Abstract
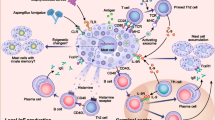
Mast cells are widely recognized as effector cells of allergic inflammatory reactions. They contribute to the pathogenesis of different chronic inflammatory diseases, wound healing, fibrosis, thrombosis/fibrinolysis, and anti-tumor immune responses. In this paper, we summarized the role of P2X and P2Y receptors in mast cell activation and effector functions. Mast cells are an abundant source of ATP which is stored in their granules and secreted upon activation. We discuss the contribution of mast cells to the extracellular ATP release and to the maintenance of extracellular nucleotides pool. Recent publications highlight the importance of purinergic signaling for the pathogenesis of chronic airway inflammation. Therefore, the role of ATP and P2 receptors in allergic inflammation with focus on mast cells was analyzed. Finally, ATP functions as mast cell autocrine/paracrine factor and as messenger in intercellular communication between mast cells, nerves, and glia in the central nervous system.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ART:
-
ADP-ribosyltransferase
- BMMC:
-
Bone marrow-derived mast cell
- CBMC:
-
Cord blood mast cell
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- HLMC:
-
Human lung mast cell
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- MIP:
-
Macrophage inflammatory protein
- NAD:
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
- NGF:
-
Nerve growth factor
- oATP:
-
Oxidized ATP
- OVA:
-
Ovalbumin
- PAMPS:
-
Pathogen-associated molecular patterns
- PKC:
-
Protein kinase C
- RBL:
-
Rat basophilic leukemia
- RANTES:
-
Regulated on activation, normal T cell expressed and secreted
- SCF:
-
Stem cell factor
- SP:
-
Substance P
- TNFα:
-
Tumor necrosis factor α
References
Dwyer KM, Deaglio S, Gao W et al (2007) CD39 and control of cellular immune responses. Purinergic Signalling 3:171–180
Colgan SP, Eltzschig HK, Eckle T et al (2006) Physiological roles for ecto-5′-nucleotidase (CD73). Purinergic Signalling 2:351–360
Dahlquist R, Diamant B (1974) Interaction of ATP and calcium on the rat mast cell: effect on histamine release. Acta Pharm Toxicol (Copenh) 34:368–384
Sugiyama K (1971) Calcium-dependent histamine release with degranulation from isolated rat mast cells by adenosine 5′-triphosphate. Jpn J Pharmacol 21:209–226
Cockcroft S, Gomperts BD (1979) ATP induces nucleotide permeability in rat mast cells. Nature 279:541–542
Cockcroft S, Gomperts BD (1980) The ATP4− receptor of rat mast cells. Biochem J 188:789–798
Osipchuk Y, Cahalan M (1992) Cell-to-cell spread of calcium signals mediated by ATP receptors in mast cells. Nature 359:241–244
McCloskey M, Fan Y, Luther S (1999) Chemotaxis of rat mast cells towards adenine nucleotides. J Immunol 163:970–977
Bulanova E, Budagian V, Orinska Z et al (2005) Extracellular ATP induces cytokine expression and apoptosis through P2X7 receptor in murine mast cells. J Immunol 174:3880–3890
Ehrlich P (1878) Beiträge zur Theorie und Praxis der histologischen Färbung. Dissertation, Leipzig University
Galli SJ, Tsai M (2008) Mast cells: versatile regulators of inflammation, tissue remodeling, host defense and homeostasis. J Dermatol Sci 49:7–19
Heib V, Becker M, Taube C et al (2008) Advances in the understanding of mast cell function. Br J Haematol 142:683–694
Rao KN, Brown MA (2008) Mast cells: multifaceted immune cells with diverse roles in health and disease. Ann NY Acad Sci 1143:83–104
Kalesnikoff J, Galli SJ (2008) New developments in mast cell biology. Nat Immunol 9:1215–1223
Stelekati E, Orinska Z, Bulfone-Paus S (2007) Mast cells in allergy: innate instructors of adaptive responses. Immunobiology 212:505–519
Galli S, Maurer M, Lantz C (1999) Mast cells as sentinels of innate immunity. Curr Opin Immunol 11:53–59
Di Virgilio F, Chiozzi P, Ferrari D et al (2001) Nucleotide receptors: an emerging family of regulatory molecules in blood cells. Blood 97:587–600
Sayed BA, Christy A, Quirion MR et al (2008) The master switch: the role of mast cells in autoimmunity and tolerance. Ann Rev Immunol 26:705–739
