Abstract
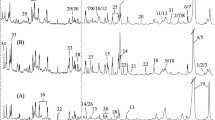
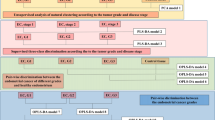
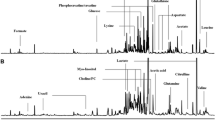
Colorectal cancer is one of the most frequent and most lethal forms of cancer in the western world. The aim of this study is to characterize by 1H high resolution magic angle spinning NMR spectroscopy (HRMAS) the metabolic fingerprint of both tumoral and healthy tissue samples obtained from a cohort of patients affected by primary colorectal adenocarcinoma. By analyzing HRMAS data using multivariate statistical analysis (PLS-DA), the two types of tissues could be discriminated with a high level of confidence. The identification of the metabolites at the origin of this discrimination revealed that adenocarcinomas are richer in taurine, glutamate, aspartate, and lactate whereas healthy tissues contain a higher amount of myo-inositol and β-glucose. The statistical model resulting from the PLS-DA analysis was subsequently used to perform a blind test on tumoral and healthy colon biopsies. The results of the classification showed that the HRMAS analysis has very high sensitivity and specificity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akoka, S., Barantin, L., & Trierweiler, M. (1999). Concentration measurement by proton NMR using the ERETIC method. Analytical Chemistry, 71(13), 2554–2557. doi:10.1021/ac981422i.
Andrew, E. R., Bradbury, A., & Eades, R. G. (1958). Removal of dipolar broadening of nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of solids by specimen rotation. Nature, 183, 1802–1803. doi:10.1038/1831802a0.
Cheng, L. L., Anthony, D. C., Comite, A. R., et al. (2000). Quantification of microheterogeneity in glioblastoma multiforme with ex vivo high-resolution magic-angle spinning (HRMAS) proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Neuro-Oncology, 2(2), 87–95. doi:10.1215/15228517-2-2-87.
Cheng, L. L., Chang, I. W., Louis, D. N., & Gonzalez, R. G. (1998). Correlation of high-resolution magic angle spinning proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy with histopathology of intact human brain tumor specimens. Cancer Research, 58(9), 1825–1832.
Cheng, L. L., Ma, M. J., Becerra, L., et al. (1997). Quantitative neuropathology by high resolution magic angle spinning proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 94(12), 6408–6413. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.12.6408.
Cusack, J. R., Giacco, G. G., Cleary, K., et al. (1996). Survival factors in 186 patients younger than 40 years old with coloractal adenocarcinoma. Journal of the American College of Surgeons, 183, 105–112.
Davis, A. L., Keeler, J., Laue, E. D., & Moskau, D. (1992). Experiments for recording pure-absorption heteronuclear correlation spectra using pulsed field gradients. Journal of Magnetic Resonance (San Diego Calif), 98(1), 207–216.
Elbayed, K., Dillmann, B., Raya, J., Piotto, M., & Engelke, F. (2005). Field modulation effects induced by sample spinning: application to high-resolution magic angle spinning NMR. Advances in Magnetic Resonance, 174, 2–26. doi:10.1016/j.jmr.2004.11.017.
Fearon, E., Cho, K. R., Nigro, J., et al. (1990). Identification of a chromosome 18q gene that is altered in colorectal cancers. Science, 247, 49–56. doi:10.1126/science.2294591.
Jemal, A., Siegel, R., Ward, E., et al. (2007). Cancer Statistics. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 57, 43–66.
Leichman, C. G., Lentz, H. J., Danenberg, K., et al. (1997). Quantitation of intratumoral thymidylate synthase expression predicted for disseminated colorectal cancer response and resistance to protracted infusion of 5-fluorouracil and weekly leucovorin. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 15, 3223–3229.
Libutti, S. K., Saltz, L. B., & Tepper, J. E. (2008). Principles and practice in oncology. In V. T. De Vita, T. S. Lawrence, & S. A. Rosemberg (Eds.), Colon cancer in cancer (pp. 1232–1285). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Lippens, G., Bourdonneau, M., Dhalluin, C., et al. (1999). Study of compounds attached to solid supports using high resolution magic angle spinning NMR. Current Organic Chemistry, 3, 147–169.
