28160–28169
Nallamsetty S, Waugh DS (2007) A generic protocol for the expression and purification of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli using a combinatorial His6-maltose binding protein fusion tag. Nat Protoc 2:383–391
Pumroy RA, Cingolani G (2015) Diversification of importin-alpha isoforms in cellular trafficking and disease states. Biochem J 466:13–28
Reiterer V, Grossniklaus L, Tschon T, Kasper CA, Sorg I, Arrieumerlou C (2011) Shigella flexneri type III secreted effector OspF reveals new crosstalks of proinflammatory signaling pathways during bacterial infection. Cell Signal 23:1188–1196
Rosner M, Schipany K, Hengstschlager M (2013) Merging high-quality biochemical fractionation with a refined flow cytometry approach to monitor nucleocytoplasmic protein expression throughout the unperturbed mammalian cell cycle. Nat Protoc 8:602–626
Sansonetti PJ, d’Hauteville H, Formal SB, Toucas M (1982) Plasmid-mediated invasiveness of “Shigella-like” Escherichia coli. Ann Microbiol 133:351–355
Sasakawa C, Kamata K, Sakai T, Makino S, Yamada M, Okada N, Yoshikawa M (1988) Virulence-associated genetic regions comprising 31 kilobases of the 230-kilobase plasmid in Shigella flexneri 2a. J Bacteriol 170:2480–2484
Zhu Y, Li H, Long C, Hu L, Xu H, Liu L, Chen S, Wang DC, Shao F (2007) Structural insights into the enzymatic mechanism of the pathogenic MAPK phosphothreonine lyase. Mol Cell 28:899–913
Zurawski DV, Mitsuhata C, Mumy KL, McCormick BA, Maurelli AT (2006) OspF and OspC1 are Shigella flexneri type III secretion system effectors that are required for postinvasion aspects of virulence. Infect Immun 74:5964–5976
Zurawski DV, Mumy KL, Faherty CS, McCormick BA, Maurelli AT (2009) Shigella flexneri type III secretion system effectors OspB and OspF target the nucleus to downregulate the host inflammatory response via interactions with retinoblastoma protein. Mol Microbiol 71:350–368
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Professor Feng Shao at National Institute of Biological Science (NIBS) for expert technical support and kindly give the plasmids. This study was supported by New Century Excellent Talents in University (Grant No. NCET-08-0912, to H.T. Li), Peking Union Medical College Youth Fund/the fundamental research Funds for the central University (Grant No. 3332016048, to H.M. Zhao); Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Innovation Fund for medical Sciences (Grant No. 2016-I2M-006, to H.M. Zhao), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. XDJK2016C158, to Y. Zhang).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, H., Zhang, Y., Wu, P. et al. The Shigella type three secretion system effector OspF invades host nucleus by binding host importin α1. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 35, 71 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-019-2635-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-019-2635-8