Bankl HC, Valent P (2002) Mast cells, thrombosis, and fibrinolysis: the emerging concept. Thromb Res 105:359–365
Theoharides TC, Cochrane DE (2004) Critical role of mast cells in inflammatory diseases and the effect of acute stress. J Neuroimmunol 146:1–12
Piliponsky AM, Levi-Schaffer F (2000) Regulation of apoptosis in mast cells. Apoptosis 5:435–441
Di Virgilio F (2005) Purinergic mechanism in the immune system: a signal of danger for dendritic cells. Purinergic Signalling 1:205–209
Novak I (2003) ATP as a signaling molecule: the exocrine focus. News Physiol Sci 18:12–17
Gordon JL (1986) Extracellular ATP: effects, sources and fate. Biochem J 233:309–319
Nakanishi M, Furuno T (2008) Molecular basis of neuroimmune interaction in an in vitro coculture approach. Cell Mol Immunol 5:249–259
Cotrina ML, H-C LJ, Alves-Rodrigues A et al (1998) Connexins regulate calcium signaling by controlling ATP release. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:15735–15740
Barber MT, Monyer H, Bruzzone R (2006) Cell–cell communication beyond connexins: pannexin channels. Physiology 21:103–114
Locovei A, Bao L, Dahl G (2006) Pannexin 1 in erythrocytes: function without a gap. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:7655–7659
Schenk U, Westendorf AM, Radaelli E et al (2008) Purinergic control of T cell activation by ATP released through pannexin-1 hemichannels. Sci Signal 1:85–97
Mariathasan S, Monack DM (2007) Inflammasome adaptors and sensors: intracellular regulators of infection and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 7:31–40
Stefan C, Jansen S, Bollen M (2006) Modulation of purinergic signaling by NPP-type ectophosphodiesterases. Purinergic Signalling 2:361–370
Hauswirth AW, Escribano L, Pardos A et al (2008) CD203c is overexpressed on neoplastic mast cells in systemic mastocytosis and is upregulated upon IgE receptor cross-linking. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 21:797–806
Burnstock G (1978) A basis for distinguishing two types of purinergic receptor. In: Straub RW, Bolis L (eds) Cell membrane receptors for drugs and hormones: a multidisciplinary approach. Raven, New York, pp 107–118
Fredholm BB, Ijzerman AP, Jacobson KA et al (2001) XXV. Nomenclature and classification of adenosine receptors. Pharmacol Rev 53:527–552
Burnstock G (2007) Purine and pyrimidine receptors. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:1471–1483
Van Kolen K, Slegers H (2006) Integration of P2Y receptor-activated signal transduction pathways in G protein-dependent signaling networks. Purinergic Signalling 2:451–469
Abbracchio MP, Boeynaems JM, Barnard EA et al (2003) Characterization of the UDP-glucose receptor (re-named here the P2Y14 receptor) adds diversity to the P2Y receptor family. Trends Pharmacol Sci 24:52–55
North RA (2002) Molecular physiology of P2X receptors. Physiol Rev 82:1013–1067
Markwardt F (2007) Activation kinetics of single P2X receptors. Purinergic Signalling 3:249–253
Adinolfi E, Pizzirani C, Idzko M, Panther E, Norgauer J, Di Virgilio F, Ferrari D (2005) P2X7 receptor: death or life? Purinergic Signalling 1:219–227
Surprenant A, Rassendren F, Kawashima E et al (1996) The cytolytic P2Z receptor for extracellular ATP identified as a P2X receptor (P2X7). Science 272:735–738
Seman M, Adriouch S, Scheuplein F et al (2003) NAD-induced T cell death: ADP-ribosylation of cell surface proteins by ART2 activates the cytolytic P2X7 purinoceptor. Immunity 19:571–582
Hong S, Schwarz N, Brass A et al (2009) Differential regulation of P2X7 receptor activation by extracellular nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and ecto-ADP-ribosyltransferases in murine macrophages and T cells. J Immunol 183:578–592
Di Virgilio F (2007) Purinergic signalling in the immune system: a brief update. Purinergic Signalling 3:1–3
Gachet C (2006) Regulation of platelet functions by P2 receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 46:277–300
Jamieson GP, Snook MB, Thurlow PJ et al (1996) Extracellular ATP causes of loss of L-selectin from human lymphocytes via occupancy of P2Z purinoceptors. J Cell Physiol 166:637–642