Lowe, I. J. (1959). Free induction decays of rotating solids. Physical Review Letters, 2, 285–287. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.2.285.
Martínez-Bisbal, M. C., Martí-Bonmatí, L., Piquer, J., et al. (2004). 1H and 13C HR-MAS spectroscopy of intact biopsy samples ex vivo and in vivo 1H MRS study of human high grade gliomas. NMR in Biomedicine, 17(4), 191–205. doi:10.1002/nbm.888.
Martínez-Granados, B., Monleon, D., Martínez-Bisbal, M. C., et al. (2006). Metabolite identification in human liver needle biopsies by high-resolution magic angle spinning 1H NMR spectroscopy. NMR in Biomedicine, 19(1), 90–100. doi:10.1002/nbm.1005.
Moreno, A., & Arús, C. (1996). Quantitative and qualitative characterization of 1H NMR spectra of colon tumors, normal mucosa and their perchloric acid extracts: Decreased levels of myo-inositol in tumours can be detected in intact biopsies. NMR in Biomedicine, 9(1), 33–45. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1099-1492(199602)9:1<33::AID-NBM391>3.0.CO;2-G.
Piotto, M., Bourdonneau, M., Furrer, J., et al. (2001). Destruction of magnetization during TOCSY experiments performed under magic angle spinning: Effects of Radial B1 inhomogeneities. Journal of Magnetic Resonance (San Diego, Calif.), 149, 114–118. doi:10.1006/jmre.2001.2287.
Seierstad, T., Røe, K., Sitter, B., et al. (2008). Principal component analysis for the comparison of metabolic profiles from human rectal cancer biopsies and colorectal xenografts using high-resolution magic angle spinning 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Molecular Cancer, 7, 1–13. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-7-33.
Shaka, A. J., Lee, C. J., & Pines, A. (1988). Iterative schemes for bilinear operators: Application to spin decoupling. Journal of Magnetic Resonance (San Diego, Calif.), 77, 274–293.
Sitter, B., Sonnewald, U., Spraul, M., Fjosne, H. E., & Gribbestad, I. S. (2002). High-resolution magic angle spinning MRS of breast cancer tissue. NMR in Biomedicine, 15(5), 327–337. doi:10.1002/nbm.775.
Sjøbakk, T. E., Johansen, R., Bathen, T. F., et al. (2008). Characterization of brain metastases using high-resolution magic angle spinning MRS. NMR in Biomedicine, 21(2), 175–185. doi:10.1002/nbm.1180.
Tenenhaus, M. (1998). La régression PLS: Théorie et Pratique. Paris.
Tzika, A. A., Cheng, L. L., Goumnerova, L., et al. (2002). Biochemical characterization of pediatric brain tumors by using in vivo and ex vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Journal of Neurosurgery, 96(6), 1023–1031.
Westerhuis, J. A., Hoefsloot, H. C. J., Smit, S., et al. (2008). Assessment of PLSDA cross validation. Metabolomics, 4(1), 81–89. doi:10.1007/s11306-007-0099-6.
Wider, G., & Dreier, L. (2006). Measuring protein concentrations by NMR spectroscopy. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 128(8), 2571–2576. doi:10.1021/ja055336t.
Acknowledgments
This work is part of the CARMeN project and was supported by grants from Région Alsace, Oséo, Communauté Urbaine de Strasbourg, Conseil Départemental du Bas-Rhin, Bruker BioSpin, University Louis Pasteur and University Hospitals of Strasbourg. The technical assistance of Dr. J. Raya, Mrs. H. Kada, and Mrs. T. Tong is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piotto, M., Moussallieh, FM., Dillmann, B. et al. Metabolic characterization of primary human colorectal cancers using high resolution magic angle spinning 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Metabolomics 5, 292–301 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-008-0151-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-008-0151-1