Gu B, Bendall LJ, Wiley JS (1998) Adenosine triphosphate-induced shedding of CD23 and L-selectin (CD62L) from lymphocytes is mediated by the same receptor but different metalloproteases. Blood 92:946–951
Myrtek D, Idzko M (2007) Chemotactic activity of extracellular nucleotides on human immune cells. Purinergic Signalling 3:5–11
Ferrari D, Pizzirani C, Adinolfi E et al (2006) The P2X7 receptor: a key player in IL-1 processing and release. J Immunol 176:3877–3883
MacKenzie A, Wilson HL, Kiss-Toth E et al (2001) Rapid secretion of interleukin-1β by microvesicle shedding. Immunity 15:825–835
Bianco F, Pravettoni E, Colombo A et al (2005) Astrocyte-derived ATP induces vesicles shedding and IL-1β release from microglia. J Immunol 174:7268–7277
Suzuki T, Hide I, Ido K et al (2004) Production and release of neuroprotective tumor necrosis factor by P2X7 receptor-activated microglia. J Neurosci 24:1–7
Le Gall SM, Bobe P, Reiss K et al (2009) ADAMs 10 and 17 represent differentially regulated components of a general shedding machinery for membrane proteins such as transforming growth factor α, L-selectin, and tumor necrosis factor α. Mol Biol Cell 20:1785–1794
Bulanova E, Budagian V, Orinska Z et al (2009) ATP induces P2X7 receptor-independent cytokine and chemokine expression through P2X1 and P2X3 receptors in murine mast cells. J Leukoc Biol 85:692–702
Royle SJ, Bobanovic LK, Murrell-Lagnado RD (2002) Identification of non-canonical tyrosine-based endocytic motif in an ionotropic receptor. J Biol Chem 277:35378–35385
Wang L, Jakobsen SEW, Bengtsson A et al (2004) P2 receptor mRNA expression profiles in human lymphocytes, monocytes and CD34+ stem and progenitor cells. BMC Immunol 5:16–22
Bradding P, Okayama Y, Kambe N et al (2003) Ion channel gene expression in human lung, skin, and cord blood-derived mast cells. J Leukoc Biol 73:614–620
Schulman ES, Glaum MC, Post T et al (1999) ATP modulates anti-IgE-induced release of histamine from human lung mast cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 20:530–537
Feng C, Mery AG, Beller EM et al (2004) Adenine nucleotides inhibit cytokine generation by human mast cells through a Gs-coupled receptor. J Immunol 173:7539–7547
Cockcroft S, Gomperts BD (1979) Activation and inhibition of calcium-dependent histamine secretion by ATP ions applied to rat mast cells. J Physiol 296:229–243
Tatham PER, Lindau M (1990) ATP-induced pore formation in the plasma membrane of rat peritoneal mast cells. J Gen. Physiol 95:459–476
Jaffar ZH, Pearce FL (1993) Some characteristics of the ATP-induced histamine release from and permeabilization of rat mast cells. Agents Actions 40:18–27
Izushi K, Tasaka K (1991) Essential role of ATP and possibility of activation of protein kinase C in Ca2+-dependent histamine release from permeabilized rat peritoneal mast cells. Pharmacology 42:297–308
Buell G, Michel AD, Lewis C et al (1996) P2X1 receptor activation in HL60 cells. Blood 87:2659–2664
Qian YX, McCloskey MA (1993) Activation of mast cells K+ channels through multiple G protein-linked receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:7844–7848
Saito H, Ebisawa M, Reason DC et al (1991) Extracellular ATP stimulates interleukin-dependent cultured mast cells and eosinophils through calcium mobilization. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 94:68–70
Pelegrin P, Surprenant A (2006) Pannexin-1 mediates large pore formation and interleukin-1β release by the ATP-gated P2X7 receptor. EMBO J 25:5071–5082
Pelegrin P, Surprenant A (2007) Pannexin-1 couples to maitotoxin- and nigericin-induced interleukin-1β release through a dye uptake-independent pathway. J Biol Chem 282:2386–2394
Lee YH, Lee SJ, Seo MH et al (2001) ATP-induced histamine release is in part related to phospholipase A2-mediated arachidonic acid metabolism in rat peritoneal mast cells. Arch Pharm Res 24:552–556
Sudo N, Tanaka K, Koga Y et al (1996) Extracellular ATP activates mast cells via a mechanism that is different from the activation induced by the cross-linking of Fc receptors. J Immunol 156:3970–3979
Chakravarty N (1980) The role of plasma membrane Ca++–Mg++ activated adenosine triphosphatase of rat mast cells on histamine release. Acta Pharm Toxicol (Copenh) 47:223–225
Chakravarty N, Nielesen EH (1981) Adenosine triphosphatase in non-secreting and secreting mast cells. Agents Actions 11:67–69
Schnurr M, Toy T, Schin A et al (2005) Extracellular nucleotides signaling by P2 receptors inhibits IL-12 and enhances IL-23 expression in human dendritic cells: a novel role for the cAMP pathway. Blood 105:1582–1589
Swanson KD, Reigh C, Landreth GE (1998) ATP-stimulated activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinases through ionotrophic P2X2 purinoreceptors in PC12 cells: difference in purinoreceptor sensitivity in two PC12 cell lines. J Biol Chem 273:19965–19971
Neary JT, McCarthy M, Kang Y et al (1998) Mitogenic signaling from P1 and P2 purinergic receptors to mitogen-activated protein kinase in human fetal astrocyte cultures. Neurosci Lett 242:159–162
Humphreys BD, Rice J, Kertesy SB et al (2000) Stress-activated protein kinase/JNK activation and apoptotic induction by the macrophage P2X7 nucleotide receptor. J Biol Chem 275:26792–26798
Budagian V, Bulanova E, Brovko L et al (2003) Signaling through P2X7 receptor in human T cells involves p56lck, MAP kinases, and transcription factors AP-1 and NF-κB. J Biol Chem 278:1549–1560
Gabel CA (2007) P2 purinergic receptor modulation of cytokine production. Purinergic Signalling 3:27–38
Cox MA, Gomes B, Plamer K et al (2005) The pyrimidinergic P2X6 receptor mediates a novel release of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines in monocytic cells stimulated with UDP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 330:467–473
Takayama K, Garsia-Gardena G, Sukhova GK et al (2002) Prostaglandin E2 suppresses chemokine production in human macrophages through the EP4 receptor. J Biol Chem 277:44147–44154
Okamoto T, Murayama Y, Hayashi Y et al (1991) Identification of a Gs activator region of the β2-adrenergic receptor that is autoregulated via protein kinase A-dependent phosphorylation. Cell 67:723–730
Rossi L, Manfredini R, Bertolini F et al (2007) The extracellular nucleotide UTP is a potent inducer of hematopoietic stem cell migration. Blood 109:533–542
Zheng LM, Zychlinsky A, Liu C-C et al (1991) Extracellular ATP as a trigger for apoptosis or programmed cell death. J Cell Biol 112:279–288
Zanovello P, Bronte V, Rosato A et al (1990) Responses of mouse lymphocytes to extracellular ATP. II. Extracellular ATP causes cell type-dependent lysis and DNA fragmentation. J Immunol 145:1545–1550
Pfeiffer ZA, Aga M, Prabhu U et al (2004) The nucleotide receptor P2X7 mediates actin reorganization and membrane blebbing in RAW 264.7 macrophages via p38 MAP kinase and Rho. J Leuk Biol 75:1173–1182
Nihei OK, de Carvalho AC, Salvino W et al (2000) Pharmacologic properties of P2Z/P2X7 receptor characterized in murine dendritic cells: role in the induction of apoptosis. Blood 96:996–1005
Mackenzie AB, Young MT, Adinolfi E et al (2005) Pseudoapoptosis induced by brief activation of ATP-gated P2X7 receptors. J Biol Chem 280:33968–33976
Shum BOV, Rolph MS, Sewell WA (2008) Mechanisms in allergic airway inflammation—lessons from studies in the mouse. Expert Rev Mol Med 10:e15
Long AA (2009) Immunomodulators in the treatment of asthma. Allergy Asthma Proc 30:109–119
Barrett NA, Austen KF (2009) Innate cells and T helper 2 cell immunity in airway inflammation. Immunity 31:425–437
Idzko M, Hammad H, van Nimwegen M et al (2007) Extracellular ATP triggers and maintains asthmatic airway inflammation by activating dendritic cells. Nat Immunol 13:913–919
Pellegrino R, Wilson O, Jenairi G et al (1996) Lung mechanics during induced bronchoconstriction. J Appl Physiol 81:964–975
Pelleg A, Schulman ES (2002) Adenosine 5′-triphosphate axis in obstructive airway disease. Am J Ther 9:454–464
Kulka M, Sheen CH, Tancowny BP et al (2009) Neuropeptides activate human mast cell degranulation and chemokine production. Immunology 123:398–410
Gu BJ, Wiley JS (2006) Rapid ATP-induced release of matrix metalloproteinase 9 is mediated by the P2X7 receptor. Blood 107:4946–4953
Kanbe N, Tanaka A, Kanbe M et al (1999) Human mast cells produce matrix metalloproteinase 9. Eur J Immunol 29:2645–2649
Akdis CA, Akdis M (2009) Mechanisms and treatment of allergic disease in the big picture of regulatory T cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol 123:735–746
Borsellino G, Kleinewietfeld M, Di Mitri D et al (2007) Expression of ectonucleotidase CD39 by Foxp3+ Treg cells: hydrolysis of extracellular ATP and immune suppression. Blood 110:1225–1232
Kobie JJ, Shah PR, Yang L et al (2006) T regulatory and primed uncommitted CD4 T cells express CD73, which suppresses effector CD4 T cells by converting 5′-adenosine monophosphate to adenosine. J Immunol 177:6780–6786
Schlosser SF, Burgstahler AD, Nathanson MH (1996) Isolated rat hepatocytes can signal to other hepatocytes and bile duct cells by release of nucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:9948–9953
Guthrie PB, Knappenberger J, Segal M et al (1999) ATP released from astrocytes mediates glial calcium waves. J Neurosci 19:520–528
Grierson JP, Meldolesi J (1995) Shear stress-induces [Ca2+]i transients and oscillations in mouse fibroblasts are mediated by endogenously released ATP. J Biol Chem 270:4451–4456
Deitmer JW (2001) Strategies for metabolic exchange between glial cells and neurons. Respir Physiol 129:71–81
Koizumi S, Fujishita K, Inoue K et al (2004) Ca2+ waves in keratinocytes are transmitted to sensory neurons: the involvement of extracellular ATP and P2Y2 receptor activation. Biochem J 380:329–338
Ossovskaya VS, Bunnett NW (2004) Protease-activated receptors: contribution to physiology and disease. Physiol Rev 84:579–621
Dimitriadou V, Buzzi MG, Moskowitz MA et al (1991) Trigeminal sensory fiber stimulation induces morphological changes reflecting secretion in rat dura mater mast cells. Neuroscience 41:97–112
Suzuki R, Furuno T, Okamoto K et al (2007) ATP plays a role in neurite stimulation with activated mast cells. J Neuroimmunol 192:49–56
Suzuki R, Furuno T, McKay DM et al (1999) Direct neurite–mast cell communication in vitro occurs via the neuropeptide substance P. J Immunol 163:2410–2415
Suzuki A, Suzuki R, Furuno T et al (2004) N-cadherin plays a role in the synapse-like structures between mast cells and neuritis. Biol Pharm Bull 27:1891–1894
Hudson CA, Christophi GP, Gruber RC et al (2008) Induction of IL-33 expression and activity in central nervous system glia. J Leuk Biol 84:631–643
Dropp JJ (1976) Mast cells in mammalian brain. Acta Anal (Basel) 94:1–21
Kovacs P, Hernadi I, Wilhelm M (2006) Mast cells modulate maintained neuronal activity in the thalamus in vivo. J Neuroimmunol 171:1–7
Rozniecki JJ, Hauser SL, Strein M et al (1995) Elevated mast cell tryptase in cerebrospinal fluid of multiple sclerosis patients. Ann Neurol 37:63–66
Bo L, Olsson T, Nyland H et al (1991) Mast cells in brain during experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in Lewis rats. J Neurol Sci 105:135–142
Brown MA, Tanzola MB, Robbie-Ryan M (2001) Mechanisms underlying mast cell influence on EAE disease course. Mol Immunol 38:1373–1378
Dietsch GN, Hinrichs DJ (1991) Mast cell proteases liberate stable encephalitogenic fragments from intact myelin. Cell Immunol 135:541–548
Johnson D, Seeldrayers PA, Weiner HL (1988) The role of mast cells in demyelination. 1. Myelin proteins are degraded by mast cell proteases and myelin basic protein and P2 can stimulate mast cell degranulation. Brain Res 44:195–198
Ferrero ME (2009) A new approach to the inflammatory/autoimmune diseases. Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov 4:108–113
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. Zane Orinska for critical reading of the manuscript and to Annette Wallisch for editorial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bulanova, E., Bulfone-Paus, S. P2 receptor-mediated signaling in mast cell biology. Purinergic Signalling 6, 3–17 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-009-9173-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-009-9173-z